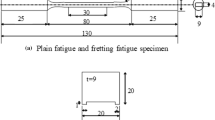
Abstract
Fretting fatigue behavior of IMI 834 titanium alloy has been investigated at room temperature, 400 and 590 °C. For comparison plain fatigue tests were also carried out. Finite element analysis was done to evaluate the tangential stress coefficient and relative slip amplitude during fretting fatigue at room temperature and high temperatures. The fracture surface and fretting contact surface were examined using scanning electron microscope. The result showed that, the fatigue strength has reduced due to fretting both at room temperature and high temperature. With an increase in temperature the fretting fatigue strength reduced. It reduced significantly at 400 °C and drastically at 590 °C, due to the increase in severity of damage in fretting contact surface with an increase in test temperature. The results were discussed based on the relative slip amplitude values, tangential stress coefficient values and the surface damage observations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waterhouse R B, Int Mater Rev 37 (1992) 77.
Lindley T C, Int J Fatigue 19 (1997) S39.
Mutoh Y, JSME Int J Ser A 38 (1995) 405.
Mutoh Y, Nishida T, and Sakamoto I, J Soc Mater Sci Jpn 37 (1988) 649.
Sabelkin V, Martinez S A, Mall S, Sathish S, and Blodett M P, Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 28 (2004) 321.
Jayaprakash M, Mutoh Y, Asai K, Ichikawa K, and Sukurai S, Int J Fatigue 32 (2010) 1788.
Jayaprakash M, and Ganesh Sundara Raman S, Trans Indian Inst Met 59 (2006) 431.
Ruiz C, Boddington P H B, and Chen K C, Exp Mech 24 (1984) 208.
Szolwinski M P, and Farris T N, Wear 198 (1996) 93.
Mutoh Y, and Jayaprakash M, Tribol Int 4 (2011) 1394.
Jayaprakash M, Anchalee S, Otsuka Y, and Mutoh Y, Int J Fatigue 54 (2013) 99.
Jayaprakash M, Mutoh Y, and Yoshii K, Mater Des 32 (2011) 3911c.
Hamdy M M, and Waterhouse R B, Wear 71 (1981) 237.
Hamdy M M, and Waterhouse R B, Wear 56 (1979) 1.
Mutoh Y, and Satoh T, in Fretting Fatigue, (eds) Waterhouse R B, and Lindley T C, Mechanical Engineering Publications (1994), p 389.
Lutjering G, and Williams J C, Titanium, 2nd edn, Springer, Berlin (2003).
Singh N, Gouthama, and Singh V, Mater Sci Eng A 325 (2002) 324.
JSME S015, Test Method for Fretting Fatigue, JSME (2002).
Mentat II Users Guide, USA: Marc Analysis Research Corporation (1996).
Xu J Q, and Mutoh Y, JSME Int J 45 (2002) 510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayaprakash, M., Komatsu, D., Okazaki, M. et al. High Temperature Fretting Fatigue Behavior of IMI 834 Titanium Alloy. Trans Indian Inst Met 69, 439–444 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0815-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0815-2