Abstract
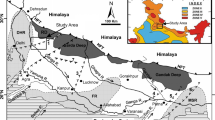
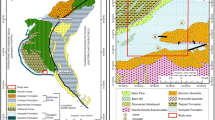
The northeastern region (NER) of India has several complex regional geological structures, out of which the Dauki fault (DF) is a prominent one. The E–W trending reverse DF, which is inferred to go through the southern margin of Shillong Plateau (SP), has played major role in the regional deformation of the adjoining areas and was believed to be active during the Late Quaternary time. Previous paleoseismological studies conducted on the eastern and western part of the DF, Bangladesh, revealed that the fault ruptured in AD 849–920 and AD 1548, respectively. However, there were no studies on the DF from southern side of the SP, India. For the first time, from Indian side, soft sediment deformation structures (SSDS) are reported from five trenches in and around the DF zone, SP. Close to the Dauki village, five trenches in the eastern part of the DF, SP, show micro faulting, sand dykes, disturbed strata, and water escape structures. The detailed investigation of SSDS indicates that the origin of deformation is seismic trigger. The 14C AMS dating of deformation structures generated by earthquakes suggests three seismic events occurred between 130 and 920 year BP, 5415 to 9140 year BP, and at about 4285 year BP. This study confirms that DF is indeed active, at least, since the mid-Holocene. More trenching and dating of seismically induced deformation features are needed to accurately calculate the recurrence interval of significant earthquakes that can strike the fast-expanding urban areas in India and Bangladesh.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 May 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10435-4
References
Alam M, Alam MM, Cyrrey JR, Chowdhury MLR, Gani MR (2003) An overview of the sedimentary geology of the Bengal Basin relation to the regional tectonic framework and basin-fill history. Sed Geol 155:179–208
Alfaro P, Moretti M, Soria JM (1997) Soft-sediment deformation structures induced by earthquakes (seismites) in Pliocene lacustrine deposits (Guadix Baza Basin, Central Betic Cordillera). Eclogae Geol Helv 90:531–540
Allen CR (1975) Geological criteria for evaluating seismicity. Geol Soc Am Bull 86:1041–1057
Allen JRL (1982) Sedimentary structures, their characters and physical basis, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 459–463
Allen JRL (1985) Wrinkle marks: an intertidal sedimentary structure due to aseismic soft sediment loading. Sed Geol 41:75–95
Alves TM (2015) Submarine slide blocks and associated soft-sediment deformation in deep-water basins: a review. Mar Pet Geol 67:262–285
Ambraseys NN (1988) Engineering seismology. Earthquake Eng Struct Dynam 17:1–105
Ambraseys NN, Douglas J (2004) Magnitude calibration of north Indian earthquakes. Geophys J Int 159:165–206
An Y, Dubey CS, Webb AAG, Kelty TK, Grove M, Gehrels GE, Burgess WP (2010) Geologic correlation of the Himalayan orogen and Indian craton: Part 1. Structural geology, U-Pb zircon geochronology and tectonicevolution of the Shillong Plateau and its neighboring regions in NE India. Geol Soc Am Bull 122:336–359
Anand A, Jain AK (1987) Earthquakes and deformational structures (seismites) in Holocene sediments from the Himalayan-Andaman Arc India. Tectonophys 133:105–120
Angelier J, Baruah S (2009) Seismotectonics in Northeast India: a stress analysis of focal mechanism solutions of earthquakes and its kinematic implications. Geophys J Int 178:303–326
Bilham R, England P (2001) Plateau “pop up” in the great 1897 Assam earthquake. Nature 410:806–809
