Abstract
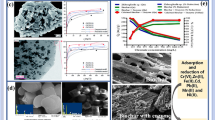
Removal of excessive sulfate from the low-temperature groundwater environment in the Longdong area is important for protecting human health. The effects of naturally occurring hydrochemical ions and pH on sulfate adsorption were examined to verify the applicability of magma-derived scoria and determine whether scoria could be reused. Hydrochemical ions and pH of the natural groundwater environment in the study area improved the adsorption capabilities of scoria for sulfate. Additionally, 2% AlCl3 was sufficiently stable for use as a high-efficiency regenerant for sulfate desorption from the scoria. The adsorption characteristics of scoria were determined using a continuous dynamic column system. The effects of flow rate, initial sulfate concentration, and column height on breakthrough curves were investigated at low temperatures. The scoria adsorption capacity increased with increasing sulfate initial concentrations and decreased with increasing flow rates and column heights. The maximum adsorption capacity was 10.14 mg/g at a flow rate of 5 mL/min, initial concentration of 500 mg/L, and column height of 10 cm. The breakthrough time increased with increasing column heights and decreased with increasing flow rates and initial concentrations. Model comparison to analyze adsorption kinetics showed that the Bohart–Adams model is an excellent fit for the dynamic experimental data. Electron microscopy and spectroscopy methods confirmed the surface changes before and after adsorption. Thus, scoria is a highly efficient, economical, and environmentally friendly adsorbent for removing sulfate from groundwater, providing a foundation for the application of scoria for groundwater environment restoration in cold regions in China.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu Z, Gönen F (2004) Biosorption of phenol by immobilized activated sludge in a continuous packed bed: prediction of breakthrough curves. Process Biochem 39:599–613
Al-Madhlom Q, Al-Ansari N, Hamza BA, Laue J, Hussain HM (2020) Seepage velocity: large scale mapping and the evaluation of two different aquifer conditions (silty clayey and sandy). Hydrology 7:60
Al-Omran AM, Mousa MA, AlHarbi MM, Nadeem ME (2018) Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in Al-Hasa, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 11:1–12
Alshameri A, He H, Zhu J, Xi Y, Zhu R, Ma L, Tao Q (2018) Adsorption of ammonium by different natural clay minerals: characterization, kinetics and adsorption isotherms. Appl Clay Sci 159:83–93
Álvarez-Ayuso E, Nugteren HW (2005) Synthesis of ettringite: a way to deal with the acid wastewaters of aluminium anodising industry. Water Res 39:65–72
Araujo SF, Caldeira CL, Ciminelli VS, Silva A, Amorim CC (2018) Versatility of iron-rich steel waste for the removal of high arsenic and sulfate concentrations in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:4266–4276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3168-7
Aregu MB, Asfaw SL, Khan MM (2018) Identification of two low-cost and locally available filter media (pumice and scoria) for removal of hazardous pollutants from tannery wastewater. Environ Syst Res 7:10
Back W, Hanshaw BB (1965) Chemical geohydrology. Advances in hydroscience. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 49–109
Baral S, Das N, Ramulu T, Sahoo S, Das S, Chaudhury GR (2009) Removal of Cr (VI) by thermally activated weed Salvinia cucullata in a fixed-bed column. J Hazard Mater 161:1427–1435
Bertolino SM, Rodrigues IC, Guerra-Sá R, Aquino SF, Leão VA (2012) Implications of volatile fatty acid profile on the metabolic pathway during continuous sulfate reduction. J Environ Manag 103:15–23
Bohart GS, Adams EQ (1920) Some aspects of the behaviour of charcoal with respect to chlorine. J Am Chem Soc 189:669–660
Dong T, Zhang Y, Su X, Li R (2017) Removal of nitrogen from simulated ground water by scoria: dynamic processes and modeling. Desalin Water Treat 87:240–248
Dou W, Zhou Z, Jiang LM, Jiang A, Huang R, Tian X, Zhang W, Chen D (2017) Sulfate removal from wastewater using ettringite precipitation: magnesium ion inhibition and process optimization. J Environ Manag 196:518–526
Farrell J, Bostick WD, Jarabek RJ, Fiedor JN (2010) Uranium removal from ground water using zero valent iron media. Groundwater 37:618–624
Fondu L, De Bo I, Van Hulle S (2015) Phosphate adsorption capacity testing of natural and industrial substrates in view of application in swimming and fish pond water treatment systems. Desalin Water Treat 54:2461–2467
Gao Y, Wen Z, Xu Y, Song H, Li W, Yu Y, Ke C (2020) Geochemical characteristics of the Chang7 organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rocks and its relationship with the tight oil in Longdong area, Northwest China. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 10:1803–1816
Garcia-Pacheco R, Rabadan J, Rodriguez-Saez L, Molina S, Landaburu-Aguirre S (2016) Fouling prevention, preparing for re-use and membrane recycling. Desalination 393:16–30
Geldenhuys AJ, Maree JP, Beer MD, Hlabela P (2003) An integrated limestone/lime process for partial sulphate removal. J South Afr Inst Min Metall 103:345–354
General Administration of Quality Supervision I, Quarantine of China SAoC (2017) Standards for groundwater quality (GB/T 14848-2017). Standards Press of China Beijing (in Chinese)
Golui D, Datta S, Rattan R, Dwivedi B, Meena M, Bandyopadhayay K (2015) Release of zinc and cadmium from sludge amended soils as influenced by varying levels of moisture and temperature. J Environ Biol 36:979–984
Gustafsson JP (2001) Modelling competitive anion adsorption on oxide minerals and an allophane-containing soil. Eur J Soil Sci 52:639–653
Huaixin M, Xiaorong R, Lihui Z, Yan L (2014) Groundwater quality analysis and vulnerability assessment in Longdong area. Meteorol Environ Res 5:49
