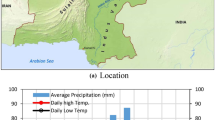
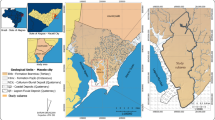
Abstract
This study aims to create soil zonation maps (SZM) using a spatial interpolation approach relying on vast geotechnical subsoil data gathered through field and laboratory analysis. Islamabad, a rapidly growing city and capital of Pakistan, is used as a case study. The sub-soil data were evaluated from 210 geotechnical investigation reports in terms of soil type, standard penetration (SPT-N value), undrained shear strength, and consolidation parameters. The data were digitally analyzed in ArcGIS using the ordinary kriging interpolation technique, and SZM were developed based on SPT-N and soil type. For the developed SZM, settlement and allowable bearing capacity (ABC) are evaluated for shallow foundations. The results showed that the study area was divided into three main zones based on SPT-N [i.e., zone-1(4–15), zone-2(16–30), and zone-3(> 30)], and six sub-zones based on lithology. The lean/silty clay is predominant up to 15 m, underlain by gravel and shale/sandstone up to 50 m. Correlations were presented based on linear regression analysis with R2 = 0.98 to predict the SPT-N with depth for expeditious appraisal of stiffness and strength of sub-soils throughout preliminary planning and feasibility studies of several construction projects. The ABC for the shallow foundation in Islamabad found to be above 100 kPa, indicating an excellent safe ABC to support foundations of lightly loaded structures. Moreover, the correlation coefficient to predict SPT-N values is around 85%, while about 94% for soil type. Furthermore, reliable information on geotechnical properties of the subsoil’s layers will work as a complement for the site characterization and identification of hazard for upcoming projects.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Abdul-husain HA (2016) Comparison of theoretical ultimate bearing capacity of cohesionless soils with experimental and field DATA. J Babylon Univ Sci 24:596–603
Ahmad M, Iqbal Q, Khan FA (2013) Profiling and zoning of geotechnical sub-soil data using geographic information system. Sci Int 25:531–537
Ahmad M, Jamal A, Tang XW et al (2020) Assessing potable water quality and identifying areas of waterborne diarrheal and fluorosis health risks using spatial interpolation in Peshawar, Pakistan. Water 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/W12082163
Ahmed C, Mohammed A, Tahir A (2020) Geostatistics of strength, modeling and GIS mapping of soil properties for residential purpose for Sulaimani City soils, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Model Earth Syst Environ 6:879–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00715-y
Akbarimehr D, Aflaki E (2019) Site investigation and use of artificial neural networks to predict rock permeability at the Siazakh Dam. Iran. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 52:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2017-048
Akhter K, Khan AJ, Khan Q, Asim M (2014) Soil bearing capacity modelling a case study on Islamabad and Rawalpindi. Proc Second Int Conf Mod Trends Sci Eng Technol. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.3665.1925
Al-Ani H, Eslami-Andargoli L, Oh E, Chai G (2013) Categorising geotechnical properties of surfers paradise soil using geographic information system (GIS). Int J Geomate 5:690–695. https://doi.org/10.21660/2013.10.3114a
Alcaras E, Falchi U, Parente C (2020) Digital terrain model generalization for multiscale use. Int Rev Civ Eng 11:52–59. https://doi.org/10.15866/irece.v11i2.17815
Alcaras E, Amoroso PP, Parente C (2022) The influence of interpolated point location and density on 3D bathymetric models generated by kriging methods: an application on the Giglio Island Seabed (Italy). Geosci 12:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12020062
Al-Mamoori SK, Jasem Al-Maliki LA, Al-Sulttani AH et al (2020) Horizontal and vertical geotechnical variations of soils according to USCS classification for the city of An-Najaf, Iraq using GIS. Geotech Geol Eng 38:1919–1938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01139-x
Alshameri B (2020) Maximum dry density of sand–kaolin mixtures predicted by using fine content and specific gravity. SN Appl Sci 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03481-9
Arshid MU, Shabbir F, Hussain J et al (2013) Assessment of variation in soil parameters, for design of lightly loaded structural foundations. Life Sci J 12:217–220
Arun PV (2013) A comparative analysis of different DEM interpolation methods. Egypt J Remote Sens Sp Sci 16:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2013.09.001
Ashraf KM, Hanif M (1980) Availability of ground water in selected sectors/areas of Islamabad-Phase I and II. Pakistan
Aziz M, Khan TA, Ahmed T (2017) Spatial interpolation of geotechnical data: a case study for Multan city, Pakistan. Geomech Eng 13:475–488. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2017.13.3.475
Bargaoui ZK, Chebbi A (2009) Comparison of two kriging interpolation methods applied to spatiotemporal rainfall. J Hydrol 365:56–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.11.025
