Abstract
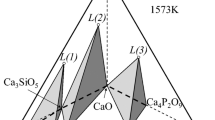
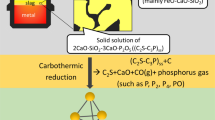
The high P content in steel slag limits its use in the next heats of steelmaking. Therefore, in this experiment, P2O5-containing slag was reduced by carbon at high temperatures in the flowing N2 and P-containing substances in the off-gas were water-cooled and collected. Both XRD analysis and thermodynamic calculations indicate that the reduction products are mainly composed of P2. The analysis with scanning electron microscope shows that the plate-like 2CaO·SiO2 and 3CaO·SiO2 phases in the steel slag were smashed into granular shape by the gas (P2 and CO) generated during the reduction. The reduction of P2O5 in the P-rich 2CaO·SiO2 and 3CaO·SiO2 phases in the steel slag is insufficient, while that in P-lean RO phase is complete. The single-factor experiments proves that the phosphorus vaporization rate increases with the moderate increase in temperature, FeO content and N2 flow rate, but decreases with the increase in of basicity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogawa Y, Yano M, Kitamura S, and Hirata H, Testu-to-Hagane87 (2001) 21.
Iwasaki M and Matsuo M, Nippon Steel Tech Rep39 (2011) 88.
Turkdogan E T, ISIJ Int40 (2000) 964.
Kitamura S, Aoki H, and Okohira K, ISIJ Int34 (1994) 401.
Jiang M F, Cui Y Y, Wang D Y, Min Y, and Liu C J, J Iron Steel Res Int20 (2013) 17.
Jung S M, and Do Y J, Steel Res Int77 (2006) 312.
Suk M O, Jo S K, Kim S H, Lee K Y, and Park J M, Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci37 (2006) 99.
Ishikawa M, ISIJ Int46 (2006) 530.
Wu X R, Nan J N, and Chen R H, J Anhui Univ Technol (Nat Sci)27 (2010) 24.
Li G Q, Zhang F, Zhang L, and Sui Z T, J Mater Metall03 (2003) 167.
Wang N, Liang Z G, Chen M, and Zou Z S, J Northeast Univ (Nat Sci)31 (2011) 814.
Wang Y C, Li H Y, Li S W, and Luo G P, J Iron Steel Res06 (2016) 31.
Wang S H, Wu Y Q, Liu X S, and Xu Z R, Iron Steel43 (2008) 31.
Wang S H, Wu Y Q, Xu Z R, Lv X F, and Zhang X, Steelmaking 24 (2008) 31.
Li C X, Li H, and Zhou B, China Metall25 (2015) 28.
Chen J X, Data Manual for Commonly Used Icons in Steelmaking (1984).
Wang J Y, German association of steel engineers (Slag Atlas) (1983).
Ono-Nakazato H, Yonezawa T, and Usui T, ISIJ Int.43 (2003) 1502.
Shurygin P M, Kryulk, V I, and Revebtsov V V, Izv VUZ8 (1965) 23.
Huang Z Z, and Xiao X G, J Northeast Univ (Nat Sci)2 (1994) 140.
Frank-Kamenetskii D A, Diffusion and Heat Exchange in Chemical Kinetics (1955) p 58.
Du J X, and Sun Z L, Sulphur Phosphorus Des Powder Eng 02 (2015) 31.
Cui H X, Chen Q W, Shen Y Y M C, China Metall20 (2010) 35.
Chen S J, Sulphur Phosphorus Des Powder Eng05 (2010) 33.
Xiao Y, Matsuura H, and Tsukihashi F, Tetsu-to-Hagané3 (2009) 268.
Wu Q F, and Bao Y P, J Wuhan Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci Ed)39 (2014) 411.
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by Tangshan Key Laboratory of Special Metallurgy and Material Manufacture (Grant No. 17130202D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Tian, P., Li, C. et al. Reduction Mechanism of P2O5 in Steel Slag. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 251–258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01829-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01829-3