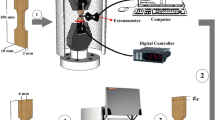
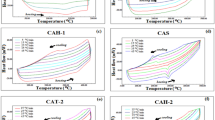
Abstract
Copper based shape memory alloys have received much focus in recent times because of their good ductility, ease of production and processing and low cost. Earlier investigations have shown that ductility and other mechanical properties of the Cu-Al based shape memory alloys can significantly be improved by adding ternary elements such as Ni and Mn. While Cu-Al-Ni shape memory alloys have better thermal stability and higher operating temperatures, their practical applications are limited because of their poor workability. Cu-Al-Mn shape memory alloys on the other hand, have good ductility and workability, but their operating temperatures are lower. A similar approach is followed in Ni-Al alloys to overcome their brittleness by the addition of Fe. There is paucity of literature on the role of ternary addition of Fe to Cu-Al shape memory alloys. In the present work, therefore, the effect of aluminium and iron on the transformation temperatures has been studied. As the aluminium content increases the transformation temperatures decrease, while the ternary addition of Fe increases the transformation temperatures. The results are presented and discussed in detail in the paper.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Otsuka K and Wayman C M, Shape memory materials, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U K (1998) 97.
Fristov G S, Van Humbeeck J and Koval Y N, Mater. Sci.Eng. A, 378 (2004) 2.
Duerig T W, Albrecht J and Gessinger G H, J Metals, (1982)14
Recarte V, Perez-Saez R B, Bocanegra E H, No M L, San Juan J, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 273–275 (199) 380.
Dutkiewicz J, Pons J and Ceasri E, Mater. Sci.Eng. A, 158 (1992) 119.
Suresh N and Ramamurthy, J. Alloys and Compounds, 449 (2008) 113.
Agafonov V, Naudot P, Dubertret and Dubois B, Scripta Met., 22 (1988) 489.
Vandenberg J M and Daper C W, Mater. Letters, 2 (1984) 386.
Dutkiewicz J, Martynov and Messerschmidt U, J. Mater. Sci. 24 (1989) 3904.
Blazquez M L, Lopez Del Castillo C and Gomez C, Metallography, 23 (1989) 119.
Mallik U S and Sampath V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 481–482 (2008) 680.
Swann P R and Warlimont H, Acta Met. 11 (1963) 511.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raju, T.N., Sampath, V. Influence of aluminium and iron contents on the transformation temperatures of Cu-Al-Fe shape memory alloys. Trans Indian Inst Met 64, 165 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-011-0032-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-011-0032-6