Bhattacharjee S, Mitra P, Ghosh SK (2014) Spatial interpolation to predict missing attributes in GIS using semantic kriging. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52:4771–4780. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2013.2284489
Bowles JE (1997) Foundation engineering. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Burrough PA, McDonnell R. (1998) Principles of Geographic Information Systems
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Novak JM et al (1994) Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1501–1511. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x
Chabala LM, Mulolwa A, Lungu O (2017) Application of ordinary kriging in mapping soil organic carbon in Zambia. Pedosphere 27:338–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60321-7
Chang TJ, Wang WL (2008) Spatial analysis using gis to study performance of highway culvers in Ohio. In Pipelines 2008: pipeline asset management: maximizing performance of our pipeline infrastructure. ASCE, Reston, VA, USA, pp 1–10
Childs C (2004) Interpolating Surfaces in ArcGIS Spatial Analyst
Chilès J-P, Delfiner P (2013) Geostatistics: Modeling Spatial Uncertainty. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Ching J, Phoon KK, Chen YC (2010) Reducing shear strength uncertainties in clays by multivariate correlations. Can Geotech J 47:16–33. https://doi.org/10.1139/T09-074
Chung JW, Rogers JD (2010) GIS-based virtual geotechnical database for the St. Louis Metro Area Environ Eng Geosci 16:143–162. https://doi.org/10.2113/gseegeosci.16.2.143
Corps A (1992) Engineering and Design-Bearing Capacity of Soils. U.S. Army Corps Eng, Washington, DC, 20314–10000
Dell’Arciprete D, Bersezio R, Felletti F et al (2012) Comparison of three geostatistical methods for hydrofacies simulation: a test on alluvial sediments. Hydrogeol J 20:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-011-0808-0
Din M, Ali J, Khan AQ, Sami F (2019) Geotechnical characteristics of subsoil for different sectors of Islamabad. NUST J Eng Sci 11:33–40. https://doi.org/10.24949/njes.v11i1.179
Eberly S, Swall J, Holland D et al (2004) Developing spatially interpolated surfaces and estimating uncertainty. United States Environ Prot Agency, Washington, DC, USA, pp 28–40
Erdogan S (2009) A comparison of interpolation methods for producing digital elevation models at the field scale. Earth Surf Process Landforms 34:366–376. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp
Gill WD (1951) The stratigraphy of Siwalik series in the northern Potwar, Punjab, Pakistan. Geol Soc London Q J 10:375–394
Hassan W, Ahmad M, Farooq A et al (2017) Correlation of maximum laboratory dry density and optimum moisture content of soil with soil parameters. NFC-IEFR J Eng Sci Res 5:1–6. https://doi.org/10.24081/nijesr.2016.1.0003
Ijaz Z, Zhao C, Ijaz N et al (2021) Spatial mapping of geotechnical soil properties at multiple depths in Sialkot region, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 80:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10084-z
Jardaneh I (2007) Geotechnical Map for the City of Nablus - Palestine. An-Naja Univ J Res Sc 21:201–219
Jian X, Olea RA, Yu YS (1996) Semivariogram modeling by weighted least squares. Comput Geosci 22:387–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-3004(95)00095-X
Johnson NM, Stix J, Tauxe L et al (1985) Paleomagnetic chronology, fluvial processes, and tectonic implications of the Siwalik deposits near Chinji Village, Pakistan. J Geol 93:27–40
Kamal MA, Arshad MU, Zaidi BA (2015) Appraisal of Geotechnical Characteristics of Soil for Different Zones of Faisalabad (Pakistan)
Khalid MH, Alshameri B, Abid U (2021) Application of Kriging for development of SPT N value contour maps and USCS-based soil type qualitative contour maps for Islamabad, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 80:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09720-5
Khan SH (2019) Use of gypsum and bagasse ash for stabilization of low plastic and high plastic clay. J Appl Res Ind Eng 6:251–267
Khan S, Waseem M, Khan MA (2021) A seismic hazard map based on geology and shear-wave velocity in Rawalpindi-Islamabad, Pakistan. Acta Geol Sin 95:659–673. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.14405
Kieft P, Aquino M, Dodson A (2014) Using ordinary kriging for the creation of scintillation maps. In: Notarpietro R et al (eds) In mitigation of ionospheric threats to GNSS: an appraisal of the scientific and technological outputs of the TRANSMIT project. IntechOpen, London
Kleinbaum DG, Kupper LL, Muller KE, Nizam A (1988) Applied regression analysis and other multivariable methods, PWS Publis
Koçkar MK, Akgün H (2008) Development of a geotechnical and geophysical database for seismic zonation of the Ankara Basin, Turkey. Environ Geol 55:165–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0973-6
Kolat Ç, Doyuran V, Ayday C, Lütfi Süzen M (2006) Preparation of a geotechnical microzonation model using geographical information systems based on multicriteria decision analysis. Eng Geol 87:241–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.07.005
Krivoruchko K (2012) Empirical bayesian Kriging-Implemented in ArcGIS geostatistical analyst. ArcUser Fall 6:1–5
