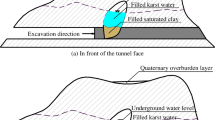
Abstract
The chief objective of the article is to learn the spatial characteristics of stress distribution around a shallow buried spherical Karst cave containing fill materials in limestone strata. First, considering the effect of external load, stress field in the Earth’s crust, internal filling and Karst geomorphology characteristics in China, a spatial axisymmetrical model was established. Concurrently, combing available work and the concept of elasticity, the boundary conditions are determined. Subsequently, the Love displacement method was introduced, and stress component expressions were obtained. The diagram characteristics of each stress component are summarized, which are affected by various influencing factors. Finally, to prove the rationality of the general solution, a numerical simulation was carried out based on practical engineering, and the maximum error is less than 5%. Thus, the analytical solution could represent the spatial characteristics of stress distribution around a shallow buried spherical karst cave containing fill materials in limestone strata.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodier JN (1933) Concentrations of stress around spheroidal and cylindrical inclusions and flaws [J]. J Appl Mech 55:39–44
Gutierrez F, Parise M, Dewaele J, Jourde H (2014) A review on natural and human-induced geohazards and impacts in karst [J]. Earth Sci Rev 138:61–88
Harris P, Purkis S, Reyes B (2018) Statistical pattern analysis of surficial karst in the Pleistocene Miami oolite of South Florida[J]. Sed Geol 367:84–95
Howland RCJ, Knight RC (1939) Stress functions for a plate containing groups of circular holes[J]. Philos Trans R Soc Math Phys Sci 238(2):357–392
Kaufmann G, Romanov D, Tippelt T, Vienken T, Werban U, Dietrich P, Mai F, Börner F (2018) Mapping and modelling of collapse sinkholes in soluble rock: the Münsterdorf site, northern Germany[J]. J Appl Geophys 154:64–80
Li QQ, Zhang DL, Fang Q (2014) Analytic solution to initial damage of cavern strata by complex function method [J]. Chin J Geotech Eng 36(11):2110–2117 (in Chinese)
Liao LP, Yang WK, Wang QZ (2010) Stability analysis of an ellipsoidal cavity in foundation[J]. Rock Soil Mech 31(S2):138–147 (in Chinese)
Piccini L, Mecchia M (2009) Solution weathering rate and origin of karst landforms and caves in the quartzite of Auyan-tepui (Gran Sabana, Venezuela)[J]. Geomorphology 106:15–25
Rao JY, Fu HL, Liu YS, Yin Q (2015) Stress analysis of rocks surrounding a tubular filled elliptical karst cave with complex function of elastic mechanics[J]. J Central South Univ (sci Technol) 46(7):2605–2612 (in Chinese)
Scotto AS, Forte SA (2018) Analysis of sinkhole triggering mechanisms in the hinterland of Naples (southern Italy) [J]. Eng Geol 237:42–52
Shi GP, Zhu JH, Li BH, Yang JH (2014) Elastic analysis of hole-edge stress of rectangular roadway [J]. Rock Soil Mech 35(9):2587–2593 (in Chinese)
Timoshenko S, Goodier JN (1965) Theory of elasticity [M], Xu Zhilun, Wu Yongzhen translation. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Wan DD (2018) The Traders’ Cave of Niah (NW Borneo): morphology and features as indicators of speleogenesis and karstification[J]. Carbonates Evaporites 33:315–329
Williams PW (2008) The role of the epikarst in karst and cave hydrogeology: a review[J]. Int J Speleol 37:1–10
Xie P, Wen H, Wang G, Hu J (2018a) Theoretical analytical solution of deformation and stress distribution of underground gas storage cavern in bedded salt rock. Arch Civil Eng LXIV(4):37–53
Xie P, Wen HJ, Xiao P, Zhang YY (2018b) Evaluation of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and geology survey for slope stability study in mantled karst region[J]. Environ Earth Sci 77:122
Xie P, Wen H, Wang G (2018c) An analytical solution of stress distribution around underground gas storage cavern in bedded salt rock[J]. J Renew Sustain Energy 10(3):034101
Xie P, Wen H, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Hu J (2020) A method for identification and reconstruction of hard structural planes, weak interlayer and cavities in the limestone near surface. Eur J Environ Civil Eng 24(14):2489–2511. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2018.1512902
Zhang LF, Zeng XS, Yao YS, Liao WL (2007) Review on karst collapse in China [J]. Chin J Geol Haz Control 18(3):126–130 (in Chinese)
Zhao HJ, Ma FS, Guo J (2012) Regularity and formation mechanism of Large-scale abrupt karst collapse in southern China in the first half of 2010 [J]. Nat Haz 60:1037–1045
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Yanyan Zhang, Jing Hu and Xiaoxuan Zhang for their assistance.
Funding
The research on which this article is based has been supported by Grants: the Systematic Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Disaster Prevention Structural Safety (Grant No: 2019ZKX015), the Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No. E2020210006), Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 520QN229), the Scientific Research Startup Foundation of Hainan university (Grant No: KYQD(2R)1723), Key Research and Development Project of Cangzhou Municipal Science and Technology bureau, China(Grant No. 183305006) and National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFC1505501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PX carried out the theoretical analysis; SM and HW carried out the numerical simulation; LL carried out the data statistics. All the authors have given final approval for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, P., Ma, S., Wen, H. et al. Theoretical analysis on stress distribution characteristics around a shallow buried spherical Karst cave containing fill materials in limestone strata. Environ Earth Sci 81, 97 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10112-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10112-y