Abstract
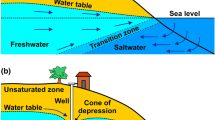
The Menzel Horr coastal aquifer in Northeastern Tunisia, Mediterranean basin, suffers for decades, from severe water resource depletion and seawater intrusion due to overexploitation. To address this issue, the study focused on using geophysical subsurface imaging techniques to understand seawater flow in porous media and define the geological framework of the study area. Regional ground gravity data supported by a seismic reflection profile was analyzed to highlight the structural control of the Plio-Quaternary to Miocene aquifer system in this region. The study area is located above a hidden folded structure called “the Menzel Horr pop-up” affected by three major faults. In a second step, a time domain electromagnetic (TDEM) survey integrated with an electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) profile was conducted. These surveys were calibrated using detailed well log lithostratigraphy, to dissociate the deep clayey substratum from the sandy shallow aquifer and were able to detect the brackish water signature that impacted the sandy/sandstone aquifer. Finally, at a local scale, a set of nine ERT profiles were performed along the coastline with the Wenner–Schlumberger array to image the porous zone in the first 20 m of depth. The obtained data were smoothed and filtered then inversed. The density transition zone between freshwater/saltwater was imaged as a distinct plume of seawater. Finally, a “Pseudo-3D” electrical resistivity image was built aiming to provide a very useful tool to help hydrogeologists develop effective strategies for managing and conserving water resources and mitigating seawater intrusion in the Menzel Horr coastal aquifer.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not available.
References
Aarhus GeoSoftware (2017) Aarhus SPIA. Aarhus GeoSoftware, Aarhus C
Abdelkader R, Larbi D, Rihab H, Fethi B, Chemseddine F, Azzedine H (2012) Geochemical characterization of groundwater from shallow aquifer surrounding Fetzara Lake NE Algeria. Arab J Geosci 5(1):1–13
Abdennadher J, Boukthir M (2006) Numerical simulation of the barotropic tides in the Tunisian Shelf and the Strait of Sicily. J Mar Syst 63:162–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2006.07.001
Abu Heen Z, Muhsen S (2016) Application of vertical Electrical sounding for delineation of sea water intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of southern governorate of Gaza strip Palestine. IUG J Nat Sci IUGNS 24(2):07–20p
Atoui A, Brahim M, Sammari C, Aleya L (2016) Surface sediment dynamics along the shore of Hammamet Gulf (Tunisia, southern Mediterranean). J Afr Earth Sci 121:168–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.06.001
Azaiez H, Gabtni H, Chabaane A, Bedir M (2020) Geophysical study of Hammam Sidi Maamar geothermal site in Central Tunisia for sustainable development. J Afr Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2020.103897
Balwant P, Jyothi V, Pujari PR (2021) Integrated hydrochemical and ERT approach for seawater intrusion study in a coastal aquifer: a case study from Jafrabad Town, Gujarat State India. Environ Monit Assess 193:558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09251-3
Bear J, Cheng A, Sorek S, Ouazar D, Herrera I (1999) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Concepts, methods and practices. Kluwer Academic Publishers
Bédir M, Arbi A, Khomsi S, Houatmia F, Aissaoui MN (2016) Seismic tectono-stratigraphy of fluvio-deltaic to deep marine Miocene silicoclastic hydrocarbon reservoir systems in the Gulf of Hammamet, northeastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 9(19):726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2745-7
Bellali A, Jarraya Horriche F, Gabtni H, Bédir M (2018) Seismic reflection and structuring characterization of deep aquifer system in the Dakhla syncline (Cap Bon, North-Eastern Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 140:134e150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.12.012
Ben Ayed N (1986) Évolution tectonique de l’avant pays de la chaîne alpine de Tunisie du début de Mésozoïque à l’Actuel. Thèse de 3ème cycle, Univ. Paris-Sud Orsay, 327p.
Ben Hamouda M F (2008) Approche Hydrogéochimique Et Isotopique Des Systèmes Aquifères Côtiers Du Cap Bon : Cas Des Nappes De La Côte Orientale Et D’el Haouaria, Tunisie Institut National Agronomique De Tunisie Département De Génie Rural Eaux Et Forêts. Thèse De Doctorat.
Ben Salem H (1992) Contribution a` la connaissance de la géologie du Cap Bon : stratigraphie, tectonique et sédimentologie. These 3e cycle, Université de Tunis-II, Tunis, Tunisie, 203 p.
