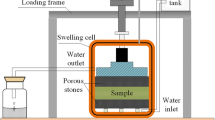
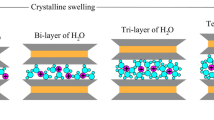
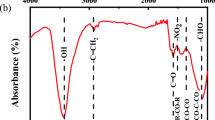
Abstract
Formation damage due to clay minerals swelling and migration is one of the major challenges in shaly reservoirs. The main objective of this study was to explore the potential of nanoparticles application as clay swelling inhibitor and investigate the effect of various parameters on nanoparticles performance. The experiments were designed using Taguchi orthogonal array and the impact of the main factors, including pH value, salinity, and temperature, and the presence of nanoparticles with concentrations of 0.05–1 wt% was inspected on the clay swelling. Zeta potential measurements were used to determine the surface charge of nanoparticles at different pH values. XRD and XRF analyses were carried out to characterize the nanoparticles and bentonite powder. The experimental results showed that after solution salinity, the most effective parameter on the clay swelling is the concentration of nanoparticles. The minimum clay swelling index was obtained in the presence of silica nanoparticles at 0.1 wt% concentration. It was observed that higher concentrations of nanoparticles not only have no effect on reducing the clay swelling but also increase the volume due to nanoparticles agglomeration. The presence of alumina nanoparticles showed an inverse effect on the clay swelling and increased the swelling index. The results of zeta potential measurements indicated that nanoparticles with negative surface charge help to decrease the clay swelling as the result of similar charge repulsion. The low swelling index detected in samples containing silica nanoparticles shows the potential of nanoparticles to prevent the formation damage due to clay swelling.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abdullah AH, Ridha S, Mohshim DF, Yusuf M, Kamyab H, Krishna S, Maoinser MA (2022) A comprehensive review of nanoparticles: effect on water-based drilling fluids and wellbore stability. Chemosphere 308:136274
Ackah FS, Hailiang W, Huaiping F, Cheng L, Feng LZ (2022) Use of Taguchi method to evaluate the unconfined compressive strength of quicklime stabilized silty clayey subgrade. Case Stud Constr Mater 17:e01417
Akhtarmanesh S, Shahrabi MA, Atashnezhad A (2013) Improvement of wellbore stability in shale using nanoparticles. J Petrol Sci Eng 112:290–295
Aksu I, Bazilevskaya E, Karpyn ZT (2015) Swelling of clay minerals in unconsolidated porous media and its impact on permeability. GeoResJ 7:1–13
Anderson R, Ratcliffe I, Greenwell C, Williams P, Cliffe S, Coveney P (2010) Clay swelling—a challenge in the oilfield. Earth Sci Rev 98(3):201–216
Asaad A, Hubert F, Ferrage E, Dabat T, Paineau E, Porion P, Savoye S, Gregoire B, Dazas B, Delville A, Tertre E (2021) Role of interlayer porosity and particle organization in the diffusion of water in swelling clays. Appl Clay Sci 207:106089
Baik MH, Lee SY (2010) Colloidal stability of bentonite clay considering surface charge properties as a function of pH and ionic strength. J Ind Eng Chem 16(5):837–841
Balaban RC, Vidal ELF, Borges MR (2015) Design of experiments to evaluate clay swelling inhibition by different combinations of organic compounds and inorganic salts for application in water base drilling fluids. Appl Clay Sci 105:124–130
Barast G, Razakamanantsoa A, Djeran-Maigre I, Nicholson T, Williams D (2017) Swelling properties of natural and modified bentonites by rheological description. Appl Clay Sci 142:60–68
Berry SL, Boles JL, Brannon HD, Beall BB (2008) Performance evaluation of ionic liquids as a clay stabilizer and shale inhibitor. In: SPE international symposium and exhibition on formation damage control, Lafayette, Louisiana, USA
Butscher C, Mutschler T, Blum P (2016) Swelling of clay-sulfate rocks: a review of processes and controls. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:1533–1549