Bapat A, Kulkarni RC, Guha SK (1983) Catalogue of earthquakes in India and neighbourhood: from historical period up to 1979. Indian Society of Earthquake Technology, Roorkee, p 211
Baro O, Kumar A (2017) Seismic source characterization for the Shillong plateau in Northeast India. J Seismol 21:1229–1249
Bilham R (2004) Earthquakes in India and the Himalaya: tectonics, geodesy and history. Ann Geophys 47:839–858
Bilham R, Hough S (2006) Future earthquakes on the Indian subcontinent: inevitable hazard, preventable risk. South Asian J 12:1–9
Binita P, Sharma A (2009) Soft-sediment deformation structures in the Late Quaternary sediments of Ladakh: evidence for multiple phases of seismic tremors in the North western Himalayan Region. J Asian Earth Sci 34:761–770
Biswas S, Greasemann B (2005) Structural modelling of the subsurface geology of the Sylhet trough, Bengal Basin. Bangladesh Geosci J 11:19–33
Bose PK, Sarkar S, Chakraborty S, Banerjee S (2001) Overview of the Meso- to Neoproterozoic evolution of the Vindhyan basin, Central India. Sedi Geol 141:395–419
Bowman D, Korjenkov A, Porat N (2004) Late-Pleistocene seismites from Lake Issyk-Kul, he Tien Shan range, Kyrghyzstan. Sed Geol 163:211–228
Calvo JP, Rodro Aguez-Pascua M, Marto An-Vela Azquez S, Jimenez S, De Vincente G (1998) Microdeformation of lacustrine laminite sequences from Late Miocene formations of SE Spain: an interpretation of loop bedding. Sedimentology 45:279–292
Chen J, Lee HS (2013) Soft-sediment deformation structures in cambrian siliciclastic and carbonate storm deposits (Shandong Province, China): differential liquefaction and fluidization triggered by storm-wave loading. Sediment Geol 288:81–94
Chen P, Molnar P (1990) Source parameters of earthquakes and interplate deformation beneath the Shillong Plateau and the Northern Indoburman Ranges. J Geophys Res 95:12527–12552
Collinson JD, Thompson DB (1982) Sedimentary Structures. Allen and Unwin, London, p 194
Cox RT, Van Arsdale RB, Harris JB, Forman SL, Beard W, Galluzzi J (2000) Quaternary faulting in the southern Mississippi Embayment and implications for tectonics and seismicity in an intraplate setting. Geol Soc Am Bull 112:1724–1735. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606
Cox RT, Lowe C, Hao Y, Mahan SA (2014) Use of small scale liquefaction features to assess paleoseismicity: an example from the Saline River fault zone, Southeast Arkansas, USA. Front Earth Sci 2:1–17
Cox RT, Harris JB, Forman SL, Brezina T, Gordon J, Gardner C (2012) Holocene faulting on the Saline River fault zone, Arkansas, along the Alabama-Oklahoma transform. In: Cox RT, Tuttle MP, Boyd OS, Locat J (eds) Recent Advances in North American Paleoseismology and Neotectonics East of the Rockies. Geological Society of America Special Paper 493:143–174
Das JD (2004) Active tectonics of the Eastern Himalayan foothills region and adjoining Brahmaputra Basin based on satellite images. Int J Remote Sens 25:549–557
Das JD, Saraf AK, Jain AK (1995) Fault tectonics of the Shillong plateau and adjoining regions, north-east India using remote sensing data. Int J Remote Sens 16:1633–1646
Dasgupta S, Pande P, Ganguly D, Iqbal Z, Sanyal K, Venkatraman NV, Sural B, Harendranath L, Mazumdar K, Sanyal S, Roy K, Das LK, Misra PS, Gupta HK (2000) Seismotectonics Atlas of India and its Environs. Geological Survey of India, Calcutta, p 87p
Duarah BP, Phukan S (2011) Understanding the tectonic behavior of Shillong Plateau, India using remote sensing data. Geol Soc India 77:105–112
Evans P (1964) The tectonic framework of Assam. J Geol Soc India 5:80–96
Galli P (2000) New empirical relationships between magnitude and distance for liquefaction. Tectonophysics 324:169–187
