Abstract
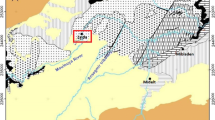
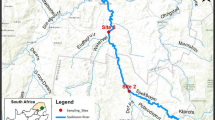
The main electric energy source in Brazil comes from hydroelectric plants, which involve the construction of large water reservoirs. The Brazilian center-west region occupies 25% of the national territory, with the Cerrado (native tropical savanna) as predominant biome. This region has many hydroelectric plants, in addition to agriculture and livestock. It has resulted at sediment inputs containing pesticides and heavy metals into water reservoirs, affecting plants and animals. The aim of this work was to evaluate the heavy metal environmental pollution indices in sediments of a model hydroelectric plant water reservoir located in the center-west region of Brazil. The sediment samples were prepared using acidic digestion in microwave oven for the determination of the metal concentrations by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). The cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), mercury (Hg), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) concentrations in sediments of the model water reservoir were compared with maximum limits stipulated by the Conama Resolution n. 454/2012. Moreover, the geoaccumulation indice (Igeo) and contamination indice (CI) were determined. According to Igeo values, the water reservoir direct influence area was classified from moderately to extremely polluted due to high metal concentrations in the study sediments. From CI values was concluded that the environmental pollution indice varied from moderate to high, corroborating the Igeo classification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Y-J, Kampbell DH (2003) Total, dissolved, and bioavailable metals at Lake Texoma marinas. Environ Pollut 122:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00291-9
Baran A, Mierzwa-Hersztek M, Gondek K et al (2019) The influence of the quantity and quality of sediment organic matter on the potential mobility and toxicity of trace elements in bottom sediment. Environ Geochem Health 41:2893–2910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00359-7
Bicudo C (2009) Limnologia by J G Tundisi and T Matsumura Tundisi. Brazilian J Biol. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1519-69842009000100032
Braga Carvalho de C, Cabral JBP, Lopes SMF et al (2018) Qualidade dos sedimentos em relação à presença de metais pesados no reservatório da usina hidrelétrica de Caçu – GO. Rev Bras Geogr Física. https://doi.org/10.26848/rbgf.v11.3.p959-972
Cabral JBP, Fernandes LA, Becegato VA, da Silva SA (2010) Caracterização sedimentológica dos modelos deposicionais do reservatório de Cachoeira Dourada-GO/MG. Geosul. https://doi.org/10.5007/2177-5230.2010v26n50p175
Campos JA, Aires URV, Da Silva DD, Calijuri ML (2019) Environmental fragility and vegetation cover dynamics in the Lapa Grande state park MG, Brazil. Acad Bras Cienc. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201920170940
Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines—Copper (2001) Canadian environmental quality guidelines Canadian council of ministers of the environment: copper. Can Environ Qual Guidel 1–5
Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines—Lead (1999) Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life—lead. Can Environ Qual Guidel 5
Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines—Zinc (1999) Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life—zinc
Cardoso-Silva S, Da Silva DCVR, Lage F et al (2016) Metals in sediments: bioavailability and toxicity in a tropical reservoir used for public water supply. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5276-5
Cetesb (2016) Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo. In: Qual. das Águas Inter. no Estado São Paulo | Apêndice D - Índices Qual. das Águas
Chan S, Gerson B, Subramaniam S (1998) The role of copper, molybdenum, selenium, and zinc in nutrition and health. Clin Lab Med
Conama CN do MA (2012) Resolução no 454, de 01 de novembro de 2012
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (2013) Resolução No 460, de 30 de dezembro de 2013. Conama
Environment Agency (2009) Contaminants in soil : updated collation of toxicological data and intake values for humans—nickel
Estigoni MV, Miranda RB, Mauad FF et al (2017) Hydropower Reservoir Sediment and Water Quality Assessment. Manag Environ Qual 28:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-07-2015-0153
Eyherabide M, Barbieri P (2014) Comparación de métodos para determinar carbono orgánico en suelo. 32:13–19
