Abstract
Flux tower is a link between ground measurements and large-scale remote sensing data. A large number of remote sensing model methods are used to estimate the regional scale Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) based on this principle. In this study, Vegetation Photosynthesis Model (VPM) and Vegetation Indexes (VIs) were used to estimate the GPP based on Earth Observing 1 (EO-1) Hyperion hyperspectral data in Changbai Mountain temperate forest. Result shows that the two different types of remote sensing input data of the VPM has similar result at the same level. For different time scope, 3-day flux data can better match remote sensing data. For different footprint, the effect of 500, 1000, 1500 m almost no difference in our area. Among the comparison of the four types of VIs, Bands Ratio (BR), Bands Subtraction (BS) and Bands Difference (BD) have a higher correlation significant than Single Band (SB). 457 nm is the optimum band for SB. The best bands combination of BR, BS, and BD mainly focus on near infrared region. Our research shows that for VPM, and other Light Use Efficiency (LUE) remote sensing model, the difference is not significant between multispectral data and hyperspectral data. At the comparison of VPM and VIs, although the estimation of former is more accurate, the latter is more convenient for that the establishment of VIs just need several bands of remote sensing data. Our findings will help to improve future research on GPP estimation based on hyperspectral observations, which is being more important with increasing availability of hyperspectral satellite data products.

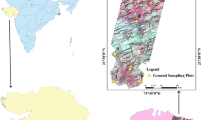
taken from the flux tower on September 2019




Similar content being viewed by others

Availability of data and material
Can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Anand A, Pandey PC, Petropoulos GP, Pavlides A, Srivastava PK, Sharma JK, Malhi RKM (2020) Use of Hyperion for mangrove forest carbon stock assessment in Bhitarkanika forest reserve: a contribution towards blue carbon initiative. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040597
Anthoni PM, Law BE, Unsworth MH (1999) Carbon and water vapor exchange of an open-canopied ponderosa pine ecosystem. Agric For Meteorol 95:151–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1923(99)00029-5
Baldocchi D (2008) Breathing of the terrestrial biosphere: lessons learned from a global network of carbon dioxide flux measurement systems. Aust J Bot 56:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1071/bt07151
Bar-On YM, Phillips R, Milo R (2018) The biomass distribution on Earth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:6506–6511. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1711842115
Benavides R, Roig S, Osoro K (2009) Potential productivity of forested areas based on a biophysical model. A case study of a mountainous region in northern Spain. Ann For Sci. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest/2008080
Black TA et al (1996) Annual cycles of water vapour and carbon dioxide fluxes in and above a boreal aspen forest. Glob Change Biol 2:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.1996.tb00074.x
Campbell PKE et al (2013) EO-1 Hyperion reflectance time series at calibration and validation sites: stability and sensitivity to seasonal dynamics. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 6:276–290. https://doi.org/10.1109/jstars.2013.2246139
Chen J, Zhang H, Liu Z, Che M, Chen B (2014) Evaluating parameter adjustment in the MODIS gross primary production algorithm based on eddy covariance tower measurements. Remote Sens 6:3321–3348. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6043321
Cheng Y-B, Middleton EM, Hilker T, Coops NC, Black TA, Krishnan P (2009) Dynamics of spectral bio-indicators and their correlations with light use efficiency using directional observations at a Douglas-fir forest. Meas Sci Technol 20. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/20/9/095107
Cook BD et al (2009) Using LiDAR and quickbird data to model plant production and quantify uncertainties associated with wetland detection and land cover generalizations. Remote Sens Environ 113:2366–2379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2009.06.017
Dhumal RK, Vibhute AD, Nagne AD, Kale KV, Mehrotra SC (2017) Performance analysis of spectral features based on narrowband vegetation indices for cotton and maize crops by EO-1 Hyperion dataset. In: Behera HS, Mohapatra DP (eds) Computational intelligence in data mining, Cidm 2016, vol 556. Advances in intelligent systems and computing, pp 581–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3874-7_55
Dong T, Meng J, Wu B (2012) overview on methods of deriving fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation(FPAR) using remote sensing. Acta Ecol Sin 32:7190–7201
DuBois S et al (2018) Using imaging spectroscopy to detect variation in terrestrial ecosystem productivity across a water-stressed landscape. Ecol Appl 28:1313–1324. https://doi.org/10.1002/eap.1733
Finnigan J (2004) The footprint concept in complex terrain. Agric For Meteorol 127:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2004.07.008
Franks S et al (2017) EO-1 data quality and sensor stability with changing orbital precession at the end of a 16 year mission. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050412
