Abstract
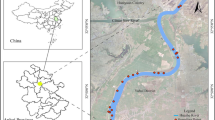
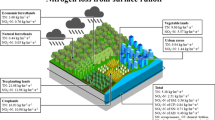
With the large-scale application of nitrogen fertilizers in the agricultural area, the karst area in southwest China is increasingly polluted by nitrogen. Understanding the distribution, transportation, and sources of nitrogen is the premise for effective pollution control in the catchment. The present study used the nitrogen and oxygen isotopes technique to explore the dynamic changes and sources of nitrates during rainfall in various land uses in a typical karst catchment in southwestern China. The results of hydrochemistry composition indicated that agricultural activities have caused the deterioration of water quality, while intensive rainfall during the wet season has played a positive role in promoting it. NO3−–N was the major inorganic N, accounting for 78.7 ± 21.6% (N = 38) of the total nitrogen. Dryland and paddy field provided a large amount of nitrogen for the water environment by rain, which contributed to high NO3−-N concentration in spring (6.1 ± 0.9 mg/L) and runoff (7.2 ± 0.9 mg/L) at the catchment outlet. Nitrate isotopic compositions (δ15N–NO3− and δ18O–NO3−) and water isotopes (δD and δ18O–H2O) revealed that isotopic composition in dryland and paddy field was mainly affected by nitrification. Source analysis showed that dryland and paddy field was dominated by chemical fertilizers and manure, while precipitation and soil organic nitrogen were the major sources in abandoned land, forest and shrub. This study highlighted that land management and nitrogen fertilizer application should be reasonable to reduce the risk of nitrogen surplus in the water environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Braker G, Conrad R (2011) Diversity, structure, and size of N2O-producing microbial communities in soils-what matters for their functioning? Adv Appl Microbiol 75:33–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-387046-9.00002-5
Canfield DE, Glazer AN, Falkowski PG (2010) The evolution and future of Earth’s nitrogen cycle. Science 330:192–196. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1186120
Chen H, Zhang Q, Cai H, Zhou W, Xu F (2018a) H2O2 mediates nitrate-induced iron chlorosis by regulating iron homeostasis in rice. Plant, Cell Environ 41:767–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13145
Chen X, Zhang Z, Soulsby C, Cheng Q, Binley A, Jiang R, Tao M (2018b) Characterizing the heterogeneity of karst critical zone and its hydrological function: an integrated approach. Hydrol Process 32:2932–2946. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13232
Chen SN, Yue FJ, Liu XL, Zhong J, Yi YB, Wang WF, Qi YL, Xiao HY, Li SL (2021) Seasonal variation of nitrogen biogeochemical processes constrained by nitrate dual isotopes in cascade reservoirs, Southwestern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:26617–26627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12505-9
Clow DW, Mast MA (2010) Mechanisms for chemostatic behavior in catchments: implications for CO2 consumption by mineral weathering. Chem Geol 269:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.014
Darwiche-Criado N, Comín FA, Sorando R, Sánchez-Pérez JM (2015) Seasonal variability of NO3− mobilization during flood events in a Mediterranean catchment: the influence of intensive agricultural irrigation. Agr Ecosyst Environ 200:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.11.002
Delesantro JM, Duncan JM, Riveros-Iregui D, Blaszczak JR, Bernhardt ES, Urban DL, Band LE (2022) The nonpoint sources and transport of baseflow nitrogen loading across a developed rural-urban gradient. Water Resourc Res 58:e2021WR031533. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021WR031533
Eller KT, Katz BG (2017) Nitrogen Source Inventory and Loading Tool: an integrated approach toward restoration of water-quality impaired karst springs. J Environ Manag 196:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.059
Fukada T, Hiscock K, Dennis PF, Grischek T (2003) A dual isotope approach to identify denitrification in groundwater at a river-bank infiltration site. Water Res 37:3070–3078. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00176-3
Gaillardet J, Dupré B, Louvat P, Allegre C (1999) Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem Geol 159:3–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00031-5
Granger J, Sigman DM, Rohde M, Maldonado M, Tortell P (2010) N and O isotope effects during nitrate assimilation by unicellular prokaryotic and eukaryotic plankton cultures. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:1030–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2009.10.044
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451:293–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06592
Gutser R, Ebertseder T, Weber A, Schraml M, Schmidhalter U (2005) Short-term and residual availability of nitrogen after long-term application of organic fertilizers on arable land. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 168:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200520510
Husic A, Fox J, Adams E, Backus J, Pollock E, Ford W, Agouridis C (2019) Inland impacts of atmospheric river and tropical cyclone extremes on nitrate transport and stable isotope measurements. Environ Earth Sci 78:36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-8018-x
