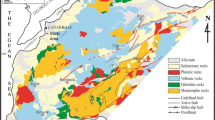
Abstract
The investigation of karst channels is an important work to ensure the safety of underground construction and mining engineering. At present, the combination of the geophysical method and drilling method is the primary and most commonly used approach in karst detection work. However, sometimes limited by conditions, it is difficult to carry out drilling work. In coastal limestone mines, karst is usually developed, so it is crucial and significant to carry out the exploration work on karst channels. Taking a coastal limestone mine in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China as a case study, electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and transient electromagnetic method (TEM) were adopted to investigate the subsurface low-resistivity anomalies. According to the results, the distribution area of karst channels was preliminarily determined by the low-resistivity responses. Then, a sluicing test was carried out to analyze the primary direction of underground karst channels in this area, and several main leakage and outflow points were identified, which could serve as evidence for the channel paths. Besides, the ERT method was used for repeated exploration in the detection area not submerged by seawater after the sluicing test, and the results showed that the low-resistivity responses were consistent before and after the sluicing test. Combining the results of the electrical exploration and the sluicing test, the direction and main pathway of underground runoff were determined, and the distribution of underground karst channels in the study area could be obtained.


(Source: China Resources Cement (Hepu) Co. LTD)













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abd El-Aal AK, Masoud AA (2017) Impacts of karst phenomena on engineering properties of limestone foundation bed, Ar Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3089-7
Ba XZ, Li LP, Wang J, Zhang W, Fang ZD, Sun SQ, Liu ZH, Xiong YF (2020) Near-surface site investigation and imaging of karst cave using comprehensive geophysical and laser scanning: a case study in Shandong, China. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09037-9
Bali BS, Wani AA, Bhat GR, Mir SA (2021) GPR investigation of mining induced subsidence and its effects on surface structures: a case study of Srinagar City, J&K, India, NW Himalayas. J Geol Soc India 97:751–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1756-5
Bermejo L, Ortega AI, Pares JM, Campana I, de Castro JMB, Carbonell E, Conyers LB (2020) Karst features interpretation using ground-penetrating radar: a case study from the Sierra de Atapuerca, Spain. Geomorphology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107311
Bharti AK, Pal SK, Priyam P, Kumar S, Srivastava S, Yadav PK (2016a) Subsurface cavity detection over Patherdih colliery, Jharia Coalfield, India using electrical resistivity tomography. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5025-z
Bharti AK, Pal SK, Priyam P, Pathak VK, Kumar R, Ranjan SK (2016b) Detection of illegal mine voids using electrical resistivity tomography: the case-study of Raniganj coalfield (India). Eng Geol 213:120–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.09.004
Bharti AK, Pal SK, Saurabh, Singh KKK, Singh PK, Prakash A, Tiwary RK (2019) Groundwater prospecting by the inversion of cumulative data of Wenner-Schlumberger and dipole-dipole arrays: a case study at Turamdih, Jharkhand, India. J Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1137-2
Bianchi M, Zheng CM, Tick GR, Gorelick SM (2011) Investigation of small-scale preferential flow with a forced-gradient tracer test. Ground Water 49:503–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00746.x
Cao RL, Feng SX (2021) Detection methods for unfavorable geology and soil caves before grouting in karst terrains. Soil Mech Found Eng 58:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-021-09744-w
Chen X, Zhang ZC, Soulsby C, Cheng QB, Binley A, Jiang R, Tao M (2018) Characterizing the heterogeneity of karst critical zone and its hydrological function: an integrated approach. Hydrol Process 32:2932–2946. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13232
Contrucci I, Balland C, Kinscher J, Bennani M, Bigarre P, Bernard P (2019) Aseismic mining subsidence in an abandoned mine: influence factors and consequences for post-mining risk management. Pure Appl Geophys 176:801–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-2015-6
Das P, Pal SK, Mohanty PR, Priyam P, Bharti AK, Kumar R (2017) Abandoned mine galleries detection using electrical resistivity tomography method over Jharia Coal Field, India. J Geol Soc India 90:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0695-7
Du CL, Zhou YS, Gan FP, Chen YX (2020) Investigation of karst collapses using integrated geophysical methods: an example from Conghua District, Guangzhou City, China. Acta Carsologica 49:255–264. https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v49i2-3.7786
Ebong ED, George AM, Ekwok SE, Akpan AE, Asfahani J (2021) 2D electrical resistivity inversion and ground penetrating radar investigation of near surface cave in New Netim area, southeastern Nigeria. Acta Geod Geophys 56:765–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-021-00364-2
Ezersky MG, Frumkin A (2017) Evaluation and mapping of Dead Sea coastal aquifers salinity using Transient Electromagnetic (TEM) resistivity measurements. CR Geosci 349:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2016.08.001
Foudili D, Bouzid A, Berguig MC, Bougchiche SS, Abtout A, Guemache MA (2019) Investigating karst collapse geohazards using magnetotellurics: a case study of M’rara basin, Algerian Sahara. J Appl Geophys 160:144–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.11.011
Fretwell JD, Stewart MT (1981) Resistivity study of a Coastal Karst Terrain, Florida. Ground Water 19:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1981.tb03454.x
Li SC, Liu B, Xu XJ, Nie LC, Liu ZY, Song J, Sun HF, Chen L, Fan KR (2017) An overview of ahead geological prospecting in tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 63:69–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2016.12.011
Liu B, Liu ZY, Li SC, Nie LC, Su MX, Sun HF, Fan KR, Zhang XX, Pang YH (2017) Comprehensive surface geophysical investigation of karst caves ahead of the tunnel face: a case study in the Xiaoheyan section of the water supply project from Songhua River, Jilin, China. J Appl Geophys 144:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2017.06.013