Goulden ML, Daube BC, Fan SM, Sutton DJ, Bazzaz A, Munger JW, Wofsy SC (1997) Physiological responses of a black spruce forest to weather. J Geophys Res-Atmos 102:28987–28996. https://doi.org/10.1029/97jd01111
Guan D-X, Wu J-B, Zhao X-S, Han S-J, Yu G-R, Sun X-M, Jin C-J (2006) CO2 fluxes over an old, temperate mixed forest in northeastern China. Agric For Meteorol 137:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.02.003
Horst TW (1999) The footprint for estimation of atmosphere-surface exchange fluxes by profile techniques. Bound-Layer Meteorol 90:171–188. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1001774726067
Hosseinjani Zadeh M, Tangestani MH, Velasco Roldan F, Yusta I (2014) Sub-pixel mineral mapping of a porphyry copper belt using EO-1 Hyperion data. Adv Space Res 53:440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2013.11.029
Houborg R, McCabe MF, Angel Y, Middleton EM, IEEE (2017) Time series from Hyperion to track productivity in pivot agriculture in Saudi Arabia. In: 2017 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. IEEE international symposium on geoscience and remote sensing IGARSS, pp 3047–3050
Hsieh CI, Katul G, Chi T (2000) An approximate analytical model for footprint estimation of scaler fluxes in thermally stratified atmospheric flows. Adv Water Resour 23:765–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0309-1708(99)00042-1
Huang X, Xiao J, Ma M (2019) Evaluating the performance of satellite-derived vegetation indices for estimating gross primary productivity using FLUXNET observations across the globe remote sensing, vol 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151823
Huemmrich KF, Campbell P, Landis D, Middleton E (2019) Developing a common globally applicable method for optical remote sensing of ecosystem light use efficiency. Remote Sens Environ 230:111190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.05.009
Huete AR, Liu HQ, Batchily K, vanLeeuwen W (1997) A comparison of vegetation indices global set of TM images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens Environ 59:440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(96)00112-5
Jiang Y, Zhang J, Xu X, Dong Z (2013) A GPP assimilation model for the southeastern Tibetan Plateau based on CO2 eddy covariance flux tower and remote sensing data. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf 23
Johnston C, Buongiorno J, Nepal P, Prestemon JP (2019) From source to sink: past changes and model projections of carbon sequestration in the global forest sector. J For Econ 34:47–72. https://doi.org/10.1561/112.00000442
Khan MJ, Khan HS, Yousaf A, Khurshid K, Abbas A (2018) Modern trends in hyperspectral image analysis: a review. IEEE Access 6:14118–14129. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2812999
Kong B, He B, Yu H, Liu Y (2017) An integrated field and hyperspectral remote sensing method for the estimation of pigments content of Stipa Purpurea in Shenzha. Tibet Math Probl Eng 2017:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4787054
Koptev SV, Tret'yakov SV, Bogdanov AP, Il'intsev AS, Demidenko SA (2017) Forest inventory norms of alder stands by the relascopic circular plot method. Lesnoy Zhurnal For J 5:53–63. https://doi.org/10.17238/issn0536-1036.2017.5.53
Kyparissis A, Markos N, Stagakis S, Levizou E, Sykioti O (2007) Ecosystem productivity and dynamics issued from multispectral and hyperspectral satellite imagery. In: Neale CMU, Owe M, Durso G (eds) Remote sensing for agriculture, ecosystems, and hydrology IX, vol 6742. Proceedings of SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.737688
Liu Z, Wu C, Peng D, Wang S, Gonsamo A, Fang B, Yuan W (2017) Improved modeling of gross primary production from a better representation of photosynthetic components in vegetation canopy. Agric For Meteorol 233:222–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.12.001
LP DAAC-MOD09A1 (2021). https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod09a1v006/
Monteith JL (1972) Solar-radiation and productivity in tropical ecosystems. J Appl Ecol 9:747–766. https://doi.org/10.2307/2401901
Peng Y, Gitelson AA (2012) Remote estimation of gross primary productivity in soybean and maize based on total crop chlorophyll content. Remote Sens Environ 117:440–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.10.021
Porcar-Castell A et al (2015) EUROSPEC: at the interface between remote-sensing and ecosystem CO2 flux measurements. Eur Biogeosci 12:6103–6124. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-12-6103-2015
Potter CS, Randerson JT, Field CB, Matson PA, Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Klooster SA (1993) Terrestrial ecosystem production—a process model-based on global satellite and surface data. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 7:811–841. https://doi.org/10.1029/93gb02725
Running SW, Baldocchi DD, Turner DP, Gower ST, Bakwin PS, Hibbard KA (1999) A global terrestrial monitoring network integrating tower fluxes, flask sampling, ecosystem modeling and EOS satellite data. Remote Sens Environ 70:108–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(99)00061-9
Soukhovolsky VG, Ivanova JD (2013) Estimation of forest-stand net primary productivity using fraction phytomass distribution model. Contemp Probl Ecol 6:700–707. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1995425513070111
