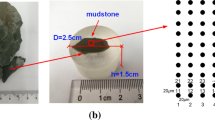
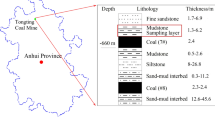
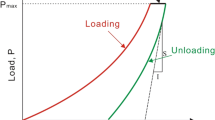
Abstract
The poor mechanical property of mudstone seriously affects the stability of various engineering buildings. For weathered mudstone, the mechanical parameters are difficult to obtain accurately by conventional mechanical experimental methods. In addition, these macroscopic measurements cannot distinguish the mechanical response of different mineral compositions. In this study, the nanoindentation test and the data analysis method of deconvolution were used to systematically evaluate the mechanical properties of various mineral compositions in mudstone at the mesoscale. Then, three upscaling models including Mori–Tanaka (MT), Kuster–Toksöz (KT), and differential effective medium (DEM) were used to obtain the macroscopic mechanical properties. The results show that mudstone can be considered as a highly heterogeneous material with multiple mineral compositions. Among them, illite and various pores constitute the clay matrix, and quartz and feldspar minerals constitute the grain skeleton. The mechanical response of mineral compositions in the interface region was complex, mainly reflecting the composite mechanical properties of clay matrix and various clastic minerals. This characteristic made the overall mechanical properties of the mudstone show good continuity in the nanoindentation test. The Young's moduli (EIT) of the clay matrix, feldspar mineral and quartz in the mudstone were 16.1, 64.84 and 149.69 GPa respectively. The EIT of the mudstone obtained by the three upscaling models was higher than the measured macroscopic values. The model can be effectively optimized by setting the EIT of interfaces to the value of clay matrix.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Berryman JG (1992) Single-scattering approximations for coefficients in Biot’s equations of poroelasticity. J Acoust Soc Am 91:551–571. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.402518
Charlton S, Goodarzi M, Rouainia M et al (2021) Effect of diagenesis on geomechanical properties of organic-rich calcareous shale: a multiscale investigation. J Geophys Res-Sol Ea 126:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB021365
Constantinides G, Chandran KSR, Ulm FJ, Van Vliet KJ (2006) Grid indentation analysis of composite microstructure and mechanics: principles and validation. Mat Sci Eng a-Struct 430:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.125
Corkum AG, Martin CD (2007) The mechanical behaviour of weak mudstone (Opalinus Clay) at low stresses. Int J Rock Mech Min 44:196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.06.004
Da Silva WRL, Nemecek J, Štemberk P (2013) Application of multiscale elastic homogenization based on nanoindentation for high performance concrete. Adv Eng Softw 62:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.04.007
Davydov D, Jir´asek, M., Kopecký, L., (2010) Critical aspects of nano-indentation technique in application to hardened cement paste. Cement Concr Res 41:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2010.09.001
Deirieh A, Ortega JA, Ulm F, Abousleiman YN (2012) Nanochemomechanical assessment of shale: a coupled WDS-in-dentation analysis. Acta Geotech 7:271–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-012-0185-4
Doebelin N, Kleeberg R (2015) Profex: a graphical user interface for the Rietveld refinement program BGMN. J Appl Crystallogr 48:1573–1580. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576715014685
Du JT, Luo SM, Hu LM et al (2021) Multiscale mechanical properties of shales: grid nanoindentation and statistical analytics. Acta Geotech 17:339–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01312-8
Eshelby JD (1957) The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proc R Soc London Ser A Math Phys Sci 241(1226):376–396. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1957.0133
Hu, M., Xu, G.Y., Hu, S.B., et al., 2013. Study of equivalent elastic modulus of sand gravel soil with Eshelby tensor and Mori-Tanaka equivalent method. Rock Soil Mech, 34, 1437–1448. (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2013.05.017.
Huang Y, Shen WQ, Shao JF et al (2014) Multi-scale modeling of time-dependent behavior of claystones with a viscoplastic compressible porous matrix. Mech Mater 79:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2014.08.003
Kang X., Hu W.X., Wang J., Cao J., Zhao Y., 2017. Fan-delta sandy sandy conglomerate reservoir: sensitmty: A case study of the Baikouquan formation in the Mahu sag, Junggar basin. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology. 46, 596–605. https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000607.
Kong LW, Zeng ZX, Bai W, Wang M (2018) Engineering geological properties of weathered swelling mudstones and their effects on the landslides occurrence in the Yanji section of the Jilin-Hunchun high-speed railway. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:1491–1503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1096-2
Kong L, Ostadhassan M, Zamiran S, Liu B, Li C, Marino GG (2019) Geomechanical Upscaling Methods: Comparison and Verification via 3D Printing. Energies 12:382. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030382
Kuster GT, Toksöz MN (1974) Velocity and attenuation of seismic waves in two-phase media: Part I. theoretical formulations. Geophysics 39:587–737. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1440450
Li C, Zhang FH, Wang X, Rao XS (2018) Investigation on surface/subsurface deformation mechanism and mechanical properties of GGG single crystal induced by nanoindentation. Appl Optics 57:3661–3668
Li, Y., Luo, S. M., et al., 2021. Cross-scale characterization of sandstones via statistical nanoindentation: Evaluation of data analytics and upscaling models. Int J Rock Mech Min, 142, 104738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104738.