Lam NSN (1983) Spatial interpolation methods: a review. Am Cartogr 10:129–150. https://doi.org/10.1559/152304083783914958
Li Y, Fan W, Chen X et al (2017) Safety criteria and standards for bearing capacity of foundation. Hindawi Math Probl Eng 2017:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3043571
Malik A (2015) Geotechnical Statistical Evaluation of Lahore Site Data and Deep Excavation Design. Paper 13
Meyerhof GG (1951) The ultimate bearing capacity of foundations. Geotechnique 2:301–332
Meyerhof GG (1970) Safety factors in soil mechanics. Can Geotech J 7:349–355
Meyerhof GG (1984) Safety factors and limit states analysis in geotechnical engineering. Can Geotech J 21:1–7
Mitas L, Mitasova H (1999) Spatial Interpolation. Geogr Inf Syst Princ Tech Manag Apllications Geoinf Int Willey. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781351243858-7
Mohammed AH (2012) Database for Baghdad soil using GIS techniques. J Eng 18:1307–1324
Mohurd G (2012) Code for design of building foundation (GB 50007–2011). China Architecture and Building Press, Beijing, China
Nawaz MM, Khan SR, Farooq R et al (2022) Development of a cost-based design model for spread footings in cohesive soils. Sustain. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095699
Orhan A, Tosun H (2010) Visualization of geotechnical data by means of geographic information system: a case study in Eskisehir city (NW Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 61:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0357-1
Ouma YO, Owiti T, Kibiiy J et al (2012) Multitemporal comparative analysis of TRMM-3B42 satellite-estimated rainfall with surface gauge data at basin scales: daily, decadal and monthly evaluations. Int J Remote Sens 33:7662–7684. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2012.701347
Panoot S, Korchoke KC, Mairaing W, Apaphant P (2001) The development of geotechnical database of bangkok subsoil using GRASS-GIS. In: 22nd Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Singapore, pp 5–9
Pham TG, Kappas M, Van HC, Nguyen LHK (2019) Application of ordinary kriging and regression kriging method for soil properties mapping in hilly region of central Vietnam. ISPRS Int J Geo-Information. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8030147
Priya B, Dodagoudar GR (2018) An integrated geotechnical database and GIS for 3D subsurface modelling: application to Chennai city, India. Appl Geomatics 10:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-018-0202-x
Raynolds RGH (1980) The Plio-Pleistocene structural and stratigraphic evolution of the eastern Potwar Plateau, Pakistan. Dissertation, Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire
Rishikeshan CA, Katiyar SK, Vishnu Mahesh VN (2014) Detailed evaluation of dem interpolation methods in GIS using DGPS data. In: Proceedings - 2014 6th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks, CICN 2014. IEEE, pp 666–671
Robinson TP, Metternicht G (2003) A comparison of inverse distance weighting and ordinary kriging for characterising within-paddock spatial variability of soil properties in Western Australia. Cartography 32:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/00690805.2003.9714231
Salekin S, Burgess JH, Morgenroth J et al (2018) A comparative study of three non-geostatistical methods for optimising digital elevation model interpolation. ISPRS Int J Geo-Information 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7080300
Salih N, Mohammed A (2017) Characterization and modeling of long-term stress–strain behavior of water confined pre-saturated gypsum rock in Kurdistan Region, Iraq. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 9:741–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2017.03.009
Shafique MA, Qayyum TI (2011) Comparison of Bearing Capacity Equations for Vertical Central Loading. In: First International Conference on Geotechnique, Construction Materials and Environmen. ISBN: 978‐4‐9905958‐0‐7 C3051, Mie, Japan, pp 583–588
Sheikh IM, Pasha MK, Williams VS et al (2007) Regional Studies of the Potwar Plateau Area, Northern Pakistan. Environmental geology of the Islamabad-Rawalpindi area, Northern Pakistan. Reg Stud Potwar Plateau Area, North Pakistan, pp 1–2
Shi C, Wang Y (2021a) Development of subsurface geological cross-section from limited site-specific boreholes and prior geological knowledge using iterative convolution XGBoost. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng 147:04021082
Shi C, Wang Y (2021b) Nonparametric and data-driven interpolation of subsurface soil stratigraphy from limited data using multiple point statistics. Can Geotech J 58:261–280
Shi C, Wang Y (2021c) Smart determination of borehole number and locations for stability analysis of multi-layered slopes using multiple point statistics and information entropy. Can Geotech J 58:1669–1689. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2020-0327
Shi C, Wang Y (2022) Data-driven construction of Three-dimensional subsurface geological models from limited Site-specific boreholes and prior geological knowledge for underground digital twin. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2022.104493
Shill SK, Hoque M (2015) Comparison of bearing capacity calculation methods in designing shallow foundations. Int J Eng Technol Manag Appl Sci 3:29–39