Ghosh SK, Pandey AK, Prabha Pandey P, Ray Y, Sinha S (2012) Soft-sediment deformation structures from the Paleoproterozoic Damtha Group of Garhwal Lesser Himalaya, India. Sed Geol 261:76–89
Gibert L, Sanz de Galdeano C, Alfaro P, Scott G, López Garrido AC (2005) Seismic induced slump in Early Pleistocene deltaic deposits of the Baza Basin (SE Spain). Sediment Geol 179:279–294
Guccione MJ (2005) Late Pleistocene and Holocene paleoseismology of an intraplate seismic zone in a large alluvial valley, the new Madrid seismic zone, Central USA. Tectonophysics 408:237–264
Hempton MR, Dewey JF (1983) Earthquake induced deformational structures in young lacustrine sediments, east Anatolian Fault, southeast Turkey. Tectonophysics 98:T7–T14
Hiller K, Elahi M (1984) Structural development and hydrocarbon entrapment in the Surma Basin, Bangladesh (NW Indo-Burman fold belt). In: 5th offshore SE Asia Conference, Singapore, p. 56–63
Islam MS, Shinjo R, Kayal JR (2011) Popup tectonics of the Shillong Plateau in northeastern India: insight from numerical simulations. Gondwana Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2010.11.007
Iyengar RN, Sharma D, Siddiqui JM (1999) Earthquake history of India in medieval times. Indian J His Sci 34(3):181–237
Jayangondaperumal R (2021) Geological evidence of great earthquakes along the eastern Himalayan Foothills. J Geol Soc India 97:823–926
Jayangondaperumal R, Thakur VC (2008) Co-seismic secondary surface fractures on southeastward extension of the rupture zone of the 2005 Kashmir earthquake. Tectonophysics 446:61–76
Jayangondaperumal R, Thakur VC, Suresh N (2008) Liquefaction features of the 2005 Muzaffarabad-Kashmir earthquake and evidence of paleoearthquakes near Jammu Kashmir Himalaya. Curr Sci 95:1071–1076
Jayangondaperumal R, Wesnousky SG, Choudhuri BK (2011) Near-surface expression of early to late Holocene displacement along the northeastern Himalayan frontal thrust at Marbang Korong Creek, Arunachal Pradesh, India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 101:3060–3066
Jayangondaperumal R, Kumahara Y, Thakur VC, Kumar A, Srivastava P, Shubhanshu D, Joe V, Dubey AK (2017) Great earthquake surface ruptures along back thrust of the Janauri anticline, NW Himalaya. J Asian Earth Sci 133:89–101
Jayangondaperumal R, Thakur VC, Joe V, Priyanka SR, Anil KG (2018) Active tectonics of Kumaun and Garhwal Himalaya. Springer Natural Hazards. ISBN 978–981–10–8242–9
Johnson SY, Alam AMN (1991) Sedimentation and tectonics of the Sylhet trough, Bangaldesh. Geol Soc Am Bull 103:1513–1527
Jones AP, Omoto K (2000) Towards establishing criteria for identifying trigger mechanisms for soft-sediment deformation: case study of Late Pleistocene lacustrine sands and clays, Onokobe and Nakayamadaira Basins, northeastern Japan. Sedimentology 47:1211–1226
Juyal N, Pant RK, Basavaiah N, Yadava MG, Saini NK, Singhvi AK (2004) Climate and seismicity in the higher Central Himalaya during 20–10 Ka: evidence from the Garbayang basin, Uttaranchal, India. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 213:315–330
Kangi A, Aryaei AA, Maasoomi A (2010) Synsedimentary deformations in member 2 of the Mila Formation in the Central Alborz Mountains, Northern Iran. Arab J Geosci 3:33–39
Karlin RE, Abella SEB (1992) Paleoearthquakes in the Pugeot Sound Region recorded in sediments from lake Washington, USA. Science 258:1617–1619
Kayal JR (2001) Micro earthquake activity in some parts of the Himalaya and the tectonic model. Tectonophysics 339:331–351
Kayal JR (2008) Microearthquake seismology and seismotectonics of South Asia. McGraw Hill Publication, Gautam Buddha Nagar
