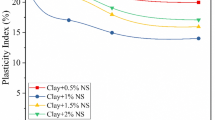
Abstract
Sandy soil has engineering characteristics, such as loose structure, non-plasticity, poor stability, and compressibility, which can readily cause engineering problems. In practical engineering, physical and chemical methods are usually used to improve the overall performance of sand to ensure the safety of the engineering. However, some reinforcement methods are complex in technology, expensive in materials, and poor in environmental protection. Polyurethane reinforcing agent was introduced in the present study to improve soil reinforcement. Sand samples with different dry densities, sisal fiber content, and polyurethane pre-polymer content were prepared, and a series of direct shear tests were carried out to evaluate the shear strength of the sand. The microscopic mechanism of the sand mixture was studied by scanning electron microscopy. The experimental results showed that the dry density of the sand mixture had a positive effect on the shear strength within the test range. Increasing the concentration of polyurethane prepolymer can increase the shear strength of sandy soil due to the more stable network structure. The cohesion reaches up to about 148 kPa as polymer content is 3%. The shear strength of sand increases first of all and then decreases with an increase in sisal fiber content, 0.4% sisal fiber is an optimum content for sand reinforcement.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdelkader B, Ahmed A, Mostéfa B, Isam S (2016) Laboratory study of geotextiles performance on reinforced sandy soil. J Earth Sci China 27:1060–1070
Anvari SM, Shooshpasha I, Kutanaei SS (2017) Effect of granulated rubber on shear strength of fine-grained sand. J Rock Mech Geotech 9:936–944
Aouali N, Benessalah I, Arab A, Ali B, Abed M (2018) Shear strength response of fibre reinforced Chlef (Algeria) silty sand: laboratory study. Geotech Geol Eng 37:1047–1057
Benessalah I, Arab A, Villard P, Sadek M, Kadri A (2016) Laboratory study on shear strength behaviour of reinforced sandy soil: effect of glass-fibre content and other parameters. Arab J Sci Eng 41:1343–1353
Cai Y, Shi B, Ng CWW, Tang C (2006) Effect of polypropylene fibre and lime admixture on engineering properties of clayey soil. Eng Geol 87:230–240
Chang I, Im J, Prasidhi AK, Cho GC (2015) Soil strengthening using thermo-gelation biopolymers. Constr Build Mater 77:430–438
Chen QS, Yu RH, Tao GL, Zhang JW, Nimbalkar S (2021) Shear behavior of polyurethane foam adhesive improved calcareous sand under large-scale triaxial test. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 39(12):1449–1458
EsmaeilpourShirvani N, TaghaviGhalesari A, Tabari MK, Choobbasti AJ (2019) Improvement of the engineering behavior of sand-clay mixtures using kenaf fiber reinforcement. Transp Geotech 19:1–8
Gatto MPA, Montrasio L, Berardengo M, Vanali M (2022) Experimental analysis of the effects of a polyurethane foam on geotechnical seismic isolation. J Earthq Eng 26(6):2948–2969
Hataf N, Ghadir P, Ranjbar N (2018) Investigation of soil stabilization using chitosan biopolymer. J Clean Prod 170:1493–1500
Hazirbaba K (2018) Large-scale direct shear and CBR performance of geofibre-reinforced sand. Road Mater Pavement 19:1350–1371
Huang W, Liu Z, Zhou C, Yang X (2020) Enhancement of soil ecological self-repair using a polymer composite material. Catena (giessen) 188:104443
Inbar A, Ben-Hur M, Sternberg M, Lado M (2015) Using polyacrylamide to mitigate post-fire soil erosion. Geoderma 239:107–114
Kalkan E, Kartal HO, Kalkan OF (2022) Experimental study on the effect of hemp fiber on mechanical properties of stabilized clayey soil. J Nat Fibers 19(16):14678–14693
Kutanaei S, Choobbasti A (2016) Triaxial behavior of fiber-reinforced cemented sand. J Adhes Sci Technol 6:579–593
Latifi N, Rashid ASA, Siddiqua S, Abd Majid MZ (2016) Strength measurement and textural characteristics of tropical residual soil stabilised with liquid polymer. Measurement 91:46–54
Li YR (2013) Effects of particle shape and size distribution on the shear strength behavior of composite soils. Bull Eng Geol Environ 72:371–381
Li L, Zhang H, Zhou X, Chen M, Lu L, Cheng X (2019) Effects of super absorbent polymer on scouring resistance and water retention performance of soil for growing plants in ecological concrete. Ecol Eng 138:237–247
Liu J, Bai YX, Song ZZ, Lu Y, Qian W, Kanungo DP (2018) Evaluation of strength properties of sand modified with organic polymers. Polymers 10(3):287
Liu J, Bai YX, Song ZZ, Kanungo DP, Wang Y, Bu F, Chen ZH, Shi X (2020) Stabilization of sand using different types of short fibers and organic polymer. Constr Build Mater 253(2020):119164
Ma G, Ran F, Feng E, Dong Z, Lei Z (2015) Effectiveness of an eco-friendly polymer composite sand-fixing agent on sand fixation. Water Air Soil Poll 226:1–12
Malidarreh NR, Shooshpasha I, Mirhosseini SM, Dehestani M (2018) Effects of reinforcement on mechanical behaviour of cement treated sand using direct shear and triaxial tests. Int J Geotech Eng 12:491–499