Skempton AW (1986) Standard penetration test procedures and the effects in sands of overburden pressure, relative density, particle size, ageing and overconsolidation. Geotechnique 36:425–447. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1986.36.3.425
Smith M (1993) Neural networks for statistical modeling. Thomson Learning
Sultan-Ul-Islam M, Shamsuzzaman M, Islam MB (2008) Geotechnical study of sub-surface sediments in sirajgonj town and its adjoining areas, Bangladesh. Pak J Sci Ind Res 51:1–10
Taharin MR, Roslee R (2021) The application of semi variogram and ordinary Kriging in determining the cohesion and clay percentage distribution in hilly area of Sabah, Malaysia. Int J Des Nat Ecodynamics 16:525–530. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijdne.160506
Terzaghi K, Peck RB (1967) Soil mechanics in engineering practice. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
Terzaghi K, RB P, G M (1996) Soil mechanics. Wiley, New York
Teves-Costa P, Almeida IM, Rodrigues I et al (2014) Geotechnical characterization and seismic response of shallow geological formations in downtown Lisbon. Ann Geophys. https://doi.org/10.4401/ag-6390
Tobler WR (1970) A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ Geogr 46:234–240
Ullah H, Imtiaz K, Jahanzaib R, Zhang G (2022) Geotechnical characterization and statistical evaluation of alluvial soils of Lahore. Arab J Geosci 15:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10154-x
Vansarochana A, Tripathi NK, Clemente R (2009) Finding appropriate interpolation techniques for topographic surface generation for mudslide risk zonation. Geocarto Int 24:313–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106040802547735
Wackernagel H (2003) Ordinary kriging. Multivariate geostatistics. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg Germany, pp 79–88
Wang Y, Zhao T (2016) Interpretation of soil property profile from limited measurement data: a compressive sampling perspective. Can Geotech J 53:1547–1559. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2015-0545
Wang Y, Zhao T (2017) Statistical interpretation of soil property profiles from sparse data using Bayesian compressive sampling. Géotechnique 67:523–536. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.16.P.143
Wang Y, Cao Z, Li D (2016) Bayesian perspective on geotechnical variability and site characterization. Eng Geol 203:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.017
Wang Y, Zhao T, Hu Y, Phoon K-K (2019) Simulation of random fields with trend from sparse measurements without detrending. J Eng Mech ASCE 145:04018130. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001560
Waters NM (1989) Spatial interpolation I, lecture 40. NCGIA Core Curriculum, Tech Issues GIS. University of California, Santa Barbara, pp 1–12
Williams VS, Pasha MK, Sheikh IM (1999) Geologic map of the Islamabad-Rawalpindi area, Punjab, northern Pakistan: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 99–0047, 16 p., 1 oversize sheet, scale 1:50,000
Wu T, Li Y (2013) Spatial interpolation of temperature in the United States using residual kriging. Appl Geogr 44:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.07.012
Yajie H, Zhen LI, Huichun YE et al (2019) Mapping soil electrical conductivity using ordinary Kriging com- bined with back-propagation network. Chinese Geogr Sci 29:270–282
Zhao T, Wang Y (2018) Determination of efficient sampling locations in geotechnical site characterization using information entropy and Bayesian compressive sampling. Can Geotech J 56:1622–1637. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2018-0286
Zhao T, Hu Y, Wang Y (2018) Statistical interpretation of spatially varying 2D geo-data from sparse measurements using Bayesian compressive sampling. Eng Geol 246:162–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.09.022
Zhu Q, Lin HS (2010) Comparing ordinary kriging and regression kriging for soil properties in contrasting landscapes. Pedosphere 20:594–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(10)60049-5
Žlender B, Jelušič P, Boumezerane D (2012) Planning geotechnical investigation using ANFIS. Geotech Geol Eng 30:975–989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-012-9520-7
Acknowledgements
This research work was supported by QWA Engineers and National Engineering Services (NESPAK) Pakistan by providing the geotechnical data of sites.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The main idea was conceptualized by Waqas Hassan, whereas the methodology was defined by Waqas Hassan and Muhammad Naqeeb Nawaz. The data was collected by Muhammad Qasim. The software’s analysis was performed by Zain Ijaz. The original draft was prepared by Waqas Hassan, and reviewed and edited by Badee Alshameri. The overall work was carried out under supervision of Badee Alshameri.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, W., Alshameri, B., Nawaz, M.N. et al. Geospatial and statistical interpolation of geotechnical data for modeling zonation maps of Islamabad, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 81, 547 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10669-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10669-2