Kayal JR, Arefiev SS, Barua S, Hazarika D, Gogoi N, Kumar A, Chowdhury SN, Kalita S (2006) Shillong plateau earthquakes in northeast India region: complex tectonic model. Curr Sci 91:109–114
Koç-Taşgın C, Altun F (2019) Soft-sediment deformation: deep-water slope deposits of a back-arc basin (middle Eocene–Oligocene Kırkgeçit Formation, Elazığ Basin) Eastern Turkey. Arab J Geosci 12(773):1–20
Kotlia BS, Rawat KS (2004) Soft sediment deformation structures in the Garbyang palaeolake: evidence for the past shaking events in the Kumaun Tethys Himalaya. Curr Sci 876:377–379
Kumar S, Wesnousky SG, Jayangondaperumal R, Nakata T, Kumahara Y, Singh V (2010) Paleoseismological evidence of surface faulting along the northeastern Himalayan front, India: timing, size, and spatial extent of great earthquakes. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB006789
Kumar D, Reddy DV, Pandey AK (2016) Paleoseismic investigations in the Kopili fault zone of North East India: evidences from liquefaction chronology. Tectonophysics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.02.016
Lohmann HH (1995) On the tectonics of Bangladesh. Swiss Assoc Pet Geol Eng Bull 62(140):29–48
Lowe DR (1975) Water escape structures in coarse-grained sediments. Sedimentology 22:157–204
Lowe DR (1976) Grain flow and grain flow deposits. J Sed Petrology 46:188–199
Lowe DR, LoPiccolo LD (1974) The characteristics and origins of dish and pillar structures. J Sed Petrol 44:484–501
Malik JN, Sahoo S, Satuluri S, Okumura K (2015) Active Fault and paleoseismic studies in Kangra Valley: evidence of surface rupture of a Great Himalayan 1905 Kangra Earthquake (Mw 7.8), Northwest Himalaya India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 105:2325–2342
Malik JN, Naik SP, Sahoo S, Okumura K, Mohanty A (2017) Paleoseismic evidence of the CE 1505 (?) and CE 1803 earthquakes from the foothill zone of the Kumaon Himalaya along the Himalayan Frontal Thrust (HFT) India. Tectonophysics 714:133–145
Maltman A (1984) On the term ‘soft-sediment deformation. J Struct Geol 6(5):89–592
Manighetti I, Perrin C, ves Gaudemer Y, Dominguez S, Stewart N, Malavieille J, Garambois S (2020) Repeated giant earthquakes on the Wairarapa fault, New Zealand, revealed by Lidar-based Paleoseismology. Sci Rep 10:2124
Marco S, Agnon A (1995) Prehistoric earthquake deformations near Massada, Dead Sea Graben. Geology 23:695–698
Masana E, Moreno X, Gràcia E, Pallàs R, Ortuño M, López R, Gómeznovell O, Ruano P, Perea H, Stepancikova P, Khazaradze G (2018) First evidence of paleoearthquakes along the Carboneras Fault Zone (SE Iberian Peninsula): Los Trances site. Geol Acta 16:461–476
Mastrogiacomo G, Moretti M, Owen G, Spalluto L (2012) Tectonic triggering of slump sheets in the Upper Cretaceous carbonate succession of the Porto Selvaggio area (Salento Peninsula, southern Italy): synsedimentary tectonics in the Apulion Carbonate Platform. Sediment Geol 269–270:15–27
Mazumder R, Van Loon AJ, Arima M (2006) Soft-sediment deformation structures in the Earth’s oldest seismites. Sed Geol 186:19–26
McCalpin JP (1996) Paleoseismology. Academic Press, San Diego, p 588
McCalpin JP, Reicherter K (2018) Introduction to the special issue: paleoseismology, active tectonics and archaeoseismology. Geomorphology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.11.001
Mishra RL, Singh I, Pandey A, Rao PS, Sahoo HK, Jayangondaperumal R (2016) Paleoseismic evidence of a giant medieval earthquake in the eastern Himalaya. Geophys Res Lett 43(11):5707–5715. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016gl068739