Suryoprayogo H, Ramdani F, Utaminingrum F (2017) Implementation of Landsat 7 ETM+ principal polar spectral indices based on EO-1 Hyperion wavebands selection. In: 2017 international symposium on geoinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1109/isyg.2017.8280664
Talbot J et al (2014) Methods to estimate aboveground wood productivity from long-term forest inventory plots. For Ecol Manag 320:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2014.02.021
Wofsy SC et al (1993) Net exchange of CO2 in a midlatitude forest. Science 260:1314–1317. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.260.5112.1314
Wu B, Zeng Y, Huang J (2004) Overview of LAI/FPAR retrieval from remotely sensed data. Adv Earth Sci 19:585–590
Wu JB, Xiao XM, Guan DX, Shi TT, Jin CJ, Han SJ (2009) Estimation of the gross primary production of an old-growth temperate mixed forest using eddy covariance and remote sensing. Int J Remote Sens 30:463–479. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160802372143
Wu JB, Zhou XY, Wang AZ, Yuan FH (2015) Comparative measurements of water vapor fluxes over a tall forest using open- and closed-path eddy covariance system. Atmos Meas Tech 8:4123–4131. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-8-4123-2015
Xiao XM, Hollinger D, Aber J, Goltz M, Davidson EA, Zhang QY, Moore B (2004) Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in an evergreen needleleaf forest. Remote Sens Environ 89:519–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.11.008
Xiao J et al (2019) Remote sensing of the terrestrial carbon cycle: a review of advances over 50 years. Remote Sens Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111383
Yang H et al (2020) Comparison of forest above-ground biomass from dynamic global vegetation models with spatially explicit remotely sensed observation-based estimates. Glob Change Biol. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15117
Yu Q et al (2014) Narrowband bio-indicator monitoring of temperate forest carbon fluxes in Northeastern China. Remote Sens 6:8986–9013. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6098986
Yuan J, Niu Z, Fu W (2007) Model simulation for sensitivity of hyperspectral indices to LAI, leaf chlorophyll and internal structure parameter. In: Ju W, Zhao S (eds) Geoinformatics 2007: remotely sensed data and information, Pts 1 and 2, vol 6752. Proceedings of SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.760656
Zarco-Tejada PJ, Morales A, Testi L, Villalobos FJ (2013) Spatio-temporal patterns of chlorophyll fluorescence and physiological and structural indices acquired from hyperspectral imagery as compared with carbon fluxes measured with eddy covariance. Remote Sens Environ 133:102–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2013.02.003
Zhang F, Zhou G (2017) Deriving a light use efficiency estimation algorithm using in situ hyperspectral and eddy covariance measurements for a maize canopy in Northeast China. Ecol Evolut 7:4735–4744. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.3051
Zhang Q et al (2016) Integrating chlorophyll fAPAR and nadir photochemical reflectance index from EO-1/Hyperion to predict cornfield daily gross primary production. Remote Sens Environ 186:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.08.026
Zhao X, Guan D, Wu J, Jin C, Han S (2005) Distribution of footprint and flux source area of the mixed forest of broad-leaved and Korean pine in Changbai Mountain. J Beijing For Univ 27:17–23
Zhao L, Liu Z, Xu S, He X, Ni Z, Zhao H, Ren S (2018) Retrieving the diurnal FPAR of a maize canopy from the jointing stage to the tasseling stage with vegetation indices under different water stresses and light conditions. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113965
Zhou X, Xin Q (2019) Improving satellite-based modelling of gross primary production in deciduous broadleaf forests by accounting for seasonality in light use efficiency. Int J Remote Sens 40:931–955. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1519285
Zhou Y, Zhang L, Xiao J, Chen S, Kato T, Zhou G (2014) A comparison of satellite-derived vegetation indices for approximating gross primary productivity of grasslands rangeland. Ecol Manag 67:9–18. https://doi.org/10.2111/rem-d-13-00059.1
Acknowledgements
The project was funded by the National Key Research and Development Project (2019YFC0409102) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870625, 31770755, 31971728).
Funding
The National Key Research and Development Project (2019YFC0409102) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870625, 31770755, 31971728).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, YZ, DG and JW; Data curation, YZ; Formal analysis, YZ; Funding acquisition, JW; Methodology, YZ; Supervision, JW; Visualization, YZ; Writing—original draft, YZ; Writing—review & editing, AW, FY, DG and JW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, A., Yuan, F. et al. The application of EO-1 Hyperion hyperspectral data to estimate the GPP of temperate forest in Changbai Mountain, Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 80, 353 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09639-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09639-x