Mirzababaei M, Arulrajah A, Horpibulsuk S, Soltani A, Khayat N (2018) Stabilization of soft clay using short fibers and poly vinyl alcohol. Geotext Geomembr 46:646–655
Moslemi A, Tabarsa A, Mousavi SY, Monfared MHA (2022) Shear strength and microstructure characteristics of soil reinforced with lignocellulosic fibers-Sustainable materials for construction. Constr Build Mater 356:129246
Naeini SA, Naderinia B, Izadi E (2012) Unconfined compressive strength of clayey soils stabilized with waterborne polymer. J Mater Civ Eng 16:943–949
Pakbaz MS, Behzadipour H, Ghezelbash GR (2018) Evaluation of shear strength parameters of sandy soils upon microbial treatment. Geomicrobiol J 35:721–726
Punthutaecha K, Puppala AJ, Vanapalli SK, Inyang H (2006) Volume change behaviors of expansive soils stabilized with recycled ashes and fibers. J Mater Civ Eng 18:295–306
Rezaeimalek S, Huang J, Bin-Shafique S (2017) Evaluation of curing method and mix design of a moisture activated polymer for sand stabilization. Constr Build Mater 146:210–220
Sharma V, Kumar A (2017) Influence of relative density of soil on performance of fiber-reinforced soil foundations. Geotext Geomembr 45:499–507
Silveira MV, Calheiros AV, Casagrande MDT (2018) Applicability of the expanded polystyrene as a soil improvement tool. J Mater Civil Eng 30:06018006
Silveira MV, Ferreira JWD, Casagrande MD (2022) Effect of surface treatment on natural aging and mechanical behavior of sisal fiber-reinforced sand composite. J Mater Civ Eng 34(6):06022001
Tang CS, Shi B, Gao W, Chen F, Cai Y (2007) Strength and mechanical behavior of short polypropylene fiber reinforced and cement stabilized clayey soil. Geotext Geomembr 25:194–202
Tang CS, Li J, Wang D, Shi B (2016a) Investigation on the interfacial mechanical behavior of wave-shaped fiber reinforced soil by pullout test. Geotext Geomembr 44:872–883
Tang CS, Wang DY, Shi B, Li J (2016b) Effect of wetting–drying cycles on profile mechanical behavior of soils with different initial conditions. CATENA 139:105–116
Tang L, Liu TL, Sun PL, Wang YH, Liu GY (2022) Sisal fiber modified construction waste recycled brick as building material: properties, performance and applications. Structures 46:927–935
Vangla P, Latha GM (2015) Influence of particle size on the friction and interfacial shear strength of sands of similar morphology. Int J Geosynth Ground 1:6–17
Wang ZH, Lin XY, Yu TY, Zhou N, Zhong HY, Zhu JJ (2019) Formation and rupture mechanisms of visco-elastic interfacial films in polymer-stabilized emulsions. J Disper Sci Technol 40(4):612–626
Wang Y, Liu J, Lin C, Qi CQ, Chen ZH, Che WY, Ma K (2022) Investigation into mechanical behavior of air-hardening organic polymer-stabilized silty sand. J Mater Civil Eng 34(11):04022305
Wei H, Zhao T, Meng Q, Wang X, He J (2018) Experimental evaluation of the shear behavior of fiber-reinforced calcareous sands. Int J Geomech 18:04018175
Whitaker JM, Vanapalli S, Fortin D (2018) Improving the strength of sandy soils via ureolytic CaCO3 solidification by sporosarcina ureae. Biogeosciences 15:4367–4380
Wu Y, Wang K, Zhang L, Peng S (2018) Sand-layer collapse treatment: an engineering example from Qingdao metro subway tunnel. J Clean Prod 197:19–24
Xiao Y, Stuedlein AW, Chen Q, Liu H, Liu P (2018) Stress-strain-strength response and ductility of gravels improved by polyurethane foam adhesive. J Geotech Geoenviron 144(2):04017108
Xue Q, Lu H, Li Z, Liu L (2014) Cracking, water permeability and deformation of compacted clay liners improved by straw fiber. Eng Geol 2014(178):82–90
Yang Q, Pei X, Huang R (2019) Impact of polymer mixtures on the stabilization and erosion control of silty sand slope. J Mt Sci 16:470–485
Yuan J, Ye C, Luo L, Pei XJ, Liao B (2020) Sand fixation property and erosion control through new cellulose-based curing agent on sandy slopes under rainfall. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:4051–4061
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41877212) and Open Project of Technology Innovation Center for Ecological Monitoring & Restoration Project on Land (Arable), Ministry of Natural Resources (Grant No. GTST2021-006).
Funding
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41877212) and Open Project of Technology Innovation Center for Ecological Monitoring & Restoration Project on Land (Arable), Ministry of Natural Resources (Grant No. GTST2021-006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shefeng Hao and Yongxiang Yu wrote the main manuscript text. Jinglei Song, Jin Liu and Zezhuo Song prepared all figures. Wenyue Che, Tingwei Huang and Zhihao Chen conducted the test. Shaorui Sun revised the syntax of the paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, S., Yu, Y., Song, J. et al. Study on direct shear strength properties of sand mixed with polyurethane prepolymer and sisal fiber. Environ Earth Sci 82, 436 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11121-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11121-9