Liu L, Shi ZM, Tsoflias GP, Peng M, Liu CC, Tao FJ, Liu CS (2021) Detection of karst cavity beneath cast-in-place pile using the instantaneous phase difference of two receiver recordings. Geophysics 86:En27–En38. https://doi.org/10.1190/Geo2020-0082.1
Loke MH, Barker RD (1995) Least-squares deconvolution of apparent resistivity pseudosections. Geophysics 60:1682–1690. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1443900
Loke MH, Barker RD (1996) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys Prospect 44:131–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2478.1996.tb00142.x
Magnabosco R, Galvao P, de Carvalho AM (2020) An approach to map karst groundwater potentiality in an urban area, Sete Lagoas, Brazil. Hydrol Sci J 65:2482–2498. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2020.1802031
Mahajan AK (2018) Applications of two-dimensional seismic tomography for subsurface cavity and dissolution features detection under Doon valley, NW Himalaya. Curr Sci India 115:962–969. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v115/i5/962-969
Park MK, Park S, Yi MJ, Kim C, Son JS, Kim JH, Abraham AA (2014) Application of electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) technique to detect underground cavities in a karst area of South Korea. Environ Earth Sci 71:2797–2806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2658-7
Ptak T, Piepenbrink M, Martac E (2004) Tracer tests for the investigation of heterogeneous porous media and stochastic modelling of flow and transport—a review of some recent developments. J Hydrol 294:122–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.01.020
Redhaounia B, Aktarakci H, Ilondo BO, Gabtni H, Khomsi S, Bedir M (2015) Hydro-geophysical interpretation of fractured and karstified limestones reservoirs: a case study from Amdoun region (NW Tunisia) using electrical resistivity tomography, digital elevation model (DEM) and hydro-geochemical approaches. J Afr Earth Sci 112:328–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.09.020
Redhaounia B, Ilondo BO, Gabtni H, Sami K, Bedir M (2016) Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) applied to karst carbonate aquifers: case study from Amdoun, Northwestern Tunisia. Pure Appl Geophys 173:1289–1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-015-1173-z
Robert T, Caterina D, Deceuster J, Kaufmann O, Nguyen F (2012) A salt tracer test monitored with surface ERT to detect preferential flow and transport paths in fractured/karstified limestones. Geophysics 77:B55–B67. https://doi.org/10.1190/Geo2011-0313.1
Schuler P, Stoeckl L, Schnegg PA, Bunce C, Gill L (2020) A combined-method approach to trace submarine groundwater discharge from a coastal karst aquifer in Ireland. Hydrogeol J 28:561–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-019-02082-0
Singh KKK, Bharti AK, Pal SK, Prakash A, Saurabh KR, Singh PK (2019) Delineation of fracture zone for groundwater using combined inversion technique. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8072-z
Srivastava S, Pal SK, Kumar R (2020) A time-lapse study using self-potential and electrical resistivity tomography methods for mapping of old mine working across railway-tracks in a part of Raniganj coalfield, India. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09067-3
Su LJ, Xu XQ, Geng XY, Liang SQ (2017) An integrated geophysical approach for investigating hydro-geological characteristics of a debris landslide in the Wenchuan earthquake area. Eng Geol 219:52–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.020
Su MX, Liu YM, Xue YG, Nie LC, Wang P, Li CC, Ma XY (2021a) Integrated geophysical detection of water inrush from foundation pit near the river: a case study of Nanjing subway station. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10015-y
Su MX, Zhao Y, Xue YG, Wang P, Xia T, Zhang K, Li CC (2021b) Progressive fine integrated geophysical method for karst detection during subway construction. Pure Appl Geophys 178:91–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-020-02636-4
Tao M, Chen X, Cheng QB, Binley A (2022) Evaluating the joint use of GPR and ERT on mapping shallow subsurface features of karst critical zone in southwest China. Vadose Zone J. https://doi.org/10.1002/vzj2.20172
Torrese P (2020) Investigating karst aquifers: Using pseudo 3-D electrical resistivity tomography to identify major karst features. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124257
Zeng HL, Loucks R, Janson X, Wang GZ, Xia YP, Yuan BH, Xu LG (2011) Three-dimensional seismic geomorphology and analysis of the Ordovician paleokarst drainage system in the central Tabei Uplift, northern Tarim Basin, western China. AAPG Bull 95:2061–2083. https://doi.org/10.1306/03111110136
Zhao JY, Li N, Liu FY (2020) Geological survey and drilling technology of karst land. Desalin Water Treat 187:144–153. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25311
Zheng XH, Liu L, Sun JZ, Li G, Zhou FB, Xu JM (2018) Imaging of underground karst water channels using an improved multichannel transient Rayleigh wave detecting method. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199030
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Grant Numbers 41877239, 51379112 and 51422904), Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (Grant Number 2019GSF111028), the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (Grant Number 2018JC044) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant Bumber ZR2014EEM028).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Grant Numbers 41877239, 51379112 and 51422904), Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (Grant Number 2019GSF111028), the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (Grant Number 2018JC044) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant Number ZR2014EEM028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PW: collecting, processing and analyzing data, writing—original draft preparation, reviewing, editing. MS: processing and analyzing data, writing—original draft preparation, reviewing, editing. YX: conceptualization, methodology, reviewing, editing. ZL: methodology, reviewing, editing. XM: collecting data, reviewing, editing. CL: collecting data, reviewing, editing. YL: collecting data, reviewing, editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Su, M., Xue, Y. et al. Integrated survey approach combining electrical methods and sluicing test for the karst channel in coastal limestone mines: a case study in Beihai, China. Environ Earth Sci 82, 492 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11181-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11181-x