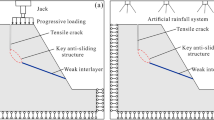
Abstract
The sliding of bedding rock slopes is primarily influenced by the presence of weak interlayers, which exhibit strong destructiveness, and complex sliding mechanisms, and pose difficulties in terms of reinforcement and treatment. This study aimed to examine the deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of the bedding rock slope at Mayanpo, located on the right bank of the Xiangjiaba Hydropower Station. To this end, field investigation, geological survey, and long-term monitoring were conducted. The results of the study revealed that Mayanpo slope is comprised of sandstone and soft mudstone interbedded layers, with an inclination that is almost equivalent to that of the rock layer. The overall slope stability is controlled by the weak interlayer (JC-1), which exhibits traction-based sliding. In light of this failure mechanism, a numerical simulation analysis of slope stability was performed and reinforcement measures, such as the implementation of anti-slide piles in combination with prestressed anchor cables and drainage tunnels, were designed. The slope deformation was continuously monitored following the reinforcement treatment. The monitoring data indicated that the slope experienced dynamic balance adjustment, leading to secondary deformations at the surface of the overburden and the weak geological parts under the weak interlayer. However, after 6 years of reinforcement, the overall dynamic adjustment of the Mayanpo slope was completed and the deformation stabilized. This research provides valuable insights into the deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of bedding rock slopes and demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed reinforcement measures in stabilizing the slope.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Abramson LW, Lee TS, Sharma S, Boyce GM (2001) Slope stability and stabilization methods. Wiley
Cai Z, Xu W, Meng Y, Shi C, Wang R (2016) Prediction of landslide displacement based on GA-LSSVM with multiple factors. Bull Eng Geol Env 75:637–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0804-z
Čarman M, Auflič MJ, Komac M (2014) Landslides at a uranium mill tailing deposit site Boršt (Slovenia) detected by radar interferometry. Landslides 11:527–536
Chen Z, Wang Z, Xi H, Yang Z, Zou L, Zhou Z, Zhou C (2016) Recent advances in high slope reinforcement in China: case studies. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 8:775–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.11.001
Duncan JM, Wright SG, Brandon TL (2014) Soil strength and slope stability. Wiley
Fookes PG, Sweeney M (1976) Stabilization and control of local rock falls and degrading rock slopes. Q J Eng Geol 9:37–55
Fourniadis IG, Liu JG, Mason PJ (2007) Regional assessment of landslide impact in the Three Gorges area, China, using ASTER data: Wushan-Zigui. Landslides 4:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-007-0080-5
Ghiassian H, Ghareh S (2008) Stability of sandy slopes under seepage conditions. Landslides 5:397–406
Glueer F, Loew S, Manconi A (2020) Paraglacial history and structure of the Moosfluh Landslide (1850–2016), Switzerland. Geomorphology 355:106677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.02.021
Hu W, Scaringi G, Xu Q, Van Asch TWJ, Huang R, Han W (2018) Suction and rate-dependent behaviour of a shear-zone soil from a landslide in a gently-inclined mudstone-sandstone sequence in the Sichuan basin, China. Eng Geol 237:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.02.005
Hu X, Liu D, Niu L, Liu C, Wang X, Fu R (2021) Development of soil–pile interactions and failure mechanisms in a pile-reinforced landslide. Eng Geol 294:106389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106389
Huang R (2007) Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 26:433–454
Huang D, Gu DM, Song YX, Cen DF, Zeng B (2018) Towards a complete understanding of the triggering mechanism of a large reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Eng Geol 238:36–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.03.008
Hungr O, Leroueil S, Picarelli L (2014) The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update. Landslides 11:167–194
Jia CJ, Xu WY, Wang RB, Wang SS, Lin ZN (2018) Experimental investigation on shear creep properties of undisturbed rock discontinuity in Baihetan Hydropower Station. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 104:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.02.011
Li S, Li X, Wu J, Liu Y (2007) Evolution process and pattern of sliding zone in large consequent bedding rock landslide. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 26:2473–2480
Lin C, Li T, Zhao L, Zhang Z, Lin C, Liu X, Niu Z (2020) Reinforcement effects and safety monitoring index for high steep slopes: a case study in China. Eng Geol 279:105861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105861
Lirer S (2012) Landslide stabilizing piles: experimental evidences and numerical interpretation. Eng Geol 149–150:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.08.002
Liu Y, Li H, Xiao K, Li J, Xia X, Liu B (2014) Seismic stability analysis of a layered rock slope. Comput Geotech 55:474–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.10.002
Lu Y, Tan Y, Li X (2018) Stability analyses on slopes of clay-rock mixtures using discrete element method. Eng Geol 244:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.021
Ma P, Cui Y, Wang W, Lin H, Zhang Y (2021) Coupling InSAR and numerical modeling for characterizing landslide movements under complex loads in urbanized hillslopes. Landslides 18:1611–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01604-2
