Abstract
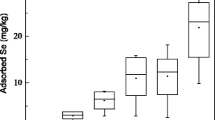
Selenium (Se) bioavailability is largely governed by its fractionation in soil constituents which is yet an unaddressed issue of severely seleniferous agricultural soils of NE Punjab, India. Five selective soils with Se content up to 6.2 mg kg−1 were examined to understand Se partitioning in different soil constituents and fraction of exchangeable soil Se. Its mobilization behavior under oxygenated and anaerobic conditions was also examined and role of NO3− and PO43− on it. Soil from Barwa, Nawanshahr with CT of 1.3% is found to be enriched in Se, Zn, Cr, Mn, Cu, Cr, Co, U and Th, while Ramgarh soil, Hoshiarpur with CT of 1.0% is least contaminated. Selenium leaching is favored under anoxic condition with rapid initial release, while no leaching has occurred in oxygenated condition. The presence of competitive anions, i.e., NO3− or PO43−, has facilitated slight greater Se leaching after 9 days, whereas leaching decreased continuously in normal milli-Q water reactors. Generation of CH4 is insignificant, whereas CO2 production increased with time in anoxic medium. Easy bioavailability of Se around the agricultural field is inferred from the extractability of soil Se through ligand exchange, phosphate exchange and water extraction. The hard bound soil Se, i.e., crystalline phase, organic matter and iron–manganese oxide-bound fractions are nil that further supports its easy bioavailability.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ayyasamy PM, Lee S (2009) Redox transformation and biogeochemical interaction of heavy metals in Korean soil using different treatment columns in the presence of Shewanella sp. Chemosphere 77:501–509
Bailey RT, Hunter WJ, Gates TK (2012) The influence of nitrate on selenium in irrigated agricultural groundwater systems. J Environ Qual 41:783–792
Bajaj M, Eiche E, Neumann T, Winter J, Gallert C (2011) Hazardous concentration of selenium in soil and groundwater in North-West India. J Hazard Mat 189:640–646
Chang C, Yin R, Wang X, Shao S, Chen C, Zhang H (2019) Selenium translocation in the soil-rice system in the Enshi seleniferous area, Central China. Sci Total Environ 669:83–90
Chiroma TM, Ebewele RO, Hymore FK (2014) Comparative assessement of heavy metal levels in soil, vegetables and urban grey waste water used for irrigation In Yola And Kano. Intern Ref J Eng Sci 3:1–9
Dereven’kov IA, Makarov SV, Brânzanic MVA, Silaghi-Dumitrescu R, Molodtsov PA, Pokrovskaya EA (2021) Formation of hydroxyl radical in aqueous solutions containing selenite and glutathione. Polyhedron 198:115072
Dhillon KS, Dhillon SK (1991) Selenium toxicity in soil, plants and animals in some parts of Punjab, India. Int J Environ Stud 37:15–24
Dhillon KS, Dhillon SK (1997) Distribution of seleniferous soils in north-west India and associated toxicity problems in the soil-plant-animal-human continuum. Land Cont Reclam 5:313–323
Dhillon KS, Dhillon SK (2003) Quality of underground water and its contribution towards selenium enrichment of soil-plant system for a seleniferous region of northwest India. J Hydrol 5:120–130
Dhillon KS, Rani N, Dhillon SK (2005) Evaluation of different extractants for the estimation of bioavailable selenium in seleniferous soils of Northwest India. Aust J Soil Res 43:639–645
Dhillon KS, Dhillon SK, Dogra R (2010) Selenium accumulation by forage and grain crops and volatilization from seleniferous soils amended with different organic materials. Chemosphere 78:548–556
EPA (1996) Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. Method no. 3052. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/3052.pdf.
Fordyce FM (2013) Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment, essentials of medical geology. Springer, pp 375–416
Goldhaber SB (2003) Trace element risk assessment: essentiality vs. toxicity. Regul Tox Pharm 38:232–242
Gong J, Yang J, Wu H, Fu Y, Gao J, Tang S, Ma S (2022) Distribution of soil selenium and its relationship with parent rocks in Chengmai County, Hainan Island, China. Appl Geochem 136:105147
Hira CK, Partal K, Dhillon KS (2003) Dietary selenium intake by men and women in high and low selenium areas of Punjab. Pub Health Nutrit 7:39–43
Hofman K, Hamm R (1967) Zur Bestimmung von Schwefelwasserstoff mit N, N-dimethyl-p-phenylendiamin und Eisen(III)-chlorid. Fresenius Zeit Anal Chem 232:167–172
Hurst R, Siyame EWP, Young SD et al (2013) Soil-type influences human selenium status and underlies widespread selenium deficiency risks in Malawi. Sci Rep 3:1425. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01425
Kulp TR, Pratt LM (2004) Speciation and weathering of selenium in Upper Cretaceous chalk and shale from South Dakota and Wyoming, USA. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:3687–3701
Lamers LPM, Govers LL, Janssen ICJM, Geurts JJM, Van der Welle MEW, Van Katwijk MM, Van der Heide T, Roelofs JGM, Smolders AJP (2013) Sulfide as a soil phytotoxin—a review. Front Plant Sci 4:268
Mast MA, Mills TJ, Paschke SS, Keith G, Linard JI (2014) Mobilization of selenium from the Mancos Shale and associated soils in the lower Uncompahgre River Basin, Colorado. Appl Geochem 48:16–27
Mills TJ, Mast MA, Thomas J, Keith G (2016) Controls on selenium distribution and mobilization in an irrigated shallow groundwater system underlain by Mancos Shale, Uncompahgre River Basin, Colorado, USA. Sci Total Environ 566–567:1621–1631
Navarro-Alarcon M, Cabrera-Vique C (2008) Selenium in food and the human body: a review. Sci Total Environ 400:115–141
Nimirciag UB, Buratto E, Ajmone-Marsan F (2013) Leaching of trace metals from soil under alternating oxic-anoxic conditions: a column study. E3S Web of Conferences 19005.
