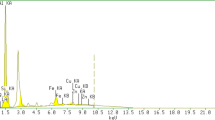
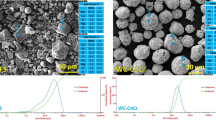
Abstract
Dry sliding wear behaviour of Al–4Mg alloy and Al–4Mg alloy/MgAl2O4 in situ composites was examined under normal loads of 10–30 N at sliding speeds of 1, 3, 5 and 7 m/s and sliding distance of 1500 m using a pin-on-disc apparatus. Al–4Mg alloy with different wt% (1, 2 and 3) of MgAl2O4 in situ composites was synthesized via ultrasonic cavitation by the addition of H3BO3 powders. Unreinforced alloy and composites were characterized to conclude the role of MgAl2O4 in modifying the wear behaviour of the composite. Worn-out samples and wear debris were examined by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction in order to obtain the major wear mechanisms of the developed composites. The addition of MgAl2O4 significantly reduces the wear rate of Al–4Mg alloy at higher loads. The operating wear mechanisms observed were delamination, oxidation, abrasion, adhesive, thermal softening and plastic deformation modes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Satish Kumar T, Shalini S, and Krishna Kumar K, Arch Metall Mater63 (2018) 689.
Satish Kumar T, Subramanian R, Shalini S, and Angelo P C, Forsch Ingenieurwes79 (2015) 123.
Raghu R, Nampoothiri J, and Kumar T S, Measurement129 (2018) 389.
Thandalam S K, Ramanathan S, and Sundarrajan S, J Mater Res Technol4 (2015) 333.
Xing L, Zhang Y, Shin C, Zhou Y, Zhao N, Liu E, and He C, Mater Sci Eng A617 (2014) 236.
Guo C, Zou T, Shi C, Yang X, Zhao N, Liu E, and He C, Mater Sci Eng A645 (2015) 1.
Raghu R, Nampoothiri J, Kumar T S, and Subramanian R, Trans Indian Inst Met72 (2019) 1013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01564-9.
Niranjan K, and Lakshminarayanan P R, Mater Des47 (2013) 167.
Naveen Kumar G, Narayanasamy R, Natarajan S, Kumaresh Babu S P, Sivaprasad K, and Sivasankaran S, Mater Des31 (2010) 1526.
Nguyen Q B, Sim Y H M, Gupta M, and Lim C Y H, Tribol Int82, (2015) 464.
Srinivasu R, Sambasiva Rao A, Madhusudhan Reddy G, and Srinivasa Rao K, Def Technol11 (2015) 140.
Yang L J, Wear263 (2005) 939.
Bowden FP, and Tabor D, The Friction and Lubrication of Solids, Part II, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1964).
Zhong X L, Wong E W L, and Gupta M, Acta Mater55 (2007) 6338.
Waterhouse R B, Wear45 (1977) 355.
Suh N P, Wear44 (1977) 1.
Stachowiak G W, and Batchelor A W, Engineering Tribology. 3rd edition, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Amsterdam (2005).
Bhushan B, Introduction to Tribology, Wiley, New York (2002).
Razavizadeh K and Eyre T S, Wear79 (1982) 325.
Shanthi M, Nguyen Q B, and Gupta M, Wear269 (2010) 473.
Taltavull C, Torres B, Lopez AJ, and Rams J, Wear301 (2013) 615.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, T.S., Nampoothiri, J., Raghu, R. et al. Development of Wear Mechanism Map for Al–4Mg Alloy/MgAl2O4 In Situ Composites. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 399–405 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01853-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01853-3