Miyata T (1990) Slump strain indicative of paleoslope in Cretaceous Izumi sedimentary basin along Median tectonic line, southwest Japan. Geology 18(5):392–394
Mohindra R, Bagati TN (1996) Seismically induced soft-sediment deformation structures (seismites) around Sumdo in the lower Spiti valley (Tethys Himalaya). Sed Geol 101:69–83
Mohindra R, Thakur VC (1998) Historic large earthquake-induced soft sediment deformation features in the Sub-Himalayan Doon valley. Geol Mag 135:269–281
Monecke K, Anselmetti FS, Becker A, Sturn M, Giardini D (2004) The record of historic earthquakes in lake sediments of Central Switzerland. Tectonophysics 394(1):21–40
Moretti M (2000) Soft-sediment deformation structures interpreted as seismites in middle-late Pleistocene aeolian deposits (Apulian foreland, southern Italy). Sed Geol 135:167–179
Moretti M, Alfaro P, Caselles O, Canas JA (1999) Modelling seismites with a digital shaking table. Tectonophysics 304(4):369–383
Moretti M, Soria JM, Alfaro P, Walsh A (2001) Asymmetrical soft sediment deformation structures triggered by rapid sedimentation in turbiditic deposits (late Miocene, Guadix Basin, southern Spain). Facies 46(47):283–294
Morino M, Kamal ASMM, Muslim D, Ali RMdE, Kamal MA, Rahman MdZ, Kaneko F (2011) Seismic event of the Dauki Fault in 16th Century confirmed by trench investigation at Gabrakhari Village, Haluaghat, Mymensingh, Bangladesh. J Asian Earth Sci 42:492–498
Morino M, Kamal ASMM, Akhter SH, Rahman MdZ, Ali RMdE, Talukder A, Khan MdMH, Matsuo J, Kaneko F (2014) A paleo-seismological study of the Dauki fault at Jaflong, Sylhet, Bangladesh: Historical seismic events and an attempted rupture. J Asian Earth Sci 491:218–226
Mugnier JL, Huyghe P, Gajurel A, Upreti B, Jouanne F (2011) Seismities in the Kathmandu basin and seismic hazard. Tectonophysics 509:33–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2011.05012
Nandy DR (2001) Geodynamics of Northeastern India and the Adjoining Region. ACB Publication, Kolkata, p 209
Nandy DR, Dasgupta S (1991) Seismotectonic domains of northeastern India and adjacent areas. Phys Chem Earth 18:371–384
Nelson AR, Atwater BF, Bobrowsky PT, Bradley LA, Clague JJ, Carver GA, Darienzo ME, Grant WC, Krueger HW, Sparks R, Stafford TW, Stuiver M (1995) Radiocarbon evidence for extensive plate-boundary rupture about 300 years ago at the Cascadia subduction zone. Nature 378:371–374
Neuwerth R, Suter F, Guzman CA, Gorin GE (2006) Soft-sediment deformation in a tectonically active area: the PlioPleistocene Zarzal Formation in the Cauca Valley (Western Colombia). Sediment Geol 186:67–88
Obermeier SF (1996a) Chapter using liquefaction-induced features for paleoseismic analysis. Int Natl Geophys 62:331–396
Obermeier SF (1996b) Use of liquefaction-induced features for paleoseismic analysis: an overview of how seismic liquefaction features can be distinguished from other features and how their regional distribution and properties of source sediment can be used to infer the location and strength of Holocene paleo-earthquakes. Eng Geol 44:1–76
Obermeier SF (1998) Liquefaction evidence for strong earthquakes of Holocene and Latest Pleistocene ages in the States of Indiana and Illinois, USA. Eng Geol 50:227–254
Oldham RD (1899) Report on the great earthquake of 12th June, 1897. Mem Geol Surv India 29:1–379
Ortner H, Kilian S (2016) Sediment creep on slopes in pelagic limestones: upper Jurassic of Northern Calcareous Alps, Austria. Sediment Geol 344:350–363
Owen G (1987) Deformation processes in unconsolidated sands. In: Jones ME, Preston RMF (eds) Deformation of sediments and sedimentary rocks. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. 29:11–24