Chen G, Yana J, Lili L, Zhang J, Gu X, Song H (2017) Preparation and performance of amine-tartaric salt as potential clay swelling inhibitor. Appl Clay Sci 138:12–16
Chen WL, Grabowski RC, Goel S (2022) Clay swelling: role of cations in stabilizing destabilizing mechanisms. ACS Omega 7(4):3185–3191
Cheraghi M, Hajipour M, Emamzadeh A (2022) Enhancement of the heat capacity of water-based drilling fluids for deep drilling applications. Braz J Chem Eng 39:77–86
Cong M, Zhao B, Long G, Sang X, Xie Y (2018) Quantitative study on strength development of earth-based construction prepared by organic clay and high-efficiency soil stabilizer. Constr Build Mater 174:520–528
Davis R, John P (2018) Application of taguchi-based design of experiments for industrial chemical processes. In: Valter Silva (ed) Statistical approaches with emphasis on design of experiments applied to chemical processes. IntechOpen
El-Diasty AI, Ragab AM (2013) Applications of nanotechnology in the oil and gas industry: latest trends worldwide and future challenges in Egypt. In: North Africa technical conference and exhibition, Cairo, Egypt
Fu L, Liao K, Ge J, Zhang G, He Y, Wang X, Zhang S, Deng S (2019) Study of ethylenediammonium dichloride as a clay stabilizer used in the fracturing fluid. J Petrol Sci Eng 179:958–965
Habibi A, Ahmadi M, Pourafshary P, Ayatollahi S, Al-Wahaibi Y (2013) Reduction of fines migration by nanofluids injection: an experimental study. SPE J 18:309–318
Hajipour M (2020) CFD simulation of turbulent flow of drill cuttings and parametric studies in a horizontal annulus. SN Appl Sci 2:1146
Hajipour M, Movahedi H, Jamshidi S (2023) Evaluation of the effect of metal oxide nanoparticles in combination with polyacrylamide on improving the filtration and rheological properties of drilling fluids. J Miner Resour Eng 8(1):1–16
Hoelscher KP, De Stefano G, Riley M, Young S (2012) Application of nanotechnology in drilling fluids. In: SPE international oilfield nanotechnology conference and exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Hu X, Hu S, Jin F, Huang S (eds) (2016) Physics of petroleum reservoirs. Springer mineralogy. Springer, Berlin
Ishimori H, Katsumi T (2012) Temperature effects on the swelling capacity and barrier performance of geosynthetic clay liners permeated with sodium chloride solutions. Geotext Geomembr 33:25–33
Jain R, Mahto V, Sharma VP (2015) Evaluation of polyacrylamide-grafted-polyethylene glycol/ silica nanocomposite as potential additive in water based drilling mud for reactive shale formation. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 26:526–537
Khan MA, Haneef J, Lalji SM et al (2021) Experimental study and modeling of water-based fluid imbibition process in Middle and Lower Indus Basin Formations of Pakistan. J Petrol Explor Prod Technol 11:425–438
Lalji S, Ali S, Ahmed R et al (2022a) Study the effects of mineral content on water diffusion mechanism and swelling characteristics in shale formations of Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 15:864
Lalji SM, Ali SI, Ahmed R et al (2022b) Influence of graphene oxide on salt-polymer mud rheology and Pakistan shale swelling inhibition behavior. Arab J Geosci 15:612
Lee DH, Park JS, Ryu MR, Park JH (2013) Development of a highly efficient low-emission diesel engine-powered cogeneration system and its optimization using Taguchi method. Appl Therm Eng 50(1):491–495
Madsen I, Scarlett N, Kern A (2011) Description and survey of methodologies for the determination of amorphous content via X-ray powder diffraction. Zeitschrift Fur Kristallographie 226:944–955
Mao H, Huang Y, Luo J, Zhang M (2021) Molecular simulation of polyether amines intercalation into Na-montmorillonite interlayer as clay-swelling inhibitors. Appl Clay Sci 202:105991