Ben Salem H (1995) Notice explicative de la carte géologique de la Tunisie à 1/50.000 Kelibia ett Menzel Horr, Feuille n° 16 et 23
Bensalem H (1998) Notice explicative de la carte géologique de la Tunisie à 1/50.000 Menzel Bou Zelfa, Feuille n° 22
Bensalem H (2002) Notice explicative de la carte géologique de la Tunisie à 1/50.000 Tazoghrane, Feuille n° 15
Biely A, Rakus M, Robinson P, Salaj J (1972) Essai de corrélation des formations miocènes au sud de dorsale Tunisienne. Notes Service Géologique, Tunisie, pp 73–92
Bouzouf B, Ouazar D, Himi M, Casas A, Elmahi I, Benkhaldoun F (2001) Integrating hydrogeochemical and geophysical data for testing a finite volume based numerical model for saltwater intrusion. Transp Porous Media 43:179–194
Brahmi S, Fehdi C, Hadji R, Brahmi S, Hamad A, Hamed Y (2023) Karst-induced sinkhole detection using a tomography imaging survey, case of Setifian high plain NE Algeria. Geotech Geol Eng 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02384-x
Burollet PF (1956) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie Centrale. Ann Mines Géol, Tunis, p 18
Chabaane A, Redhaounia B, Gabtni H, Amiri A (2018) Contribution of geophysics to geometric characterization of freshwater–saltwater interface in the Maâmoura region (NE Tunisia). Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 3:26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0068-7
Chang SW, Clement TP, Simpson MJ, Lee KK (2011) Does sea-level rise have an impact on saltwater intrusion? Adv Water Resour 34(10):1283–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.06.006
Chekirbane A, Tsujimura M, Kawachi A, Isoda H, Tarhouni J, Benalaya A (2013) Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater salinization in an ephemeral coastal food plain: Cap Bon Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 58(5):1097–1110
Clary P (1968) Rapport définitif prospection électrique dans la région de Tafelloune-Menzel Horr.
Comte JC (2008) Apport de la tomographie électrique à la modélisation des écoulements densitaires dans les aquifères côtiers: application à trois contextes climatiques contrastés (Canada, Nouvelle-Calédonie, Sénégal). Thèse de doctorat. Université d’Avignon. https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00381767v1/document
DGRE (1968) Prospection électrique région de Tafelloune - Menzel Horr: Rapport définitif
DGRE (Water Ressources Direction) (2004) Compte rendu de fin de travaux du piézomètre Menzel Horr. DGRE
DGRE (2015a) Annuaire piézométrique. DGRE
DGRE (2015b) Annuaire d’exploitation des nappes phréatique. DGRE
Duque C, Calvache ML, Pedrera A, Martín-Rosales W, López-Chicano M (2008) Combined time domain electromagnetic soundings and gravimetry to determine marine intrusion in a detrital coastal aquifer (Southern Spain). J Hydrol 349(3–4):536–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.11.031
Ennabli M (1980) Étude hydrogéologique des aquifères du Nord-Est de la Tunisie pour une gestion intégrée des ressources en eau. Thesis (PhD), University of Nice, France.
Everett ME, Meju MA (2005) Near-surface controlled-source electromagnetic induction: background and recent advances. Hydrogeophysics, 523rd edn. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 157–183
Feki M (1970) Paléoécologie du pliocène marin du nord de la Tunisie ann.mines et de Tunisie n 27
Gaaloul N, Cheng A H (2003) Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Investigation of Coastal Aquifers in Tunisia Crisis in Overexploitation and Salinization. In: Second International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers, p 13
Gabtni H, Jallouli C (2017) Regional-residual separation of potential field: An example from Tunisia. J Appl Geophys 137:8–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2016.12.011
Gharsalli R, Zouaghi T, Soussi M, Chebbi R, Khomsi S, Bédir M (2013) Seismic sequence stratigraphy of Miocene deposits related to eustatic, tectonic and climatic events, Cap Bon Peninsula, Northeastern Tunisia. CR Geosci 345(9–10):401–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2013.07.003
Glover PWJ (2015) Geophysical properties of the near surface earth: electrical properties, University of Leeds, Leeds. Elsevier BV
Goebel M, Pidlisecky A, Knight R (2017) Resistivity imaging reveals complex pattern of saltwater intrusion along Monterey coast. J Hydrol 551:746–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.02.037
Hamad A, Hadji R, Boubaya D, Brahmi S, Baali F, Legrioui R, Hamed Y (2021) Integrating gravity data for structural investigation of the Youkous-Tebessa and Foussana-Talah transboundary basins (North Africa). Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 6:1–11
Hamed Y, Hadji R, Redhaounia B, Zighmi K, Bâali F, El Gayar A (2018) Climate impact on surface and groundwater in North Africa: a global synthesis of findings and recommendations. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 3:1–15