Owen G (1996) Experimental soft-sediment deformation: Structures formed by the liquefaction of unconsolidated sands and some ancient examples. Sedimentology 43:279–293
Owen G (2003) Load structures: gravity-driven sediment mobilization in the shallow subsurface. In: Van Rensbergen P, Hillis RR, Maltman AJ, Morley CK (eds) Subsurface sediment mobilization. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. 216:21–34
Owen G, Moretti M (2008) Determining the origin of soft-sediment deformation structures: a case study from Upper Carboniferous delta deposits in south-west Wales, UK. Terra Nova 20:237–245
Owen G, Moretti M, Alfaro P (2011) Recognising triggers for soft-sediment deformation: current understanding and future directions. Sed Geol 235:133–140
Pandey A, Jayangondaperumal R, Hetényi G, Priyanka SR, Singh I, Srivastava P, Srivastava HB (2021) Establishing primary surface rupture evidence and magnitude of the 1697 CE Sadiya earthquake at the Eastern Himalayan Frontal thrust. India Sci Rep 11(1):1–14
Panthi A, Jyoti B (2013) Seismicity pattern analysis in and around Shillong great earthquake of 1897. Himal Phys 4:36–38
Philip G, Suresh N, Bhakuni SS, Gupta V (2011) Paleoseismic investigation along Nalagarh thrust: evidence of late pleistocene earthquake in Pinjaur Dun, Northwestern sub-Himalaya. J Asian Earth Sci 40:1056–1067
Poddar MC (1950) The Assam earthquake of 15th August 1950. Indian Min 4:167–176
Pope MC, Read JF, Hofmann HJ (1997) Late middle to late Ordovician seismites of Kentucky, southeast Ohio and Virginia: sedimentary recorders of earthquakes in the Appalachian Basin. Bull Geol Soc Am 109:489–503
Postma G (1983) Water escape structures in the context of a depositional model of a mass flow dominated conglomeratic fan delta. Sedimentology 30:91–103
Potter PE, Pettijohn FJ (1963) Pleocurrents and basin analysis. Springer, Berlin, p 296
Priyanka RS, Jayangondaperumal R, Pandey A, Mishra RL, Singh I, Bhushan R et al (2017) Primary surface rupture of the 1950 Tibet-Assam great earthquake along the eastern Himalayan front. India Sci Rep 7(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05644-y
Rajendran K, Rajendran CP (2011) Revisiting the earthquake sources in the Himalaya: perspectives on past seismicity. Tectonophysics 504:75–88
Rajendran CP, Rajendran K, Duarah BP, Baruah S, Earnest A (2004) Interpreting the style of faulting and paleoseismicity associated with the 1897 Shillong, northeast India, earthquake: Implications for regional tectonism. Tectonics 23(4):1–12
Rajendran CP, John B, Rajendran K (2015) Medieval pulse of great earthquakes in the central Himalaya: viewing past activities on the frontal thrust. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120:1623–1641
Rana N, Bhattacharya F, Basavaiah N, Pant RK, Juyal N (2013) Soft sediment deformation structures and their implications for Late Quaternary seismicity on the South Tibetan Detachment System, Central Himalaya. Tectonophysics 592:165–174
Reddy DV, Nagabhushanam P, Kumar D, Sukhija BS, Thomas PJ, Pandey AK, Sahoo RN, Ravi Prasad GV, Datta K (2009) The great 1950 Assam earthquake revisited: field evidences of liquefaction and search for paleoseismic events. Tectonophysics 474:463–472
Reimer PJ, Baillie MGL, Bard E, Bayliss A, Beck JW, Bertrand CJH, Blackwell PG, Buck CE, Burr GS, Cutler KB, Damon PE, Edwards RL, Fairbanks RG, Friedrich M, Guilderson TP, Hogg AG, Hughen KA, Kromer B, McCormac G, Manning S, Ramsey CB, Reimer RW, Remmele S, Southon JR, Stuiver M, Talamo S, Taylor FW, van der Plicht J, Weyhenmeyer CE (2004) IntCal04 terrestrial radiocarbon age calibration, 0–26 cal kyr BP. Radiocarbon 46:1029–1058
