Abstract
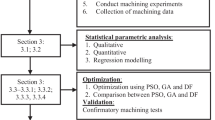
The present work is an endeavor to carry out a machining using LN2 in face milling operations and to produce the milling samples with excellent wear resistance property. The output response (wear rate) depends on appropriate choice of speed, feed, and depth of cut. The experimental data are conducted (collected) for SS316 as per central composite design. The present work exemplifies an employment of conventional and nonconventional strategies for optimizing the milling factors of cryogenically treated samples in face milling to achieve the desired wear (response). The results of nonlinear regression (desirability strategy) and nonconventional [particle swarm optimization, (PSO)] optimization techniques are compared, and PSO is found to outperform the desirability function approach. The present work even highlights the effect and results of LN2 on wear in contrast to wet condition.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cambri B M, J Mat Processing Technology 56 (1996) 786.
Shaw M C, Pigott J D, and Richardson L P, Am Soc. Mech. Eng. 71 (1951) 45.
Cassin C, and Boothroyd G, J Mech Eng Sci 7 (1965) 67.
Baradie M A, J Mater Process Technol 56 (1996b) 798.
Pusavec F, Kramar D, Krajnik P, and Kopac J, J Cleaner Prod 18 (2010) 1211.
Hong S Y, and Broomer M, Clean Prod Process 2 (2000) 157.
Hong S Y, Ding Y, and Jeong J, Mach Sci Technol 6 (2002) 235.
Bordin A, Bruschi S, Ghiotti A, and Bariani P F, Wear 328 (2015) 89.
Jerold B D, and Kumar M P, Cryogenics 52 (2012) 569.
Umbrello D, J Adv Manuf Technol 64 (2015) 633.
Umbrello D, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54 (2011) 887.
Klocke F, Settineri L, Lung D, Priarone PC, and Arft M, Wear 302 (2013) 1136.
Tandon V, Mounayri H E, and Kishawy H, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42 (2002) 595.
Basker N, Asokan P, Saravanna R, and Probhaharan G, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25 (2005) 10781088.
Mukherjee I, and Kumar R P, Comput Ind Eng 50 (2006) 15.
Raja S B, and Baskar N, Expert Syst Appl 39 (2012) 5982.
Julie Z, Joseph C, and Daniel K, J Mater Process Technol 184 (2007) 233.
Rashmi L M, Karthik Rao M C, Arun Kumar S, Shrikantha S Rao, and D’Souza R J, J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 39 (2016) 3541.
Reddy S K, and Rao P V, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28 (2006) 463.
Rashmi L M, Karthik R M C, Arun Kumar S, Shrikantha S R, D’Souza R J, Mater Manuf Process 33 (2017) 1406.
Phadke M S, Quality engineering using robust design, Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1989).
Ross P J, Taguchi techniques for quality engineering, McGraw-Hill, New York (1996).
Montgomery D C, Design and analysis of experiments, Wiley, New York (2008).
Manjunath P, Krishna P, and Parappagoudar B, Int J Adv Technol (2016), http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8416-8.
Manjunath P, Krishna P, and Parappagoudar B, Aust J Mech Eng (2015) http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14484846.2015.1093231.
Rashmi L M, Karthik R M C, Arun Kumar S, Shrikantha S R, and Mervin A H, Int J Precis Eng Manuf 19 (2018) 695.
Manjunath P, Arun Kumar S, and Parappagoudar B, J Manuf Process 32 (2018) 199.
Kovacevic R, Cherukuthota C, and Mzurkiewiez M, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 35 (1995) 1459.
Dhar N R, Paul S, and Chattopadhyay A B, Wear 249 (2002b) 932.
Chen Z, Atmadi A, Stephennon D A, and Liang S Y, Ann CIRP 49 (2000) 53.
Yakup Y, and Muammer N, Int J Mach Tool Manuf 48 (2008) 947.
Barry J, and Byrne G, Ann CIRP 51 (2002) 65.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank NITK, Surathkal, for providing facilities to carry out my research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Test Cases
Appendix: Test Cases
SL. no. | Process variables | Experimental | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
S | F | D | CT | Wear rate | Surface roughness | |
1 | 2100 | 465 | 1.1 | − 1 | 2.27 | 2.13 |
2 | 2800 | 379 | 0.7 | 0 | 2.41 | 2.62 |
3 | 1700 | 364 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.93 | 1.91 |
4 | 1200 | 420 | 1.3 | 1 | 1.74 | 1.73 |
5 | 2000 | 457 | 0.8 | 0 | 2.24 | 2.09 |
6 | 1500 | 500 | 1.2 | 1 | 1.99 | 1.83 |
7 | 2600 | 440 | 0.7 | 1 | 1.13 | 2.47 |
8 | 1285 | 520 | 1.3 | 1 | 0.62 | 1.71 |
9 | 2300 | 500 | 0.8 | 0 | 2.13 | 2.26 |
10 | 1392 | 390 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.66 | 1.77 |
11 | 2500 | 485 | 1 | − 1 | 2.32 | 2.35 |
12 | 1850 | 510 | 1.4 | 1 | 2.01 | 1.99 |
13 | 2720 | 400 | 1.1 | − 1 | 2.66 | 2.56 |
14 | 2200 | 380 | 0.8 | 0 | 2.17 | 2.22 |
15 | 2450 | 510 | 0.6 | − 1 | 2.38 | 2.31 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karthik Rao, M.C., Malghan, R.L., ArunKumar, S. et al. An Efficient Approach to Optimize Wear Behavior of Cryogenic Milling Process of SS316 Using Regression Analysis and Particle Swarm Techniques. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 191–204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1473-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1473-y