Frascareli D, Cardoso-Silva S, de Oliveira Soares-Silva Mizael J et al (2018) Spatial distribution, bioavailability, and toxicity of metals in surface sediments of tropical reservoirs, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6515-8
Froehner S, Zeni J (2009) Characterization of granulometric and chemical composition of sediments of Barigui river samples and their capacity to retain polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0020-1
Hahn J, Opp C, Ganzenmüller R et al (2019) Catchment soils as a factor of trace metal accumulation in sediments of the reservoir Klingenberg (eastern Ore Mountains, Germany). J Environ Sci (china). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.002
He Y, Men B, Yang X et al (2017) Investigation of heavy metals release from sediment with bioturbation/bioirrigation. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.177
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, AL-Mamun MH, Islam SMA (2019) Sources and ecological risks of heavy metals in soils under different land uses in Bangladesh. Pedosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60394-1
Kijowska-Strugała M, Wiejaczka Ł, Kozłowski R, Lekach J (2020) Metals content in sediments of ephemeral streams with small reservoirs (the Negev desert). Int J Sediment Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2019.12.003
Kittrick JA (1971) Handbook of geochemistry. Soil Sci Soc Am J. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1971.03615995003500030012x
Kodama H, Fujisawa C, Bhadhprasit W (2012) Inherited copper transport disorders: biochemical mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Drug Metab. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920012799320455
Lee PK, Kang MJ, Yu S et al (2017) Enrichment and geochemical mobility of heavy metals in bottom sediment of the Hoedong reservoir, Korea and their source apportionment. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.124
Li Y, Zhou H, Gao B, Xu D (2021) Science of the total environment improved enrichment factor model for correcting and predicting the evaluation of heavy metals in sediments. Sci Total Environ 755:142437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142437
Lima RMF, da Luz JAM (2001) Análise granulométrica por técnicas que se baseiam na sedimentação gravitacional: Lei de Stokes. Rev Esc Minas 54:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0370-44672001000200014
Lin L, Li C, Yang W et al (2020) Spatial variations and periodic changes in heavy metals in surface water and sediments of the three gorges reservoir, China. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124837
Lopes B, Ramos IC, Ribeiro G et al (2014) Biostatistics: fundamental concepts and practical applications. Rev Bras Oftalmol 73:16–22. https://doi.org/10.5935/0034-7280.20140004
Malavolta E (2006) Manual de nutrição mineral de plantas.
Martin S, Griswold W (2009) Human health effects of heavy metals: briefs for citizens. Environ Sci Technol
Martins RO, Hoff Brait CH, dos Santos FF (2018) Avaliação do teor de metais pesados e de parâmetros físico-químicos da água e sedimento do lago bonsucesso, Jataí – GO. Geoambiente on-Line. https://doi.org/10.5216/revgeoamb.v0i29.51072
Nogueira PF, Pereira Cabral JB, Oliveira SF, Rocha IR da (2015) Eutrofização no reservatório da uhe foz do rio claro (GO). Geogr Dep Univ Sao Paulo. https://doi.org/10.11606/rdg.v30i0.90090
Oladele AH, Digun-Aweto O, Sunday YA (2019) Relationship between cadmium, nickel relationship between cadmium, nickel and chromium contents in Oreochromis niloticus, Macrobrachium vollenhovenii, sediments and water of Lake Asejire. Nigeria 11:15–22. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wjfms.2019.15.22
Paoliello MMB, De Capitani EM, Da Cunha FG et al (2002) Exposure of children to lead and cadmium from a mining area of Brazil. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1006/enrs.2001.4311
Paulino AT, Guilherme MR, Reis AV et al (2007) Capacity of adsorption of Pb2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solutions by chitosan produced from silkworm chrysalides in different degrees of deacetylation. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.059
Paulino AT, Tessari JA, Nogami EM et al (2005) Lipid increase induced by lead accumulation in tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-005-0716-x
Pompêo M, Padial PR, Mariani CF et al (2013) Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a case study of coastal water bodies from the Rio de Janeiro State, southeastern Brazi. Geochim Bras 27:104–119. https://doi.org/10.5327/z0102-9800201300020003
Prasad AS (2008) Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells. Mol Med.