Ricci Lucchi F (1995) Sedimentographica. A photographic atlas of sedimentary structures, 2nd edn. Columbia University Press, New York, p 255
Rockwell TK, Lindvall S, Dawson T, Langridge R, Lettis W, Klinger Y (2002) Lateral offsets on surveyed cultural features resulting from the 1999 İzmit and Düzce earthquakes Turkey. Bull Seismol Soc Am 92(1):79–94. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120000809
Rodríguez-López JP, Meléndez N, Soria AR, Liesa CL, Van Loon AJ (2007) Lateral variability of ancient seismites related to differences in sedimentary facies (the syn-rift Escucha Formation, mid-Cretaceous, eastern Spain). Sediment Geolol 201:461–484
Rodriguez-Pascua MA, Calvo JP, De Vicente G, Gomez-Gras D (2000) Soft-sediment deformation structures interpreted as seismites in lacustrine sediments of the Prebetic Zone, SE Spain, and their potential use as indicators of earthquake magnitudes during the Late Miocene. Sed Geol 135:117–135
Rossetti DF (1999) Soft sediment deformation structures in late Albian to Cenomanian deposits, Sao Luis Basin, Northern Brazil: evidence for palaeoseisimity. Sedimentology 46:1065–1081
Rossetti DF, Santos AE (2003) Events of sediment deformation and mass failure in Upper Cretaceous estuarine deposits (Cameta´ Basin, northern Brazil) as evidence for seismic activity. Sediment Geol 161:107–130
Sapkota SN, Bollinger L, Klinger Y, Tapponnier P, Gaudemer Y, Tiwari D (2013) Primary surface ruptures of the great Himalayan earthquakes in 1934 and 1255. Nat Geosci 6(1):71–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1669
Sarkar S, Choudhuri A, Banerjee S, van Loon Toom AJ, Bose PK (2014) Seismic and non-seismic soft-sediment deformation structures in the Proterozoic Bhander Limestone, central India. Geologos 20(2):89–103. https://doi.org/10.2478/logos-2014-0008
Scott B, Price S (1988) Earthquake-induced structures in young sediments. Tectonophysics 147:165–170
Seilacher A (1969) Fault-graded beds interpreted as seismites. Sedimentology 13:155–159
Seilacher A (1984) Sedimentary structures tentatively attributed to seismic events. Mar Geol 55:1–12
Seth A, Sarkar S, Bose PK (1990) Synsedimentary seismic activity in an immature passive margin basin (Lower Member of the Katrol Formation, Upper Jurassic, Kutch, India). Sed Geol 68:279–291
Sieh KE (1978) Prehistoric large earthquakes produced by slip on the San Andreas Fault at Pallet Creek. Calif J Geophys Res 83(B8):3907–3939
Sims JD (1973) Earthquake induced structures in sediments of Van Norman Lake, San Fenando, CA. Science 182:161–163
Sims JD (1975) Determining earthquake recurrence intervals from deformational structures in young lacustrine sediments. Tectonophysics 29:141–152
Singh S, Jain AK (2007) Liquefaction and fluidization of lacustrine deposits from Lahaul-Spiti and Ladakh Himalaya: geological evidences of palaeoseismicity along active fault zone. Sed Geol 196:47–57
Singh BP, Mondal K, Singh A, Mittal SRK, Kanhaiya S (2020) Seismic origin of the soft-sediment deformation structures in the upper Palaeo-Mesoproterozoic Semri Group, Vindhyan Supergroup. Central India Geol J. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3872
Singh S, Jain AK (2001) Palaeoseismicity: geological evidence along the Kaurik Chago fault-zone and other related areas in Lahaul-Spiti and Ladakh Himalaya. In: Varma OP (ed) Research Highlights in Earth System Science. Department of Science and Technology, India, Special Volume, 2 pp 205–225
Singh I, Pandey A, Mishra RL, Priyanka RS, Brice A, Jayangondaperumal R, Srivastava V (2021) Evidence of the 1950 great Assam earthquake surface break along the Mishmi Thrust at Namche Barwa Himalayan Syntaxis. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL090893
