Abstract
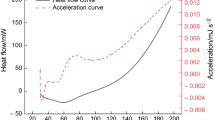
When coal and crude oil are associated, the immersion of crude oil affects the microstructure changes in coal oxidation process. In this work, thermogravimetric and in situ infrared spectroscopy experiments were used to study the oxidation characteristics and active functional groups evolution of oil-immersed coal. Results showed that the crude oil in coal slows down the oxidation process of coal and considerably affects weight gain phase due to O absorption. Considering crude oil O consumption and O attack on the active group methylene, the change law of methylene (2923 cm−1) with temperature can be used to represent the evolution of Aliphatic Functional Groups when the oil content is less than 10%. The characteristic demarcation point of the evolution rule of the active groups of coal with different oil ratios is 270 °C. The aromatic C = C of raw coal and 25% oil content coal samples satisfied the quadratic curve change relationship.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Déchaux JC, Lucquin M (1971) Inhibition by nitrogen dioxide of the slow oxidation of butane at low temperatures. Symp Combust 13(1):205–216
Dong QN, Chen XY (1997) In-situ study of low temperature oxidation of lignite by infrared emission spectroscopy. J Fuel Chem Technol 25(4):333–338
Gethner JS (1985) Thermal and oxidation chemistry of coal at low temperatures. Fuel 64(10):1443–1446
Guan RL, Hong Z (2007) Spectroscopy study of heavy oil components in shengli oilfield. Spectrosc Spectral Analy 27(11):2270–2274
Gundogar AS, Kok MV (2014) Thermal characterization, combustion and kinetics of different origin crude oils. Fuel 123:59–65
Guo AJ, Ren ZH, Tian LY et al (2007) Study on the light thermal conversion of heavy oil molecules by infrared spectrometry. J Fuel Chem Technol 35(02):169–175
He P, Wang FY, Tang XY et al (1994) Changes in the properties and chemical structure of Cheli coal during artificial oxidation. J Fuel Chem Technol 22(2):203–208
Jaroslav Č (1996) Structural dependence of C-H bond adsorptivities and consequences for FTIR analysis of coal. Fuel 75(11):1301–1306
Jing ZH, Sandra R, Ekaterina S et al (2019) Use of FTIR, XPS, NMR to characterize oxidative effects of NaClO on coal molecular structures. Int J Coal Geol 201:1–13
Liu SQ, Sang SX, Wang T, Du Y, Jia JL, Fang H (2018) FangThe effects of CO2 on organic groups in bituminous coal and high-rank coal via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Energy Explor Exploit 36(6):1566–1592
MacPhee JA, Charland JP, Giroux L (2006) Application of TG–FTIR to the determination of organic oxygen and its speciation in the Argonne premium coal samples. Fuel Process Technol 87:335–341
Peterson HI (2006) The petroleum generation potential and effective oil window of humic coals related to coal composition and age. Int J Coal Geol 67(4):221–248
Puente GDL, Iglesias MJ, Fuente E et al (1998) Changes in the structure of coals of different rank due to oxidation—effects on pyrolysis behaviour. J Anal Appl Pyrol 47(47):33–42
Shi T, Wang XF, Deng J et al (2005) The mechanism at the initial stage of room-temperature oxidation of coal. Combust Flame 140(4):332–345
Volodymyr M (2017) The Lambert-Beer law in time domain form and its application. Appl Radiat Isot 128:1–5
Wang H, Dlugogorski BZ, Kennedy EM (2003) Coal oxidation at low temperatures: oxygen consumption, oxidation products, reaction mechanism and kinetic modelling. Prog Energy Combust Sci 29(6):487–513
Wang YY, Wu JM, Wang JF et al (2016) In-situ infrared experimental study of CO formation mechanism during coal oxidation. J China Coal Soc 41(2):451–457
Wu D, Liu GJ, Sun RY, Fan X (2013) Investigation of structural characteristics of thermally metamorphosed coal by FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Energy Fuel 27(10):5823–5830
Xin HH, Wang DM, Qi XY et al (2013) Distribution and quantum chemical analysis of lignite surface functional groups. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing 35(2):135–139
Yan RG, Qian GY (1995) Molecular structure of coal and gas product of coal spontaneous combustion. J China Coal Soc 20(a01):58–64
Yan XZ, Jing Q, Yin YS et al (2016) Effect of functional groups in lignite on its combustion characteristics. Coal Sci Technol 44(4):169–174
Zhai X, Ge H, Wang T, Chi-MinShu JL (2020) Effect of water immersion on active functional groups and characteristic temperatures of bituminous coal. Energy 205(15):118076
Zhan YG, Yan L, Liu YL et al (2013) Low temperature oxidation experiments and kinetics research of light crude oil in Honghe Oilfield. Oil Gas Reservoir Evaluat Develop 3(06):43–47
Zhang X (2015) Study on the characteristics of oxidation reaction of ordinary heavy oil [D]. South China Univ Technol. 50(4):1105–1113
Zhang GS, Xie YM, Gu JM (2003) Infrared spectral analysis of microstructure change during the coal spontaneous oxidation. J China Coal Soc 28(5):473–476
Zhang YN, Chen L, Zhao JY, Deng J, Yang H (2019a) Evaluation of the spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal of different metamorphic degrees based on a temperature-programmed oil bath experimental system. J Loss Prev Process Ind 60:17–27
Zhang Y, Yang C, Li Y et al (2019b) Ultrasonic extraction and oxidation characteristics of functional groups during coal spontaneous combustion. Fuel 242:287–294
Zhang YN, Liu CH, Song JJ et al (2020) Study on transfer law of main functional groups in low temperature oxidation of long flame coal. Coal Science and Technology 48(3):188–196
Zhao JY, Deng J, Chen L, Wang T, Song JJ, Zhang YN et al (2019a) Correlation analysis of the functional groups and exothermic characteristics of bituminous coal molecules during high-temperature oxidation. Energy 181:136–147
Zhao S, Pu W, Sun B et al (2019b) Comparative evaluation on the thermal behaviors and kinetics of combustion of heavy crude oil and its SARA fractions. Fuel 239:117–125
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51874007, 51574009), National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0807900) and the University Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province (KJ2019A0133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruxiang, Q., Liang, Z., Yu, G. et al. Oxidation characteristics and active group evolution of oil-immersed coal. Environ Earth Sci 80, 433 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09671-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09671-x