Metin CO, Lake LW, Miranda CR, Nguyen QP (2011) Stability of aqueous silica nanoparticle dispersions. J Nanopart Res 13(2):839–850
Mohan KK, Vaidya RN, Reed MG, Fogler HS (1993) Water sensitivity of sandstones containing swelling and non-swelling clays. Colloids Surf A 73:237–254
Movahedi H, Jamshidi S, Hajipour M (2022) Hydrodynamic analysis and cake erosion properties of a modified water-based drilling fluid by a polyacrylamide/silica nanocomposite during rotating-disk dynamic filtration. ACS Omega 7:44223–44240
Pham H, Nguyen QP (2014) Effect of silica nanoparticles on clay swelling and aqueous stability of nanoparticle dispersions. J Nanopart Res 16:2137
Sameni A, Pourafshary P, Ghanbarzadeh M, Ayatollahi S (2015) Effect of nanoparticles on clay swelling and migration. Egypt J Pet 24(4):429–437
Scalia J, Benson C, Finnegan M (2019) Alternate procedures for swell index testing of granular bentonite from GCLs. Geotech Test J 42(5):20180075
Sensoy T, Chenevert ME, Sharma MM (2009) Minimizing water invasion in shale using nanoparticles. In: SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana
Sharifipour M, Pourafshary P, Nakhaee A (2017) Study of the effect of clay swelling on the oil recovery factor in porous media using a glass micromodel. Appl Clay Sci 141:125–131
Shirazi SM, Wiwat S, Kazama H, Kuwano J, Shaaban MG (2011) Salinity effect on swelling characteristics of compacted bentonite. Environ Prot Eng 37(2):65–74
Sruthi PL, Reddy PHP (2019) Swelling and mineralogical characteristics of alkali-transformed kaolinitic clays. Appl Clay Sci 183:105353
Sun C, Li G, Sun Y, He J, Rong H (2019) Modelling hydration swelling and weakening of montmorillonite particles in mudstone. Processes 7(7):428
Swai RE (2020) A review of molecular dynamics simulations in the designing of effective shale inhibitors: application for drilling with water-based drilling fluids. J Petrol Explor Prod Technol 10:3515–3532
Valadbeygian V, Hajipour M, Behnood M (2023) Static and dynamic evaluation of formation damage due to barium sulfate scale during water injection in carbonate reservoirs. J Petrol Explor Prod Technol 13(8):1819–1831
Wan Y, Guo D, Hui X, Liu L, Yao Y (2020) Studies on hydration swelling and bound water type of sodium and polymer-modified calcium bentonite. Adv Polym Technol 2020:9361795
Wang Z, Wu W, Bian X, Wu Y (2016) Synthesis and characterization of amorphous Al2O3 and γ-Al2O3 by spray pyrolysis. Green Process Synth 5(3):305–310
Wangler T (2023) Mechanism of clay swelling in Villarlod molasse: a Swiss sandstone. Environ Earth Sci 82:259
Wilson MJ, Wilson L (2014) Clay mineralogy and shale instability: an alternative conceptual analysis. Clay Miner 49(2):127–145
Yin C, Zhang W, Jiang X, Huang Z (2018) Effects of initial water content on microstructure and mechanical properties of lean clay soil stabilized by compound calcium-based stabilizer. Materials 11(10):1933
Yotsuji K, Tachi Y, Sakuma H, Kawamura K (2021) Effect of interlayer cations on montmorillonite swelling: comparison between molecular dynamic simulations and experiments. Appl Clay Sci 204:106034
Zaitoun A, Berton N (1992) Stabilization of montmorillonite clay in porous media by high-molecular-weight polymers. SPE Prod Eng 7:160–166
Zhou D, Abdel-Fattah AI, Keller AA (2012) Clay particles destabilize engineered nanoparticles in aqueous environments. Environ Sci Technol 46(14):7520–7526
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ali Kianersi and Mastaneh Hajipour wrote the main manuscript text and prepared figures. Mastaneh Hajipour and Ebrahim Biniaz Delijani interpreted the results and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kianersi, A., Hajipour, M. & Biniaz Delijani, E. Experimental evaluation of bentonite clay swelling and inhibition effect of nanoparticles. Environ Earth Sci 82, 526 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11210-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11210-9