Jiang S, Li Y, Ladewig BP (2017) A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci Total Environ 595:567
Kerry T (2011) 14. United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Yearbook of International Environmental Law, pp 575–579
Ko DCK, Porter JF, Mckay G (2000) Optimised correlations for the fixed-bed adsorption of metal ions on bone char. Chem Eng Sci 55:5819–5829
Kovaleschy V, Kruseman G, Rushton K (2004) Groundwater studies: an international guide for hydrogeological investigations, IHP-VI, Series on Groundwater No. 3. UNESCO
Lambrecht R, De Barros MA, Arroyo PA, Borba CE, Da Silva EA (2015) Adsorption of the dye reactive blue 5G in retorted shale. Braz J Chem Eng 32:269–281
Li R, Zhang Y, Wang J, Qian H (2017) Removal of sulfa antibiotics in low-temperature water using scoria. Pol J Environ Stud 26:2037–2045
Li S, Zhang Y, Qian H, Deng Z, Wang X, Yin S (2019) Removal characteristics of a composite active medium for remediation of nitrogen-contaminated groundwater and metagenomic analysis of degrading bacteria. Environ Pollut 254:113053
Liu X, Šimůnek J, Li L, He J (2012) Identification of sulfate sources in groundwater using isotope analysis and modeling of flood irrigation with waters of different quality in the Jinghuiqu district of China. Environ Earth Sci 69:1589–1600
Lloyd J (1965) The hydrochemistry of the aquifers of north-eastern Jordan. J Hydrol 3:319–330
Ma J, Pan F, He J, Chen L, Fu S, Jia B (2012) Petroleum pollution and evolution of water quality in the Malian River Basin of the Longdong Loess Plateau, Northwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 66:1769–1782
Madeira M, Auxtero E, Sousa E (2003) Cation and anion exchange properties of Andisols from the Azores, Portugal, as determined by the compulsive exchange and the ammonium acetate methods. Geoderma 117:225–241
Newman BD, Fuentes HR, Polzer WL (2010) An evaluation of lithium sorption isotherms and their application to ground-water transport. Groundwater 29:818–824
Plummer LN, Busby JF, Lee RW, Hanshaw BB (1990) Geochemical modeling of the Madison aquifer in parts of Montana, Wyoming, and South Dakota. Water Resour Res 26:1981–2014
Pu J, Yuan D, Zhang C, Zhao H (2013) Hydrogeochemistry and possible sulfate sources in karst groundwater in Chongqing, China. Environ Earth Sci 68:159–168
Rao SM, Sridharan A (1984) Mechanism of sulfate adsorption by kaolinite. Clays Clay Miner 32:414–418
Rosborg I, Kozisek F (2015) Macrominerals at optimum concentrations - protective against diseases. In: Drinking water minerals and mineral balance: importance, health significance, safety precautions, Springer, p 33–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09593-6_3
Runtti H, Tolonen ET, Tuomikoski S, Luukkonen T, Lassi U (2018) How to tackle the stringent sulfate removal requirements in mine water treatment—a review of potential methods. Environ Res 167:207–222
Sabatini DA (2010) Sorption and intraparticle diffusion of fluorescent dyes with consolidated aquifer media. Groundwater 38:651–656
Seyfi S, Azadmehr AR, Gharabaghi M, Maghsoudi A (2015) Usage of Iranian scoria for copper and cadmium removal from aqueous solutions. J Cent South Univ 22:3760–3769
Sincero AP, Sincero GA (2003) Physical-chemical treatment of water and wastewater. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Soucek DJ, Kennedy AJ (2010) Effects of hardness, chloride, and acclimation on the acute toxicity of sulfate to freshwater invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1204–1210
Thomas HC (1944) Heterogeneous ion exchange in a flowing system. J Am Chem Soc 66:1664–1666
Wang H, Zhang Q (2019) Research advances in identifying sulfate contamination sources of water environment by using stable isotopes. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1914
Waters CCfI (1990) GEMS/water data summary 1985–1987. Canada Centre for Inland Waters Burlington, Ontario
Wei C, Hai-Cheng L (2014) Adsorption of sulfate in aqueous solutions by organo-nano-clay: adsorption equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Cent South Univ 21:1974–1981
Willard LL (1979) Chemical equilibria in soils. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester
Yoon YH, Nelson JH (1984) Application of gas adsorption kinetics I. A theoretical model for respirator cartridge service life. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 45:517–524
Zhang Y, Zhang YL, Zhang SY, Song F, Huang JY, Zhang Y, Bai XD (2012) Utilization of scoria as PRB reactive media for the removal of petroleum hydrocarbon from groundwater. Adv Mater Res 535:2457–2461
Zhang S, Lu Y, Lin X, Su X, Zhang Y (2014) Removal of fluoride from groundwater by adsorption onto La (III)-Al (III) loaded scoria adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci 303:1–5
Zhang X, Tong J, Hu BX, Wei W (2017) Adsorption and desorption for dynamics transport of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) in soil column. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:1–10
Zong E, Wei D, Wan H, Zheng S, Xu Z, Zhu D (2013) Adsorptive removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution using zirconia-functionalized graphite oxide. Chem Eng 221:193–203
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2014ZX07201010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XB and ZC processed the data and analyzed the results; TL and SL collected groundwater samples; XB wrote the manuscript; YZ and SL reviewed the manuscript and made helpful suggestions; YZ revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, Z. et al. Application and adsorption characteristics of scoria for removing sulfate from a low-temperature groundwater environment in Longdong area, China. Environ Earth Sci 80, 729 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10053-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10053-6