Spalluto L, Moretti M, Festa V, Tropeano M (2007) Seismically-induced slumps in Lower-Maastrichtian peritidal carbonates of the Apulian Platform (southern Italy). Sed Geol 196:81–98
Srinivasan V (2003) Deciphering differential uplift in Shillong Plateau using remote sensing. J Geol Soc India 62:773–777
Sukhija BS, Rao MN, Reddy DV, Nagabhushanam P, Hussain S, Chadha RK, Gupta HK (1999) Paleoliquefaction evidence and periodicity of large prehistoric earthquakes in Shillong Plateau, India. Earth Planet Sci Lett 167:269–282
Talwani P, Schewer WT (2001) Recurrence rates of large earthquakes in the South Carolina Coastal Plain based on paleoliquefaction data. J Geophys Res 106:6621–6642
Tasgin CK, Turkmen I (2009) Analysis of soft-sediment deformation structures in Neogene fluvio-lacustrine deposits of C, aybaˇgı Formation, Eastern Turkey. Sedi Geo 218:16–30
Thomas PJ, Reddy DV, Kumar D, Nagabhushanam P, Sukhija BS, Sahoo RN (2007) Optical dating of liquefaction features to constrain prehistoric earthquakes in Upper Assam, NE India-some preliminary results. Quat Geochronol 2:278–283
Tuttle MP, Atkinson GM (2010) Localization of large earthquakes in the Charlevoix seismic zone, Quebec, Canada, during the past 10,000 years. Seismol Res Lett 81:140–147
Tuttle MP, Wolf LW, Starr ME, Villamor P, Mayne PW, Lafferty RH III, Morrow JE, Scott RJ Jr, Forman SL, Hess K, Tucker K, Dunahue J, Haynes ML (2019) Evidence for large New Madrid earthquakes about AD 0 and BC 1050, Central United States. Seismol Res Lett 90:1393–1406
Upadhyay R (2003) Earthquake-induced soft-sediment deformation in the lower Shyok river valley, northern Ladakh, India. J Asian Earth Sci 21:413–421
Vanneste K, Meghraoui M, Camelbeeck T (1999) Late Quaternary earthquake related soft sediment deformation along the Belgian portion of the Feldbiss Fault, Lower Rhine Graben system. Tectonophysics 309:57–79
Visher GS, Cunningham RD (1981) Convolute laminations-a theoretical analysis: example of a Pennsylvanian Sandstone. Sed Geol 28:175–188
Watinaro I, Swapnamita C, Sarat P (2016) Ascertaining neotectonic activities in the southern part of Shillong Plateau through geomorphic parameters and remote sensing data. Curr Sci 110:91–98
Wheeler RL (2002) Distinguishing seismic from nonseismic soft-sediment structures: Criteria from seismic-hazard analysis. In: Ettensohn FR, Rast N, Brett CE (eds) Ancient Seismites. Geol Soc Amer Spec Paper 359:1–11
Yamamoto Y (2014) Dewatering structure and soft-sediment deformation controlled by slope instability: examples from the late Miocene to Pliocene Miura-Boso accretionary prism and trench-slope basin, central Japan. Mar Geol 356:65–70
Youd TL (1991) Mapping of earthquake-induced liquefaction for seismic zonation. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Seismic Zonation, Stanford, CA, 4, 111–147
Acknowledgements
The Authors are deeply grateful to Prof. D.S. Ramesh, Director, IIG, for his support, discussions and necessary permission for publishing this paper. We would like to thank the reviewers and editor who made constructive suggestions and contributions, which helped in improving the manuscript. We acknowledge financial support from CLAIMs programme of DST-IIG.
Funding
This is DST-IIG funded CLAIMS project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmi, B.V., Gawali, P.B. Soft sediment deformation features in Dauki Fault region: evidence of paleoearthquakes, Shillong Plateau, NE India. Environ Earth Sci 81, 58 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10168-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10168-4