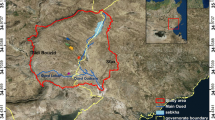
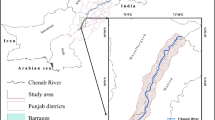
Abstract
Landsat remote sensing image is a widely used data source in water remote sensing. Normalized difference water index (NDWI), modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI) and automated water extraction index (AWEI) are commonly used water extraction classifiers. In the process of their application, because the threshold varies with the location and time of the research object, how to select the threshold with the highest classification accuracy is a time-consuming and challenging task. The purpose of this study was to explore a method that can not only improve the accuracy of water extraction, but also provide a fixed threshold, and can meet the requirements of automatic water extraction. We introduced the local spatial auto correlation statistics and calculate the Getis-Ord Gi* index to have hot spot analysis. Comparative analysis showed that the accuracy of water classification had been greatly improved through hot spot analysis. AWEIsh classifier had the best classification accuracy under the condition of INVERSE_DISTANCE neighborhood rule and Z > 1.96, and the accuracy changes least in different time, different location and different vegetation coverage images. Therefore, in the process of regional water extraction, hot spot analysis method was effective, which was helpful to improve the accuracy of water extraction.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Abolafia-Rosenzweig R, Livneh B, Small EE, Kumar SV (2019) Soil moisture data assimilation to estimate irrigation water use. J Adv Model Earth Sy 11:3670–3690. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS001797
Anselin L (1995) Local indicators of spatial association-LISA. Geogr Anal 27:93–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.1995.tb00338.x
Bousbih S, Zribi M, El Hajj M, Baghdadi N, Lili-Chabaane Z, Gao Q, Fanise P (2018) Soil moisture and irrigation mapping in A semi-arid region, based on the synergetic use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens 10:1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121953
Brocca L, Ciabatta L, Massari C, Moramarco T, Hahn S, Hasenauer S, Levizzani V (2014) Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J Geophys Res Atmospheres 119:5128–5141. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021489
Chance EW, Cobourn KM, Thomas VA (2018) Trend detection for the extent of irrigated agriculture in Idaho’s Snake river plain, 1984–2016. Remote Sens 10:145. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010145
Congalton RG, Mead RA (1983) A quantitative method to test for consistency and correctness in photointerpretation. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 49:69–74
Dalposso GH, Uribe-Opazo MA, Mercante E, Lamparelli RA (2013) Spatial autocorrelation of NDVI and GVI indices derived from Landsat/TM images for soybean crops in the western of the state of Paraná in 2004/2005 crop season. Engenharia Agrícola 33:525–537. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-69162013000300009
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ, Berrisford P, Poli P, Kobayashi S, Vitart F (2011) The ERA-interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.828
Douglas EM, Beltrán-Przekurat A, Niyogi D, Pielke RA Sr, Vörösmarty CJ (2009) The impact of agricultural intensification and irrigation on land–atmosphere interactions and Indian monsoon precipitation—a mesoscale modeling perspective. Glob Planet Change 67:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2008.12.007
Eid ANM, Olatubara CO, Ewemoje TA, Farouk H, El-Hennawy MT (2020) Coastal wetland vegetation features and digital Change Detection Mapping based on remotely sensed imagery: El-Burullus Lake. Egypt Intern Soil Water Conserv Res 8:66–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2020.01.004
FAO (2018) The Future of Food and Agriculture: Alternative pathways to 2050. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Publications: Rome, Italy 224 pp. https://www.fao.org/3/I8429EN/i8429en.pdf
Feyisa GL, Meilby H, Fensholt R, Proud SR (2014) Automated water extraction index: a new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens Environ 140:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.08.029
Gao Q, Zribi M, Escorihuela MJ, Baghdadi N, Segui PQ (2018) Irrigation mapping using Sentinel-1 time series at field scale. Remote Sens 10:1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091495
Getis A, Ord JK (1992) The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr Anal 24:189–206. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.1992.tb00261.x
Helman D, Mussery A (2020) Using Landsat satellites to assess the impact of check dams built across erosive gullies on vegetation rehabilitation. Sci Total Environ 730:138873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138873
Ji L, Zhang L, Wylie B (2009) Analysis of dynamic thresholds for the normalized difference water index. Photogrammetric Eng Rem S 75:1307–1317. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.75.11.1307
Jiang H, Feng M, Zhu Y, Lu N, Huang J, Xiao T (2014) An automated method for extracting rivers and lakes from Landsat imagery. Remote Sens 6:5067–5089. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065067
Jin N, Tao B, Ren W, Feng M, Sun R, He L, Yu Q (2016) Mapping irrigated and rainfed wheat areas using multi-temporal satellite data. Remote Sens 8:207. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030207
Kamthonkiat D, Honda K, Turral H, Tripathi NK, Wuwongse V (2005) Discrimination of irrigated and rainfed rice in a tropical agricultural system using SPOT vegetation NDVI and rainfall data. Int J Remote Sens 26:2527–2547. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160500104335
Kelly JT, Gontz AM (2018) Using GPS-surveyed intertidal zones to determine the validity of shorelines automatically mapped by Landsat water indices. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 65:92–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2017.10.007