Ribeiro ES, Pereira MP, de Castro EM et al (2015) Relações da anatomia radicular na absorção, no acúmulo e na tolerância ao chumbo em Echinodorus grandiflorus. Rev Bras Eng Agrícola e Ambient. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v19n6p605-612
Rocha H, Cabral J, Braga C (2014) Avaliação Espaço-Temporal das Águas dos Afluentes do Reservatório da UHE Barra dos Coqueiros/Goiás. Rev Bras Recur Hídricos. https://doi.org/10.21168/rbrh.v19n1.p131-142
Rząsa S, Owczarzak W (2013) Methods for the granulometric analysis of soil for science and practice. Polish J Soil Sci 46:1–50. https://doi.org/10.17951/pjss.2013.46.1.1
Rzetala M, Babicheva VA, Rzetala MA (2019) Composition and physico-chemical properties of bottom sediments in the southern part of the Bratsk Reservoir (Russia). Sci Rep 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49228-4
Santos HG et al (2018) Sistema brasileiro de classificação de solos
Segat JC, Conte RA, Barreta DA et al (2021) Effects of sheep manure in agricultural soils on the behavior of Folsomia Candida and initial growth and development of Avena Sativa. Braz J Biol 81:1030–1035
Song Z, Song G, Tang W et al (2021) Molybdenum contamination dispersion from mining site to a reservoir. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111631
Souza V De, Konrad O, Gonçalves Junior AC (2016) Contaminação por chumbo, riscos, limites legais e alternativas de remediação. Veredas do Direito Direito Ambient e Desenvolv Sustentável. https://doi.org/10.18623/rvd.v13i25.643
Spörl C, Ross JLS (2004) Análise comparativa da fragilidade ambiental com aplicação de três modelos. GEOUSP - Espaço e Tempo
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2007) Method 3051: microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils
Vareda JP, Valente AJM, Durães L (2019) Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: a review. J Environ Manage 246:101–118
Vidmar J, Zuliani T, Novak P et al (2017) Elements in water, suspended particulate matter and sediments of the Sava River. J Soils Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1512-4
Vuille M, Francou B, Wagnon P et al (2008) Climate change and tropical Andean glaciers: past, present and future. Earth-Science Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.04.002
Wolf M, Baretta D, Becegato VA et al (2017) Copper/zinc bioaccumulation and the effect of phytotoxicity on the growth of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in non-contaminated, metal-contaminated and swine manure-enriched soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3345-1
Wolf M, Paulino AT (2020) Phytotoxicity increase induced by zinc accumulation in Cichorium intybus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 105:405–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02960-4
Xu X, Cao Z, Zhang Z et al (2016) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Mar Pollut Bull 110:596–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.05.079
Yu Z, Liu E, Lin Q et al (2021) Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in lake sediment by combining total concentration and chemical. Environ Pollut 269:116212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116212
Zahra A, Hashmi MZ, Malik RN, Ahmed Z (2014) Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah-feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake reservoir, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.017
Zhong WS, Ren T, Zhao LJ (2016) Determination of Pb (lead), Cd (cadmium), Cr (chromium), Cu (copper), and Ni (nickel) in Chinese tea with high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Food Drug Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2015.04.010
Zhu L, Liu J, Xu S, Xie Z (2017) Deposition behavior, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in reservoir sediments of Northeast China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.039
Zhu L, Wang T, Liu J et al (2019) Metal distribution in sediments of a drinking water reservoir: influence of reservoir morphometry and hydrodynamics. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04424-7
Acknowledgements
JBPC thanks the Programa Nacional de Cooperação Acadêmica (PROCAD/CAPES—Brazil; Process 88881.068465/2014-01) for financial support. ATP thanks the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC—Brazil) for financial support (Grant number: 2019/TR672) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq—Brazil) for the research productivity scholarship (Grant number 312467/2019-2). This study was also funded in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES—Brazil)—Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabral, J.B.P., Oliveira, S.F., dos Santos, F.F. et al. Potentially toxic metal environmental pollution in sediments of a model hydroelectric plant water reservoir in Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 80, 506 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09808-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09808-y