Abstract
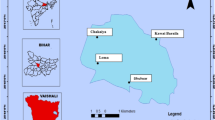
Heavy metal contamination is a significant issue because of its common usage in many anthropogenic processes and subsequent release into environmental systems. There have been very few field studies located near lighters wharfs due to the absence of population and low concentration with comparing high level in residential area and industrial complex. In this study, investigation of metal contamination in shallow marine sediment around a lighters wharf, where small ships are anchored and repaired illegally, was conducted. The contamination levels of heavy metals were measured, enrichment factor (EF) was calculated, and statistical analysis of metal correlation was carried out. High metal contamination was observed in some samples, especially of Zn, Pb, and Cu. Additionally, the EF was more than 5 which is characterized as significant level of concern. Significantly high correlation between most metals may indicate that pollution originates from a commonly occurring source and subsequently accumulates. The possibility of anthropogenic pollution from the repairing of small ships has been implied.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanian T (2012) Heavy metal contamination and risk assessment in the marine environment of Arabian Sea, along the southwest coast of India. Am J Chem 2(4):191–208
Boyd WA, Williams PL (2003) Comparison of the sensitivity of three nematode species to copper and their utility in aquatic and soil toxicity tests. Environ Toxicol Chem Int J 22(11):2768–2774
Chaudri AM, Knight BP, Barbosa-Jefferson VL, Preston S, Paton GI, Killham K, McGrath SP (1999) Determination of acute Zn toxicity in pore water from soils previously treated with sewage sludge using bioluminescence assays. Environ Sci Technol 33(11):1880–1885
Choi M, Park J, Cho D, Jang D, Kim M, Choi J (2015) Tracing metal sources in core sediments of the artificial lake An-Dong, Korea: concentration and metal association. Sci Total Environ 527:384–392
Dafforn KA, Lewis JA, Johnston EL (2011) Antifouling strategies: history and regulation, ecological impacts and mitigation. Mar Pollut Bull 62(3):453–465
Edinger EN, Azmy K, Diegor W, Siregar PR (2008) Heavy metal contamination from gold mining recorded in Porites lobata skeletons, Buyat-Ratototok district, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Mar Pollut Bull 56(9):1553–1569
Eklund B, Johansson L, Ytreberg E (2014) Contamination of a boatyard for maintenance of pleasure boats. J Soils Sediments 14(5):955–967
EPA (2002) Environmental protection agency, United states
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Hwang DW, Ryu SO, Kim SG, Choi OI, Kim SS, Koh BS (2010) Geochemical characteristics of intertidal surface sediments along the southwestern coast of Korea. Korean J Fish Aquat Sci 43(2):146–158
Isakson J, Persson TA, Lindgren ES (2001) Identification and assessment of ship emissions and their effects in the harbour of Göteborg, Sweden. Atmos Environ 35(21):3659–3666
Jeon SK, Kwon MJ, Yang JS, Lee S (2017) Identifying the source of Zn in soils around a Zn smelter using Pb isotope ratios and mineralogical analysis. Sci Total Environ 601:66–72
Jiang X, Lu WX, Zhao HQ, Yang QC, Yang ZP (2014) Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy-metal pollution around coal gangue dump. Nat Hazard 14(6):1599–1610
Kim JG, You SJ, Ahn WS (2008) Evaluation of characteristics of particle composition and pollution of heavy metals for tidal flat sediments in Julpo Bay, Korea. J Korean Soc Mar Environ Saf 14(4):247–256
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Neşer G, Kontas A, Ünsalan D, Uluturhan E, Altay O, Darılmaz E, Yercan F (2012) Heavy metals contamination levels at the Coast of Aliağa (Turkey) ship recycling zone. Mar Pollut Bull 64(4):882–887
Pearson K (1895) Notes on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc R Soc Lond 58:240–242
Salomons W, Förstner U (1984) Sediments and the transport of metals. In: Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 63–98
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39(6):611–627
Tamim U, Khan R, Jolly YN, Fatema K, Das S, Naher K, Hossain SM (2016) Elemental distribution of metals in urban river sediments near an industrial effluent source. Chemosphere 155:509–518
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1995) The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev Geophys 33(2):241–265
Thomas KV, Brooks S (2010) The environmental fate and effects of antifouling paint biocides. Biofouling 26(1):73–88
Turner A (2013) Metal contamination of soils, sediments and dusts in the vicinity of marine leisure boat maintenance facilities. J Soils Sediments 13(6):1052–1056
USPH (1997) Toxicological profile for zinc and lead on CD-ROM. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. U.S. Public Health Service
Valkirs AO, Seligman PF, Haslbeck E, Caso JS (2003) Measurement of copper release rates from antifouling paint under laboratory and in situ conditions: implications for loading estimation to marine water bodies. Mar Pollut Bull 46(6):763–779
Yebra DM, Kiil S, Dam-Johansen K (2004) Antifouling technology—past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog Org Coat 50(2):75–104
Youn ST, Koh YK, Ryu SO (1999) Distribution characteristics of surface sediments and metal elements in Hampyong Bay, the southwestern coast of Korea. Jenviron Sci Int 8(6):677–684
Young DR, Alexander GV, McDermott-Ehrlich D (1979) Vessel-related contamination of southern California harbours by copper and other metals. Mar Pollut Bull 10(2):50–56
Ytreberg E, Karlsson J, Eklund B (2010) Comparison of toxicity and release rates of Cu and Zn from anti-fouling paints leached in natural and artificial brackish seawater. Sci Total Environ 408(12):2459–2466
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, Sk. Assessment of metal contamination in sediments induced by small ships around lighters wharf in Southwest Korea. Environ Earth Sci 80, 627 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09848-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09848-4