Paikaray S (2016) Origin, mobilization and distribution of selenium in soil-water-air system: the Indian scenario. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 44:474–487
Paikaray S, Peiffer S (2022) Arsenic fractionation and mobilization in agricultural soils of NE Punjab. India Appl Geochem 139:105255
Qin H, Zhu J, Lin Z, Xu W, Tan D, Zheng L, Takahashi Y (2017) Selenium speciation in seleniferous agricultural soils under different cropping systems using sequential extraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ Poll 225:361–369
Reid ME, Duffield-Lillico AJ, Slate E, Natarajan N, Turnbull B, Jacobs E, Combs GF Jr, Alberts DS, Clark LC, Marshall JR (2008) The nutritional prevention of cancer: 400 mg per day selenium treatment. Nutrit Can 60:155–163
Schellenger AEP, Choi S, Onnis-Hayden A, Larese-Casanova P (2021) Selenium oxyanion exchange with Mg(II)-Fe(III) and Fe(II)-Fe(III) layered double hydroxides. Appl Clay Sci 200:105959
Sharma N, Prakash R, Srivastava A, Sadana U, Acharya R, Prakash N, Reddy AVR (2009) Profile of selenium in soil and crops in seleniferous area of Punjab, India by neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 281:59–62
Srivastava A, Kumar A, Singh M, Singla M, Scindia Y, Nair AGC (2002) Multi- element analysis of soil from the north-western region of India by neutron activation analysis using the single comparator method with special reference to selenium toxicity. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 254:645–648
Srivastava A, Bains GS, Acharya R, Reddy AVR (2011) Study of seleniferous soils using instrumental neutron activation analysis. Appl Radd Isot 69:818–821
Tamura H, Goto K, Yotsuyanagi T, Nagayama G (1974) Spectrophotometric determination of Iron(II) with 1,10-phenanthroline in the presence of large amounts of iron(III). Talanta 21:314–318
Tapiero H, Townsend DM, Tew KD (2003) The antioxidant role of selenium and seleno compounds. Biomed Pharmacother 57:134–144
Tessier A, Campbell FGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Wang S, Liang D, Wang D, Wei W, Fu D, Lin Z (2012) Selenium fractionation and speciation in agriculture soils and accumulation in corn (Zea mays L.) under field conditions in Shaanxi Province. China Sci Total Environ 427–428:159–164
WHO (World Health Organization) (1996) Guidelines for drinking water quality. Health criteria and other supporting information. 94/9960-MastercomlWiener Verlag-800, https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/38551
Wright WG (1999) Oxidation and mobilization of selenium by nitrate in irrigation drainage. J f Environ Qual 28:1182–1187
Yang H, Yang X, Ning Z, Kwon SY, Li M, Tack FMG, Kwon EE, Rinklebe J, Yin R (2022) The beneficial and hazardous effects of selenium on the health of the soil-plant-human system: an overview. J Hazard Mater 422:126876
Acknowledgements
The research work was funded by DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service), Germany under visiting professor scheme to Dr. Paikaray. University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India has supported field work and soil sample preparation by UGC-startup grant to Dr. Paikaray. Prof. Peiffer is thankful to funding sources to perform analysis and chemical costs. Ms. Navjot Kaur, Ms. Shefali Chander and Tanuj Mahajan, JRFs, PU, India has assisted soil sampling, acid digestion and map preparation.
Funding
The research work was funded by DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service), Germany and University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. Paikaray—field, experiment, analysis, interpretation, data compilation and writing. S. Peiffer—infrastructural support, lab and instruments, discussion, interpretation, review, editing, formatting.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Paikaray, S., Peiffer, S. Selenium enrichment, partitioning and leachability along semi-arid soils of NE Punjab, India. Environ Earth Sci 83, 272 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-024-11585-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-024-11585-3