Kendall C, Elliott EM, Wankel SD (2007) Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. In: Lajtha K, Michener R (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science, 2nd edn. Blackwell, pp 375–449
Kuypers MM, Marchant HK, Kartal B (2018) The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2018.9
Li SL, Calmels D, Han G, Gaillardet J, Liu CQ (2008) Sulfuric acid as an agent of carbonate weathering constrained by δ13C-DIC: examples from Southwest China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 270:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2008.02.039
Li SL, Liu CQ, Li J, Xue ZC, Guan J, Lang YC, Ding H, Li LB (2013) Evaluation of nitrate source in surface water of southwestern China based on stable isotopes. Environ Earth Sci 68:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1733-9
Li Z, Xu X, Xu C, Liu M, Wang K, Yi R (2017) Monthly sediment discharge changes and estimates in a typical karst catchment of southwest China. J Hydrol 555:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.10.013
Li SL, Liu X, Yue FJ, Yan ZF, Wang TJ, Li SJ, Liu CQ (2022) Nitrogen dynamics in the critical Zones of China. Progress Phys Geogr Earth Environ 46:869–888. https://doi.org/10.1177/03091333221114732
Liu CQ, Li SL, Lang YC, Xiao HY (2006) Using δ15N-and δ18O-values to identify nitrate sources in karst ground water, Guiyang, Southwest China. Environ Sci Technol 40:6928–6933. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0610129
Liu F, Wang S, Wang L, Shi L, Song X, Yeh TCJ, Zhen P (2019) Coupling hydrochemistry and stable isotopes to identify the major factors affecting groundwater geochemical evolution in the Heilongdong Spring Basin North, China. J Geochem Explor. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106352
Liu ZJ, Wang XH, Jia SQ, Mao BY (2023) Multi-methods to investigate spatiotemporal variations of nitrogen-nitrate and its risks to human health in China’s largest fresh water lake (Poyang Lake). Sci Total Environ 863:160975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160975
Luo W, Xu XL, Liu W, Liu MX, Li ZW, Peng T, Xu CH, Zhang YH, Zhang RF (2019) UAV based soil moisture remote sensing in a karst mountainous catchment. CATENA 174:478–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.11.017
Ma R, Yu K, Xiao S, Liu S, Ciais P, Zou J (2021) Data-driven estimates of fertilizer-induced soil NH3, NO and N2O emissions from croplands in China and their climate change impacts. Glob Change Biol 28:1008–1022. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15975
McIlvin MR, Casciotti KL (2011) Technical updates to the bacterial method for nitrate isotopic analyses. Anal Chem 83:1850–1856. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac1028984
Meyerhoff SB, Maxwell RM, Revil A, Martin JB, Karaoulis M, Graham WD (2014) Characterization of groundwater and surface water mixing in a semiconfined karst aquifer using time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography. Water Resour Res 50:2566–2585. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR013991
Mourad D, Van der Perk M (2009) Spatio-temporal patterns of nutrient concentrations and export in a north-eastern European lowland catchment. Hydrol Process 23:1821–1833. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7309
Pan B, Lam SK, Mosier A, Luo Y, Chen D (2016) Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: a global synthesis. Agric Ecosyst Environ 232:283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.08.019
Penna D, van Meerveld HJ, Oliviero O, Zuecco G, Assendelft R, Dalla Fontana G, Borga M (2015) Seasonal changes in runoff generation in a small forested mountain catchment. Hydrol Process 29:2027–2042. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10347
Qin CQ, Li SL, Yue FJ, Xu S, Ding H (2019) Spatiotemporal variations of dissolved inorganic carbon and controlling factors in a small karstic catchment, Southwestern China. Earth Surf Proc Land 44:2423–2436. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.4672
Qin CQ, Li SL, Waldron S, Yue FJ, Wang ZJ, Zhong J, Ding H, Liu CQ (2020) High-frequency monitoring reveals how hydrochemistry and dissolved carbon respond to rainstorms at a karstic critical zone, Southwestern China. Sci Total Environ 714:136833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136833
Sebestyen SD, Boyer EW, Shanley JB, Kendall C, Doctor DH, Aiken GR, Ohte N (2008) Sources, transformations, and hydrological processes that control stream nitrate and dissolved organic matter concentrations during snowmelt in an upland forest. Water Resour Res 44:W12410. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR006983
Slessarev EW, Lin Y, Bingham NL, Johnson JE, Dai Y, Schimel JP, Chadwick OA (2016) Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale. Nature 540:567–569. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20139
Spence J, Telmer K (2005) The role of sulfur in chemical weathering and atmospheric CO2 fluxes: evidence from major ions, δ13C-DIC, and δ34S–SO4 in rivers of the Canadian Cordillera. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:5441–5458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.07.011
