Abstract
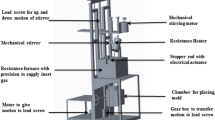
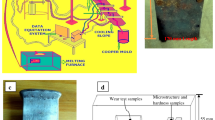
The objective of the present work is to investigate the tensile behavior on laser welded Al–Mg–Sc–Zr in situ nano TiB2 composite. Al–3.5Mg–0.15Sc–0.075Zr–1TiB2 composite was melted in a resistance heating furnace. TiB2 was formed during in situ reaction of K2TiF6 and KBF4 salt mixture at 750 °C for 60 min. Welding was done using Nd:YAG pulsed laser source JK 600 (GSI make) using a robotic (IRB1410 of ABB) laser set up. The autogenous welding experiments were carried out using some of the significant parameters such as frequency—75 Hz, laser beam energy—8.10 J, pulse width—2.5 ms and welding speed—5 mm/s. It was observed that laser beam power played a major role and lower value of energy with higher repetition rate resulted better and uniform weld bead with full penetration. Five different processing methods were utilized to investigate the mechanical and metallurgical properties namely: (a) as cast (AC), (b) as cast followed by welding (AC + W), (c) as cast followed by aging (AC + A), (d) as cast followed by aging and then welding (AC + A + W) and finally (e) as cast followed by welding and then aging (AC + W + A). The ageing treatment followed was heating the samples at 300 °C for 5 h followed by air cooling. The obtained results infered that apart from the obvious superior properties shown by as cast followed by aging treatment (AC + A: 248 MPa); the AC + W + A specimens showed better properties (235 MPa) along with AC + A + W specimens (226 MPa). The fracture surface analyses revealed the following: (a) the weld region in the laser welded as cast material did not show any TiB2 in the structure probably due to the fact that temperature experienced during laser welding process might have melted the particles and was dissolved in the solid solution, (b) the interface of the weld-base region showed the presence of few TiB2 particles which lost their hexagonal shape due to preferential melting along the edges. (c) The fracture morphology of both AC + A + W and AC + W + A specimen’s showed typical mixed mode fracture with fine precipitates along the interface. The strength increased in AC + W + A at the expense of ductility due to formation of Al3Sc precipitates.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salvador M D, Amigó V, Martinez N, and Ferrer C, J Mater Process Technol, 143–144 (2003) 598–604.
Mandal A, Murty B S, and Chakraborty M, Wear 266 (2009) 865–872.
Yijie Z, Naiheng M A, Haowei W, Yongkang L, and Xianfeng L, Mater Des 28 (2007) 628–632.
Fjellstedt J, and Jarfors A E W, Mater Sci Eng A 413414 (2005) 527–532.
Prasad K V S, Murty B S, Pramanik P, Mukunda P G, and Chakraborty M, Mater Sci Technol 12 (1996) 766–770.
Murty B S, Kori S A, Venkateswarlu K, Bhat R R, and Chakraborty M, J Mater Process Technol 89–90 (1999) 152–158.
Lohar A K, Mondal B N, and Panigrahi S C, J Mater Eng Perform 20 (2011) 1575–1582.
Cam G, and Kocak M, Int Mater Rev 43 (1998) 1–44.
Cui H C, Lu F G, Tang X H, and Yao S, Trans China Weld Inst 31 (2010) 68–72.
Jun D, Zheng L, Li Y, Yang W, Chiyu Z, and Yaocheng Z, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 467 (2007) 132–138.
Banerjee A J, Biswal M K, Lohar A K, Chattopadyay H, and Hanumaiah N, Int J Eng Technol Ger 5 (2016) 92–101.
Grabowski A, Nowak M, and Śleziona J, J Achiev Mater Manuf Eng 3 (2008) 233–240.
Grabowski A, Nowak M, and Śleziona J, J Achiev Mater Manuf Eng 17 (2006) 61–64.
Niu J, Zhang D, and Ji G, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 13 (2003) 289–293.
Schubert E, Klassen M, Zerner I, and Sepold G, J Mater Process Technol 4 (1998) 17–20.
Emamy M, Mahta M, and Rasizadeh J, Compos Sci Technol 66 (2006) 1063–1066.
Nampoothiri J, Raj B, and Ravi K R, Mater Sci Forum 830–831 (2015) 463–466.
Katayama S, Usui R, Matsunawa A, in Proc 5th International Conference-Trends in Welding Research (1999) ASM International, pp 467–472.
Pastor M, Zhao H, and Debroy T, in Proc. 5th International Conference—Trends in Welding Research (1999) ASM International, pp 455–460.
Kendig K L, and Miracle D B, Acta Mater 50 (2002) 4165–75.
Thadela S, Mandal B, Das P, Roy H, Lohar A K, and Samanta S K, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 25 (2015) 2827–2832.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Director, CSIR-Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute (CMERI) for his kind permission to carry out and publish this work. The authors would like to acknowledge the help rendered by Central Research Facility, CMERI-Durgapur, for material characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, A.J., Roy, H., Biswal, M.K. et al. Investigation on Tensile Behaviour of Laser Welded Al–Mg–Sc–Zr In Situ TiB2 Reinforced Metal Matrix Composite. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 2071–2077 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-1028-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-1028-z