Li, M.Y., Peng, L., Zuo, Z.P., et al. 2022. Study on multi-scale mechanical properties of granite based on DIP-FFT numerical method. 41(11), 2254–2267. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2022.0029.
Liu L, Li YC, Wu YK et al (2022) Strengthening mechanisms in cement-stabilized kaolinite revealed by cross-scale nanoindentation. Acta Geotech 17:5113–5132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01493-w
Luo TY, Zhang QS, Liu ZB et al (2022) Nanoindentation experimental study on mechanical properties of red mudstone in Hechi, Guangxi Province. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering 33:174–181 ((in Chinese))
Ma ZY, Gamage RP, Zhang CP (2020) Application of nanoindentation technology in rocks: a review. Geomech Geophys Geo 6:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00178-6
Magnenet V, Auvray C, Francius G, Giraud A (2011) Determination of the matrix indentation modulus of Meuse/Haute-Marne argillite. Appl Clay Sci 52:266–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2011.03.001
Miller M, Bobko C, Vandamme M, Ulm FJ (2007) Surface roughness criteria for cement Paste nanoindentation. Cement Concr Res 38:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.11.014
Mori T, Tanaka K (1973) Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions. Acta Metall 21:571–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(73)90064-3
Němeček J (2009) Creep effects in nanoindentation of hydrated phases of cement pastes. Mater Charact 60:1028–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2009.04.008
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (1992) An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater Res 7:1564–1583. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1992.1564
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (2004) Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J Mater Res 19:3–20. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2004.19.1.3
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (2011) Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J Mater Res 19:3–20. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2004.19.1.3
Perras, M.A., Wannenmacher, H., Diederichs, M.S., 2015. Underground Excavation Behaviour of the Queenston Formation: Tunnel Back Analysis for Application to Shaft Damage Dimension Prediction. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 48, 1647–71. https://https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0656-z.
Sheng P (1990) Effective-medium theory of sedimentary rocks. Phys Rev B 41:4507. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.41.4507
Shi, X., Jiang, S., Lu, S.F., et al., 2019. Investigation of mechanical properties of bedded shale by nanoindentation tests: A case study on Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation of Youyang area in southeast Chongqing, China. Pet Explor Dev. 46(1), 155–164. https://doi.org/10.11698/PED.2019.01.16.
Sun CL, Li G, Gomah ME et al (2021) Experimental investigation on the nanoindentation viscoelastic constitutive model of quartz and kaolinite in mudstone. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8:925–937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00393-2
Sun CL, Li GC, Gomah ME, Xu JH, Rong HY (2020) Meso-scale mechanical properties of mudstone investigated by nanoindentation. Eng Fract Mech. 238:107245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107245.
Ulm FJ, Vandamme M, Bobko C et al (2007) Statistical Indentation Techniques for Hydrated Nanocomposites: Concrete, Bone, and Shale. J Am Ceram Soc 90:2677–2692. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.02012.x
Wand MP (1997) Data-based choice of histogram bin width. Am Stat 51:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/00031305.1997.10473591
Wu, J., Liu, S.Y., Deng, Y.F., et al., 2022. Microscopic phase identification of cement-stabilized clay by nanoindentation and statistical analytics. Appl Clay Sci. 224, 106531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106531.
Xu, D.P., Liu, X.Y., Xu, H.S., et al., 2021. Meso-mechanical properties of deep granite using nanoindentation test and homogenization approach. J Cent South Univ. 52, 2762–2771. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.08.022.
Yin YP, Hu RL (2004) Engineering geological characteristics of purplish-red mudstone of middle tertiary formation at the three gorges reservoir. J Eng Geol 12:124–135 ((in Chinese))
Zhang ZH, Liu W, Han L, Chen XC, Cui Q, Yao HY et al (2018a) Disintegration behavior of strongly weathered purple mudstone in drawdown area of three gorges reservoir. China Geomorphol 315:68–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.05.008
Zhang F, Guo HQ, Hu DW, Shao JF (2018b) Characterization of the mechanical properties of a claystone by nano-indentation and homogenization. Acta Geotech 13:1395–1404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0691-0
Zhang, Z.P., Zhang, S.C., Shi, S.Z., et al., 2022. Evaluation of multi-scale mechanical properties of conglomerate using nanoindentation and homogenization methods: A case study on tight conglomerate reservoirs in southern slope of Mahu sag. Chinese Journal of rock mechanics and engineering. 41(5), 926–940. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.1186.
Zhu W, Hughes JJ, Bicanic N, Pearce CJ (2007) Nanoindentation mapping of mechanical properties of cement paste and natural rocks. Mater Char 58:1189–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2007.05.018
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41877240).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 41877240).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qingsong Zhang: Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. Zhibin Liu: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing—review and editing. Yasen Tang: Visualization, Investigation. Yongfeng Deng: Methodology. Tingyi Luo: Investigation. Yuting Wang: Visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Liu, Z., Tang, Y. et al. Mechanical property characterization of mudstone based on nanoindentation technique combined with upscaling method. Environ Earth Sci 82, 485 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11161-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11161-1