Abstract
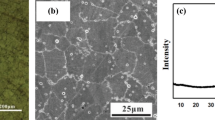
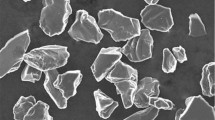
In this study, different amounts of iron are added to nickel–aluminum bronze produced by mechanical alloying and its effects on microstructure, hardness, and wear behaviors are investigated. Four different amounts of Fe (3.5, 4, 4.5, and 5 wt%) was added to Cu10Al5Ni alloy and mechanically alloyed for 60 min. After cold pressing (600 MPa), the alloy powders were sintered at 800 °C and cooled in furnace to room temperature. The samples were characterized with scanning electron microscope (SEM + EDS), X-ray diffraction and hardness and density measurements. Wear tests were performed using a block-on-ring wear testing device with 0.2 m/s sliding velocity, four different sliding distances (400–1600 m) and three different loads (10 N, 20 N, and 30 N). As a result of the studies, it was found that the hardness value increased, and the density decreased with increasing Fe amount. Cu10Al5Ni containing 5% Fe was measured with the highest hardness value (55.74 HV) and the lowest density value (7.72 g/cm3). Also, Fe- and Ni-rich κ intermetallic compounds were formed in the microstructure of the alloy. The wear tests showed that the alloy containing 5% Fe had the lowest weight loss and wear rate as well.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lotfollahi M, Shamanian M, Saatchi A, Mater Des62 (2014) 282.
Thapliyal S, Dwivedi D K, Tribo Int97 (2016) 124.
Donatus U, Omotoyinbo J A, Momoh I M, J Min Mater Charac Eng11 (2012) 1020.
Lv Y, Wang L, Xu X, Lu W, Metals5 (2015) 1695.
Culpan E A, Rose G, J Mater Sci13 (1978) 1647.
Sekunowo O I, Adeosun S O, Lawal G I, Balogun S A, Int J Sci Technol Res2 (2013) 179.
Hasan F, Jahanafrooz A, Lorimer G W, Ridley N, Metall Trans A13 (1982) 1337.
Neodo S, Carugo D, Wharton J A, Stokes K R, J Electroanal Chem695 (2013) 38.
Zhai W, Lu W, Zhang P, Zhou M, Liu X, Zhou L, Mater Sci Eng A707 (2017) 325.
Li Y, Ngai T L, Xia W, Wear197 (1996) 130.
Özyürek D, Tuncay T, Değirmenci C, 5 th International Advanced Technologies Symposium. (IATS’09), 13–15 May 2009, Karabuk, Turkey.
Łabanowski J, Olkowski T, Arch Found Eng14 2014 73.
Torralba J D, Da Costa, C E, Velasco F, J Mater Process Technol133 (2003) 203.
Duggirala R, Shivpuri R, J Mater Eng Perf1 (1992) 505.
Arifin A, Sulong A B, Muhamad N, Syarif J, Ramli M I, Mater Des55 (2014) 165.
Oh-Ishi K, McNelley T R, Metall Mater Trans A35 (2004) 2951.
Wu Z, Cheng Y F, Liu L, Lv W, Hu W, Corros Sci98 (2015) 260.
Kaplan M, Yildiz A K, Mat Lett57 (2003) 4402.
Koçak T U, Yanar H, Pürçek G, Birol F, II. International Iron & Steel Symposium (IISS’15), 1–3 April 2014, Karabuk, Turkey.
Özyürek D, Tekeli S, Sci Eng Compos Mater17 (2010) 31.
Meyer L, Thedens M, Beyer M, J Loss Prevent Process Ind49 (2017) 947.
Thossatheppitak B, Suranuntchai S, Uthaisangsuk V, Manonukul A, Mungsuntisuk P, Adv Mater Res683 (2013) 82.
Straffelini G, Maines L, Pellizzari M, Scardi P, Wear259 (2005) 506.
Sağlam I, Özyürek D, Çetinkaya K, Bull Mater Sci34 (2011) 1465.
Li W S, Wang Z P, Lu Y, Jin Y H, Yuan L H, Wang F, Wear261 (2006),155.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sımsek, D., Colak, N.Y., Sımsek, I. et al. Dry Sliding Wear Behaviors of Iron Addition to Nickel–Aluminum Bronze Produced by Mechanical Alloying. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 319–326 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01837-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01837-3