Pouya A, Léonard C, Alfonsi P (2007) Modelling a viscous rock joint activated by rainfall: application to the La Clapière landslide. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.05.004
Sarma Sarada K (1979) Stability analysis of embankments and slopes. J Geotech Eng Div 105:1511–1524. https://doi.org/10.1061/AJGEB6.0000903
Song D, Chen Z, Ke Y, Nie W (2020) Seismic response analysis of a bedding rock slope based on the time-frequency joint analysis method: a case study from the middle reach of the Jinsha River, China. Eng Geol 274:105731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105731
Tang H, Li C, Hu X, Su A, Wang L, Wu Y, Criss R, Xiong C, Li Y (2015) Evolution characteristics of the Huangtupo landslide based on in situ tunneling and monitoring. Landslides 12:511–521
Tang H, Yong R, Ez Eldin MAM (2017) Stability analysis of stratified rock slopes with spatially variable strength parameters: the case of Qianjiangping landslide. Bull Eng Geol Env 76:839–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0876-4
Tao Z, Wang Y, Zhu C, Xu H, Li G, He M (2019) Mechanical evolution of constant resistance and large deformation anchor cables and their application in landslide monitoring. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:4787–4803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-01446-2
Wang S, Xu W (2020) A coupled elastoplastic anisotropic damage model for rock materials. Int J Damage Mech 29:1222–1245. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789520904093
Wang FW, Zhang YM, Huo ZT, Matsumoto T, Huang BL (2004) The July 14, 2003 Qianjiangping landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 1:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-004-0020-6
Wang J, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Wang Q, Xiang C, Fu H, Wang P, Zhao JX, Zhao L-H (2021a) Back-analysis of Donghekou landslide using improved DDA considering joint roughness degradation. Landslides 18:1925–1935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01586-1
Wang M, Ma G, Wang F (2021b) Numerically investigation on blast-induced wave propagation in catastrophic large-scale bedding rockslide. Landslides 18:785–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01537-w
Xu W, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Wang R, Wang R (2013) Deformation and control engineering related to huge landslide on left bank of Xiluodu reservoir, south-west China. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 17:s249–s268
Xu L, Dai F, Chen J, Iqbal J, Qu Y (2014) Analysis of a progressive slope failure in the Xiangjiaba reservoir area, Southwest China. Landslides 11:55–66
Xu G, Li W, Yu Z, Ma X, Yu Z (2015) The 2 September 2014 Shanshucao landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 12:1169–1178
Xu Q, Liu H, Ran J, Li W, Sun X (2016) Field monitoring of groundwater responses to heavy rainfalls and the early warning of the Kualiangzi landslide in Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Landslides 13:1555–1570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0717-3
Yan G, Yin Y, Huang B, Zhang Z, Zhu S (2019a) Formation mechanism and characteristics of the Jinjiling landslide in Wushan in the Three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Landslides 16:2087–2101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01234-3
Yan L, Xu WY, Wang HL, Wang RB, Meng QX, Yu J, Xie WC (2019b) Drainage controls on the Donglingxing landslide (China) induced by rainfall and fluctuation in reservoir water levels. Landslides 16:1583–1593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01202-x
Zhang Y (2018) Study on strength attenuation characteristics of slip soil and failure mechanism of Shanshucao landslide. China University of Geosciences
Zhang S-L, Zhu Z-H, Qi S-C, Hu Y-X, Du Q, Zhou J-W (2018) Deformation process and mechanism analyses for a planar sliding in the Mayanpo massive bedding rock slope at the Xiangjiaba Hydropower Station. Landslides 15:2061–2073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1041-x
Zhou J-W, Jiao M-Y, Xing H-G, Yang X-G, Yang Y-C (2017) A reliability analysis method for rock slope controlled by weak structural surface. Geosci J 21:453–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-016-0058-1
Zuo S, Zhao L, Tan H, Li L, Deng D, Song Z (2021) Reliability parameter back analysis of bedding rock slope with multi-layer slide surfaces. Bull Eng Geol Env 80:7227–7239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02355-7
Funding
The work presented in this paper was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1965204); Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin (China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Grant No: IWHR-SKL-KF202016 and SKL2022ZD05), Scientific Research Project of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research (No. GE110145B0022021), and State Grid Company Limited Headquarters Management Technology Projects (No. 5108-202218280A-2-301-XG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Long Jiang: Conducted feld studies and experiments. Chaojun Jia: Conducted field studies, data interpretation, and manuscript writing. Qiang Zhang: Read the manuscript and provide comments. Jun Yu: Read the manuscript and provide comments. Qingfu Huang: Drawing and preparing all fgures and data interpretation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Zhang, Q., Jia, C. et al. Investigating on deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of bedding rock slope: field study, long-term monitoring, and reinforcement measures. Environ Earth Sci 83, 45 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11372-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11372-6