Kotchenova SY, Vermote EF, Matarrese R, Klemm FJ Jr (2006) Validation of a vector version of the 6S radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data. Part i: Path Radiance Appl Optics 45:6762–6774. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.45.006762
Kowe P, Mutanga O, Odindi J, Dube T (2020) A quantitative framework for analysing long term spatial clustering and vegetation fragmentation in an urban landscape using multi-temporal landsat data. Int J Appl Earth Obs 88:102057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2020.102057
Lawston PM, Santanello JA Jr, Hanson B, Arsensault K (2020) Impacts of Irrigation on Summertime Temperatures in the Pacific Northwest. Earth Interact 24:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1175/EI-D-19-0015.1
McFeeters SK (1996) The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int J Remote Sens 17:1425–1432. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169608948714
Ord JK, Getis A (1995) Local spatial autocorrelation statistics: distributional issues and an application. Geogr Anal 27:286–306. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.1995.tb00912.x
Ord JK, Getis A (2001) Testing for local spatial autocorrelation in the presence of global autocorrelation. J Regional Sci 41:411–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/0022-4146.00224
Peña-Arancibia JL, McVicar TR, Paydar Z, Li L, Guerschman JP, Donohue RJ, Chiew FH (2014) Dynamic identification of summer cropping irrigated areas in a large basin experiencing extreme climatic variability. Remote Sens Environ 154:139–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.08.016
Pickens AH, Hansen MC, Hancher M, Stehman SV, Tyukavina A, Potapov P, Sherani Z (2020) Mapping and sampling to characterize global inland water dynamics from 1999 to 2018 with full Landsat time-series. Remote Sens Environ 243:111792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111792
Pielke RA Sr, Pitman A, Niyogi D, Mahmood R, McAlpine C, Hossain F, Reichstein M (2011) Land use/land cover changes and climate: modeling analysis and observational evidence. Wiley Interdiscip Rev 2:828–850. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.144
Rogers AS, Kearney MS (2004) Reducing signature variability in unmixing coastal marsh Thematic Mapper scenes using spectral indices. Int J Remote Sens 25:2317–2335. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160310001618103
Ryan EM, Ogle K, Peltier D, Walker AP, De Kauwe MG, Medlyn BE, Harper AB (2017) Gross primary production responses to warming, elevated CO2, and irrigation: Quantifying the drivers of ecosystem physiology in a semiarid grassland. Global Ghange Biol 23:3092–3106. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13602
Schroeder TA, Cohen WB, Song C, Canty MJ, Yang Z (2006) Radiometric correction of multi-temporal Landsat data for characterization of early successional forest patterns in western Oregon. Remote Sens Environ 103:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2006.03.008
Sharma AK, Hubert-Moy L, Buvaneshwari S, Sekhar M, Ruiz L, Bandyopadhyay S, Corgne S (2018) Irrigation history estimation using multitemporal landsat satellite images: Application to an intensive groundwater irrigated agricultural watershed in India. Remote Sens 10:893. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060893
Teillet PM, Staenz K, William DJ (1997) Effects of spectral, spatial, and radiometric characteristics on remote sensing vegetation indices of forested regions. Remote Sens Environ 61:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(96)00248-9
Tuinenburg OA, de Vries JPR (2017) Irrigation patterns resemble ERA-Interim Reanalysis soil moisture additions. Geophys Res Lett 44:10–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL074884
Worden J, de Beurs KM (2020) Surface water detection in the Caucasus. Int J Appl Earth O B S 91:102159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2020.102159
Xiang K, Ma M, Liu W, Dong J, Zhu X, Yuan W (2019) Mapping Irrigated Areas of Northeast China in Comparison to Natural Vegetation. Remote Sens 11:825. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070825
Xiao X, Boles S, Liu J, Zhuang D, Frolking S, Li C, Moore B III (2005) Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens Environ 95:480–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.12.009
Xu H (2006) Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int J Remote Sens 27:3025–3033. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160600589179
Yao F, Wang J, Wang C, Crétaux JF (2019) Constructing long-term high-frequency time series of global lake and reservoir areas using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens Environ 232:111210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111210
Young NE, Anderson RS, Chignell SM, Vorster AG, Lawrence R, Evangelista PH (2017) A survival guide to Landsat preprocessing. Ecology 98:920–932. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1730
Zohaib M, Kim H, Choi M (2019) Detecting global irrigated areas by using satellite and reanalysis products. Sci Total Environ 677:679–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.365
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (Grant no. 2018YFC0407703-1, 2017YFC0403301), Anhui University of Science and Technology Master's and Doctor's Fund Projects (Grant no. ZY030), Natural Science Foundation of the Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant no. KJ2017A072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Xingyuan Cui and Lei Wang; Data curation, Jian Wang and Lei Wang; Formal analysis, Lei Wang; Funding acquisition, Xingyuan Cui; Methodology, Tao Su; Software, Jian Wang; Supervision, Lei Wang; Validation, Tao Su and Xingyuan Cui.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, T., Wang, J., Cui, X. et al. Study on monitoring water area in irrigation area by local space self-correlation index. Environ Earth Sci 82, 18 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10703-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10703-3