Hamed Y, Hadji R, Ahmadi R, Ayadi Y, Shuhab K, Pulido-Bosch A (2023) Hydrogeological investigation of karst aquifers using an integrated geomorphological, geochemical, GIS, and remote sensing techniques (Southern Mediterranean Basin—Tunisia). Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-02994-8
Hazreek ZAM, Hashim MMM, Asmawisham AMN, Hafiz ZM, Fairus YM, Fahmy KA, Ashraf MIM, Rosli S, Nordiana MM (2018) Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity imaging (Eri) at Malaysian coastal area. Int J Civil Eng Technol 9(9):1185–1193
Huntley D (1986) Relations between permeability and electrical resistivity in granular aquifers. Gr Water 24(4):466
Idowu TE, Lasisi KH (2020) Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of East and Horn of Africa: A review from a regional perspective. Sci Afr 8:e00402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00402
Ivanov Y, Kisyov A (2016) Geophysical approach for monitoring saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Annual of the University of Mining and Geology “st. Ivan rilski”, vol. 59, part I, Geology and Geophysics, Conference Paper
Kallel A, Ksibi M, Dhia HB, Khélifi N (2018) Recent advances in environmental science from the Euro-Mediterranean and surrounding regions: proceedings of Euro-Mediterranean conference for environ integration (EMCEI-1) Tunisia 2017. Springer International Publishing
Karamouz M, Ahmadi A, Akhbari M (2011) Groundwater hydrology engineering, planning, and management. CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group
Kazakis N, Pavlou A, Vargemezis G, Voudouris KS, Soulios G, Pliakas F, Tsokas G (2016) Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data. An application in the coastal area of eastern Thermaikos Gulf Greece. Sci Total Environ 543:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.041
Kerrou J, Renard P, Lecca G, Tarhouni J (2010) Grid-enabled Monte Carlo analysis of the impacts of uncertain dischargerates on seawater intrusion in the Korba aquifer (Tunisia). Hydrol Sci J 55(8):1325–1336. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2010.519706
Kim JH, Lee J, Cheong TJ, Kim RH, Koh DC, Ryu JS, Chang HW (2005) Use of time series analysis for the identification of tidal effect on groundwater in the coastal area of Kimje Korea. J Hydrol 300(1–4):188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.06.004
Kim KY, Seong H, Kim T, Park KH, Woo NC, Park YS, Koh GW, Park WB (2006) Tidal effects on variations of fresh–saltwater interface and groundwater flow in a multilayered coastal aquifer on a volcanic island (Jeju Island, Korea). J Hydrol 330(3–4):525–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.04.022
Kouzana L, Benassi R, Ben Mammou A, Sfar M (2010) Journal of African earth sciences geophysical and hydrochemical study of the seawater intrusion in Mediterranean semi arid zones. Case of the Korba coastal aquifer (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 58(2):242–254
Kwader T (1985) Estimating aquifer permeability from formation resistivity factors. Gr Water 23(6):762
Loke MH, Dahlin T, Rucker DF (2014) Smoothness-constrained time-lapse inversion of data from 3D resistivity surveys. Near Surf Geophys 12(1):5–24
Loke MH (2004) Tutorial: 2-D and 3-D electrical imaging surveys. Geotomo Software, Res2dinv 3.5 Software, 29–31
Loke MH, Chambers JE, Rucker DF, Kuras O, Wilkinson PB (2013) Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J Appl Geophys 95:135–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2013.02.017
Maamri R (2020) Evolution Structurale Du Nord-Est De La Tunisie A Partir Des Données De Surface Et De Subsurface : Implication Sur Les Risques Sismiques Dans La Région Du Grand Tunis, Bir Mcherga Et Du Cap Bon Université De Carthage Departement De Geologie These De Doctorat
Mahlknecht J, Merchán D, Rosner M, Meixner A, Ledesma-Ruiz R (2017) Assessing seawater intrusion in an arid coastal aquifer under high anthropogenic influence using major constituents, Sr and B isotopes in groundwater. Sci Total Environ 587–588:282–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.137
Mao X, Enot P, Barry DA, Li L, Binley A, Jeng DS (2006) Tidal influence on behaviour of a coastal aquifer adjacent to a low-relief estuary. J Hydrol 327(1–2):110–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.11.030
Melloul A, Collin M (2006) Hydrogeological changes in coastal aquifers due to sea level rise. Ocean Coast Manag 49:281–297
Muzzillo R, Zuffianò LE, Rizzo E, Canora F, Capozzoli L, Giampaolo V, De Giorgio G, Sdao F, Polemio M (2021) Seawater intrusion proneness and geophysical investigations in the Metaponto coastal plain (Basilicata, Italy). Water 13:53. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13010053
Ncibi K, Hamed Y, Hadji R, Busico G, Benmarce K, Missaoui R, Wederni K (2023) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in groundwater and their relationship with the ecosystem: case study in Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-25016-y
Nguyen F, Kemna A, Antonsson A, Engesgaard P, Kuras O, Ogilvy R, Gisbert J, Jorreto S, Pulido-Bosch A (2009) Characterization of seawater intrusion using 2D electrical imaging. Near Surf Geophys. https://doi.org/10.3997/1873-0604.2009025
