Abstract
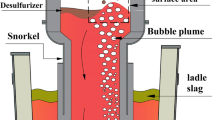
In secondary refining operations, injection of inert gases into the metal bath is required to generate stirring in order to produce cleaner steels with low sulfur, ultra-low contents of nitrogen and hydrogen gases as well as improving both temperature and composition homogenization of the steel and control the inclusions and floating of them. To demonstrate the viability and competitiveness of the non-consumable lance versus porous plugs, a series of experiments in a model of secondary refining ladle were carried out in previous research (Liu et al. in ISIJ Int 57:1971, 2017). Simulation of gas injection was carried out to test the two methods: porous plug and non-consumable lance. It was found that the porous plug injection involves shorter mixing times (10–12 s) when it is positioned in an intermediate point between the center and edge of the ladle and with the increase in the airflow injected, as compared to the lance. However, one problem with this technique in the actual plant is the metal oxidation because the liquid metal is exposed to air as a result of excessive agitation. In this work, gas injection through porous plug and non-consumable lance into secondary refining ladle was simulated by the addition of oils of different densities, to simulate the behavior of the slag of different viscosities. The results show that the non-consumable lance exhibits less water surface area exposed compared with the porous plug. This means less metal is exposed to the environment and less oxidation of it, under the same agitation conditions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Z, Li L, and Li B, ISIJ Int57 (2017) 1971.
Szekely J, Fluid Flow Phenomena in Metals Processing, Academic Press, Inc., New York (1979), p 392.
Barrera C G, Master’s Thesis, McGill University, Montreal (1985).
Tu S T, Zhang H, and Zhou W W, Eng Fail Anal6 (1999) 363.
Maldonado-Parra F D, Ramírez-Argáez M A, Conejo A N, and Gonzáles C, ISIJ Int51 (2011) 1110.
Ramírez-Argáez M A, Mater Manuf Processes23 (2007) 59.
Mazumdar D, and Guthrie R I L, Metall Mater Trans B17B (1986) 725.
Krishnakumar K, and Ballal N B, ISIJ Int39 (1999) 1120.
Krishnapisharody K, and Irons G A, Metall Mater Trans B38B (2007) 377.
Jardón Péreza E, Amaro-Villeda A, Conejo A N, González-Rivera C, and Ramírez-Argáez M A, Mater Manuf Processes23 (2007) 59.
Mazumdar D, Dhandapani P, and Sarvanakumar R, ISIJ Int57 (2017) 286.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrera-Cardiel, G., Aparicio-Fernández, R., Arcos-Gutiérrez, H. et al. Physical Simulation Behavior of the Slag in Gas Injection with Non-consumable Lance and Porous Plug for Secondary Refining Operations. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 3261–3268 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01794-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01794-x