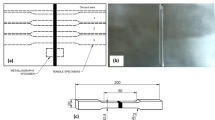
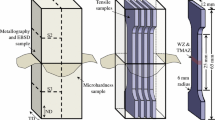
Abstract
The influence of parent metal condition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of friction welds of Ti6Al4V alloy has been investigated. Welds are observed to contain predominantly martensite. Stress relieving results in improvement in the strengths of α + β and β treated parent metal and their welds. β welds are observed to contain coarser prior β grains. Studies reveal that welds of α + β solution treated parent metal exhibit higher strength than all the other welds. In plain tensile tests, the location of failure is away from the welds in all the conditions, suggesting that the welds are stronger than their respective parent metals. Parent metal in α + β and β solution treated conditions is observed to respond to stress relieving such that, hardness is improved after stress relieving. Stress relieving results in reduced ductility and improvement in the strength of the welds. Notch tensile strength of the welds is observed to be higher than their parent metals and stress relieving results in further improvement. The notch tensile ratio of the welds has been observed to be ~1.4 in all the conditions indicating that the welds are not notch sensitive.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donachie M J Jr., Titanium: A Technical Guide, 2nd ed. ASM International, Almere (2000).
Moiseyev V N, Titanium Alloys: Russian Aircraft and Aerospace Applications, Taylor & Francis, New York (2006).
Leyens C, and Peters M, Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2003).
Boyer R R, Mater Sci Eng A 213 (1996) 103.
Gilbert S, and Shannon R, Heat Treating of Titanium and Titanium Alloys, ASM Handbook Volume 4: Heat Treating, ASM International (1991), p 2043–2071.
Baeslack W A III, Davis J R, and Cross C E, Selection and Weldability of Conventional Titanium Alloys, ASM Handbook Volume 6: Welding, Brazing and Soldering, ASM International, (1995) p 507–523.
Holsberg P W, Cracking and Porosity In Titanium Alloy Weldments, U.S. Navy DTNSRDC report (1979).
Mazumder J, and Steen W M, Metall Trans A 13 (1982) 865.
Lindh D V, and Peshak G M, Weld J 48 (1966) 45.
Mohandas T, Mechanical Property Studies on Electron Beam and Friction Welds of an Alpha + Beta Titanium Alloy, Ph D Thesis (Banaras Hindu University, India) (1994).
Mohandas T, Srinivas M, and Kutumba Rao V V, Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 23 (2000) 33.
Savage W F, and Aronson A H, Weld J 45 (1966) 85.
Mohandas T, Banerjee D, and Kutumba Rao V V, Mater Sci Eng A 254 (1998) 147.
Nessler C G, Rutz D A, Eng R D, and Vozzela P A, Weld J 50 (1971) 379s.
Sun D, Ren Z, and Zhou A, J Mater Sci Technol 16 (2000) 59.
Thomas G, Ramachandra V, Nair M J, Nagarajan K V, and Vasudevan R, Weld J Res Suppl 71 (1992) 15s.
Sundaresan S, Janaki Ram G D, and Reddy G M, Mater Sci Eng A 262 (1999) 88.
Tsay L W, Shan Y P, Chao Y H, and Shu W Y, J Mater Sci 41 (2006) 7498.
Xiong J T, Li J L, Wei Y N, Zhang F S, and Huang W D, Acta Mater 61 (2013) 1662.
Kishore Babu N, Sundara Raman S G, Srinivasa Murty C V, and Reddy G M, Mater Sci Eng A 471 (2007) 113.
Tsay L W, Hsu C L, and Chen C, Mater Chem Phys 120 (2010) 715.
Lu M Y, Tsay L W, and Chen C, Mater Trans 53 (2012) 1042.
Mohandas T, Banerjee D, and Kutumba Rao V V, Mater Sci Eng A 289 (2000) 70.
Ji S D, Zhuo B, Gao S S, Huang Y X, Zhang L G, Li J Z, and Ma Y N, Eng Rev 35 (2015) 27.
Hirth J P, and Froes F H, Metall Trans A 8A (1977) 1165.
Baeslack W A, and Banas C M, Weld J Res Suppl 61 (1981) 121s.
Baeslack W A III, Becker D W, and Froes F H, JOM 36 (1984) 46.
Baeslack W A III, and Becker D W, Metall Mater Trans A 11A (1980) 605.
Meshram S, and Mohandas T, Def Sci J 61 (2011) 590.
Mohandas T, Banerjee D, and Kutumba Rao V V, Metall Mater Trans A 30 (1999) 789.
Fujii H, Mater Sci Eng A 243 (1998) 103.
Romero J, Attallah M M, Preuss M, Karadge M, and Bray S E, Acta Mater 57 (2009) 5582.
Lütjering G, Mater Sci Eng A 243 (1998) 32.
Balasubramanian T S, Balakrishnan M, Balasubramanian V, and Muthu Manickam M A, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 21 (2011) 1253.
Meshram S D, and Mohandas T, Mater Des 31 (2010) 2245.
Chu C Y, Hsieh C T, and Tsay L W, Mater Des 63 (2014) 14.
Hsieh C T, Chu C Y, Shiue R K, and Tsay L W, Mater Des 59 (2014) 227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahul, R., Rajulapati, K.V., Reddy, G.M. et al. Studies on Effect of Parent Metal Condition on the Room Temperature Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Friction Welds. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 2277–2291 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1084-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1084-z