Nowroozi AA, Horrocks SB, Henderso P (1999) Saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer in the eastern shore of Virginia: a reconnaissance electrical resistivity survey. J Appl Geophys 42:1–22
Othmani A, Béjaoui B, Chevalier C, Elhmaidi D, Devenon J, Lotfi Aleya L (2017) High-resolution numerical modelling of the barotropic tides in the Gulf of Gabes, eastern Mediterranean Sea (Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.01.007
Paniconi C, Khlaif I, Giuditta L, Giacomelli A, Tarhouni J (2001) Modeling and analysis of Seawater Intrusion in the coastal aquifer of eastern Cap-Bon, Tunisia, kluwer academic publishers, Netherlands. Trans Porous Media 43:3–28
Reynolds JM (2011) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics. Wiley, Hoboken
Robain H, Bobachev A (2017) X2IPI, toolbox for 2D electrical resistivity tomography and IP measurements. User manual, p 54
Schamper C, Pedersen JB, Auken E, Christiansen AV, Vittecoq B, Deparis J, Jaouen T, Lacquement F, Nehlig P, Perrin J, Reninger PA (2013) Airborne transient EM methods and their applications for coastal groundwater investigations. Coast Res Libr 1:21–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5648-9_7
Telford WM, Geldart LP, Sheriff RE, Key DA (1990) Applied geophysics. Cambridge University Press, London
White NJ, Church JA, Gregory JM (2005) Coastal and global averaged sea level rise for 1950 to 2000. Geophys Res Lett 32:L01601. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021391
Whitehead N, Musselman C (2008) Montaj Grav/Mag Interpretation: processing, analysis and visualization system for 3D inversion of potential field data for oasis montaj v6. 3, Geosoft Incorporated, 85 Richmond St. " W., Toronto, Ontario, M5H 2C9. Canada.
Wilson SR, Ingham M, McConchie JA (2006) The applicability of earth resistivity methods for saline interface definition. J Hydrol 316:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.05.004
Zghibi A, Tarhouni J, Zouhri L (2013) Assessment of seawater intrusion and nitrate contamination on the groundwater quality in the Korba coastal plain of Cap-Bon (North-east of Tunisia). Afr Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2013.07.009
Zghibi A, Mirchi A, Zouhri L, Taupin JD, Chekirbane A, Tarhouni J (2019) Implications of groundwater development and seawater intrusion for sustainability of a Mediterranean coastal aquifer in Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7866-5
Ziadi A, Hariga TN, Tarhouni J (2017) Use of time-domain electromagnetic (TDEM) method to investigate seawater intrusion in the Lebna coastal aquifer of eastern Cap Bon Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 10:492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3265-9
Ziadi A, Hariga NT, Tarhouni J (2019) Mineralization and pollution sources in the coastal aquifer of Lebna, Cap Bon Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.01.004
Zouhri L, Arbi Toto E, Carlier E, Debieche TH (2010) Salinité des ressources en eau: intrusion marine et interaction eaux–roches (Maroc occidental). Hydrol Sci J 55(8):1337–1347. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2010.520561
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Water Research and Technologies Center (CERTE), Technopole Borj-Cedria, Tunisia. In addition, it is part of the project “Water Task Force WTF, Porous Media, Fluid Transfers and Global Changes for Better Resource Management, CERTE/MERES, Tunisia, 2019-2022”. The authors are very grateful to ONM and ETAP for, respectively, providing gravity and seismic data. The authors would like, also to thank Oussama Kortas and Mohamed Hamrouni Ph.D. students (CERTE) for their support during the ERT acquisition, to Thank Dr. Nesrine Ghouili for the reviews of part of this article. In addition, we tend to thank the CRDA (Regional Office of Agricultural Development) of Nabeul for providing us with the 2020 Static level data of the sallow aquifer of the western coast. Finally, the authors would like to express their appreciation to anonymous reviewers for taking the time and effort required to carefully review the article.
Funding
The authors declare that this research did not receive any specific grant or other support from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors commented, edited, read, and approved final versions of the manuscript. Methodology preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by SA and HG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SA and all authors commented on previous versions. Review, editing, and supervising of the hydrogeology part were conducted by LZ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ayari, S., Gabtni, H. & Zouhri, L. Imaging seawater flow in porous media under climate change water stress using geophysics: a case study of Menzel Horr coastline in Northeastern Tunisia, Mediterranean basin. Environ Earth Sci 82, 499 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11199-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11199-1