Abstract
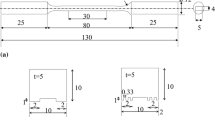
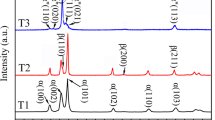
Fretting is a form of adhesive wear normally occurring at the contact points gradually leading to premature failure of load bearing medical implants made of titanium alloys. The aim of this work is to characterize the fretting fatigue damage features of PVD TiN coated, plasma nitrided, ion implanted, laser nitrided and thermally oxidized Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-7Nb contact pairs. The surface layers were characterized. The damage progression during fretting process is apparently explained with tangential force coefficient curves. Plasma nitrided pairs showed highest fretting fatigue life compared to others. PVD TiN coated pairs have experienced early failures due to third body mode of contact interaction with irregular tangential force coefficient pattern. Ion implanted layers showed similar damage as unmodified alloys. Laser nitrided and thermally oxidized pairs experienced early failures due to brittle and irregular modified layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamachi Mudali U, Sridhar T M, Eliaz N and Baldev Raj, Corrosion Reviews, 21 (2003) 231.
Hallab N, Journal of Bone Joint Surgery, 83A (2001) 428.
Teoh S H, International Journal of Fatigue, 22 (2000) 825.
Antoniou R A, Radtke T C, Materials Science and Engineering, A 237 (1997) 229.
Marc Long and Rack H J, Biomaterials 19 (1998) 1621.
Huang nan, Chen Yuanru, Cai Guangjun, Lin Chenggang, Wang Zhongguang, Yiao Guo, Su Huehe, Liu Xianghuai, Zhen Zhihong, Surface and Coatings Technology 88 (1996) 127.
Shenhar A, Gotman I, Radin S, Ducheyne P, and Gutmanas E Y, Surface and Coatings Technology, 126 (2000) 210.
Bekir S. Yilbas, Ahemt Z. Sahin, Ahmed Z. Al-Garni, Syed A M, Zaki Ahmed, Abdulaleem B J and Muhammed Sami, Surface and Coatings Technology, 8 (1996) 287.
Elder J E, Tahmburaj R and Patnaik P C, Surface Engineering, 5 (1989) 55.
Man H C, Zaho N Q and Cui Z D, Surface and Coatings Technology, 192 (2005) 241.
Sumita M, Hanawa T, Ohnishi I and Yoneyama T, Comprehensive Structural Integrity, 9 (2003) 131.
Starosvetsky D and Gotman I, Biomaterials, 22 (2001) 1853.
Laure Duisabeau, Pierre Combrade, Bernard Forest, WEAR 256 (2004) 805.
Schmidt H, Schminke A, Schmiedgen M and Baretzky B, Acta Materialia, 49 (2001) 487.
Geetha M, Kamachi Mudali U, Pandey N D, Asokamani R and Baldev Raj: Surface Engineering, 20 (2004) 68.
Ueda M, Silva M M, Otani C, Reuther H, Yatsuzuka M, Lepienski C M and Berni L A, Surface and Coatings Technology, 170 (2003) 408.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vadiraj, A., Kamaraj, M. Fretting fatigue behavior of surface modified biomedical titanium alloys. Trans Indian Inst Met 63, 217–223 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-010-0030-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-010-0030-0