Sprenger M, Tetzlaff D, Tunaley C, Dick J, Soulsby C (2017) Evaporation fractionation in a peatland drainage network affects stream water isotope composition. Water Resour Res 53:851–866. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR019258
Tondera K, Blecken G, Tournebize J, Mander Ü, Tanner C (2018) Nutrient removal from variable stormwater flows. In: Tondera K, Blecken G, Chazarenc F, Tanner C (eds) Ecotechnologies for the treatment of variable stormwater and wastewater flows. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 31–55
Wang T, Zhu B (2011) Nitrate loss via overland flow and interflow from a sloped farmland in the hilly area of purple soil, China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 90:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-011-9431-7
Wang SJ, Liu QM, Zhang DF (2004) Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: geomorphology, landuse, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degrad Dev 15:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.592
Wang ZJ, Li SL, Yue FJ, Qin CQ, Buckerfield S, Zeng J (2020) Rainfall driven nitrate transport in agricultural karst surface river system: insight from high resolution hydrochemistry and nitrate isotopes. Agric Ecosyst Environ 291:106787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2019.106787
Wang XH, Xu YJ, Zhang L (2022a) Watershed scale spatiotemporal nitrogen transport and source tracing using dual isotopes among surface water, sediments and groundwater in the Yiluo River Watershed Middle of China. Sci Total Environ 833:155180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155180
Wang ZX, Wu R, Huang K, Qiu Y, Li ZX, Lv Y, Wan JW (2022b) Structure identification of a karst groundwater system based on high-resolution rainfall-hydrological response characteristics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:26922–26935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17880-x
Wang ZJ, Yue FJ, Xue LL, Wang YC, Qin CQ, Zeng J, Ding H, Fu YC, Li SL (2023) Soil nitrogen transformation in different land use and implications for karst soil nitrogen loss controlling. CATENA 225:107026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2023.107026
Xia XH, Zhang SB, Li SL, Zhang LW, Wang GQ, Zhang L, Wang JF, Li ZH (2018) The cycle of nitrogen in river systems: sources, transformation, and flux. Environ Sci Process Impacts 20:863–891. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8em00042e
Yang PH, Dan L, Groves C, Xie SY (2019) Geochemistry and genesis of geothermal well water from a carbonate-evaporite aquifer in Chongqing, SW China. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-8004-3
Yu Z, Elliott EM (2017) Novel method for nitrogen isotopic analysis of soil-emitted nitric oxide. Environ Sci Technol 51:6268–6278. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00592
Yu ZQ, Nakagawa K, Berndtsson R, Hiraoka T, Suzuki Y (2021) Groundwater nitrogen response to regional land-use management in South Japan. Environ Earth Sci 80:634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09936-5
Yue FJ, Li SL, Liu CQ, Lang YC, Ding H (2015) Sources and transport of nitrate constrained by the isotopic technique in a karst catchment: an example from Southwest China. Hydrol Process 29:1883–1893. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10302
Yue FJ, Li SL, Waldron S, Oliver DM, Chen X, Li P, Peng T, Liu CQ (2023) Source availability and hydrological connectivity determined nitrate-discharge relationships during rainfall events in karst catchment as revealed by high-frequency nitrate sensing. Water Res 231:119616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.119616
Zhang YZ, Jiang YJ, Yuan DX, Cui J, Li Y, Yang J, Gao M (2020) Source and flux of anthropogenically enhanced dissolved inorganic carbon: a comparative study of urban and forest karst catchments in Southwest China. Sci Total Environ 725:138255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138255
Zhang Z, Chen X, Li S, Yue F, Cheng Q, Peng T, Soulsby C (2021) Linking nitrate dynamics to water age in underground conduit flows in a karst catchment. J Hydrol 596:125699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125699
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Numbers 42073076 and 41403105]; the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences [XDB40000000]; the Independent Innovative Foundation of Tianjin University (Grant No. 2022XJS-0123); the construction project of Key Laboratory of State Ethnic Affairs Commission ([2020] No 0.91 of DDA office, i.e., The karst environmental geological hazard prevention laboratory of Guizhou Minzu University) and Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (20JCQNJC01600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PZ: data curation, formal analysis, and writing the original draft. F-JY: conceptualization, supervision, investigation, writing, review, and editing. X-DW: formal analysis, methodology, supervision, writing, review and editing. S-NC, Z-HL, ML, and Z-YS: review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Wang, XD., Yue, FJ. et al. Dynamic characteristics of nitrogen transport in various land use in a typical karst catchment during rainfall events. Environ Earth Sci 82, 332 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10980-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10980-6