Abstract
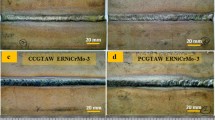
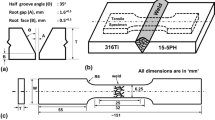
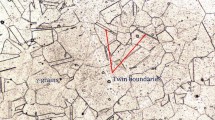
Nitrogen alloyed austenitic stainless steels are recently developed and are finding applications in defence because of improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Welding is the main fabrication technique to join the structural components. During welding, it may result in porosity, solidification cracking in weld zone, liquation cracking in heat affected zone and inferior properties compared to base metal. Selection of filler wire plays a major role to obtain a sound weld and to have a better mechanical and corrosion resistance. In the present work, gas tungsten arc welding of 5 mm thick nickel free high nitrogen stainless steels were carried out. As no suitable matching filler wires have been developed, commercially available high strength fillers of precipitation hardenable (PH) 13-8Mo filler and nickel based (MDN 250) 18Ni filler were used for welding high nitrogen stainless steel. Microstructural studies were carried out using optical microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD) technique was used to determine the grain size, phase analysis and orientation mapping. Hardness values were recorded using Vickers hardness tester. Results of the present investigation established that the weld zone/fusion zone was observed to have delta-ferrite in the austenite matrix for both the welds. Welds made with (MDN 250) 18Ni filler had an unmixed zone adjacent to the weld zone near fusion boundary. Welds made with (PH) 13-8Mo filler had high hardness which might be attributed to relatively finer grains in the weld zone. Improved pitting corrosion resistance for welds made with (PH) 13-8Mo filler might be attributed to the composition of the filler wire. The presence of chromium and molybdenum helped in enhancing the stable passive film when compared to that of welds made with MDN 250 filler.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Speidel M O, and Uggowitzer P J, Stickstofflegierte Stahle, Ergebnisse der Werkstoff Forschung Band 4, Thubal-Kain, Zurich (1991).
Byrnes M L G, Grujicic M, and Owen W S, Acta Metall 35 (1987) 1853.
Werner E, Mater Sci Eng A 101 (1988) 93.
Reed R P, J Metals (1989) 16.
Kikuchi M, Kajihara M, and Frisk K, in HNS 88, Lille, France, May 1988, (eds) Foct J, and Hendry A, The Institute of Metals, London, (1989) p 63.
Simmons J W, Microstructural Science, vol 21, ASM International, Metals Park, OH, (1994) p 33.
Speidel M O, in HNS 88, Lille, France, May 1988, (eds) Foct J, and Hendry A, The Institute of Metals, London, (1989) p 92.
Shankar V, Gill T P S, Mannan S L, and Sundaresan S, Mat Sci Engg A 343 (2003) 170.
Hazra M, Rao K S, Reddy G M, J Mater Res Technol (2014) 90.
Raj B, Shankar P, Jayakumar T, Adv Stainl Steel (2010) 342.
Du Toit M, J Mater Eng Perform 11 (2002) 312.
Mohammed R, Reddy G M, and Rao K S, Def Technol 11 (2015) 25.
Corrosion of weldments, ASM International (2006) 01.
Ghali E, Sastri V S, Elboujdaini M, Corrosion prevention and protection: practical solutions, Wiley, New York (2009) 380.
Namjou A, Dehmoloei R, Ashrafi A, Int J Nat Eng Sci (2014) 22.
Parvathavarthini N, Dayal R K, Seshadri S K, Gnanamoorthy J B, J Nucl Mater (1989) 83.
Fu Y, Wu X, Han E H, Ke W, Yang K, Jiang Z, J Electrochem Acta (2009) 1618.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Director, Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory Hyderabad, India for his continued encouragement and permission to publish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, R., Reddy, G.M. & Rao, K.S. Effect of Filler Wire Composition on Microstructure and Pitting Corrosion of Nickel Free High Nitrogen Stainless Steel GTA Welds. Trans Indian Inst Met 69, 1919–1927 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0851-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0851-6