Abstract
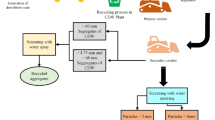
Due to urban development worldwide, disposing sewage sludge (SS) has become a major concern for many countries. SS produced from the New Waste Water Treatment Plant (NWWTP) in Nicosia has not been used for soil application as it was planned since late 2013 due to absence of legislations regarding this route. This issue has been and still a major concern for of Nicosia Turkish Municipality and its society for many years. This study investigates the potential use of SS as construction material by producing an artificial lightweight aggregate (ALWA) and cement replacement material. Fine dry sludge (FDS) and sewage sludge ash (SSA) were used as raw materials for ALWA production. FDS was incinerated at 850 °C for 1 and 2 h to produce SSA1 and SSA2, respectively. Both SSA1 and SSA2 were mixed separately with FDS in different proportions and incinerated at 1100 °C to produce lightweight aggregate AG1 and AG2, respectively. Potential use of SSA1 and SSA2 as cement replacement materials was assessed by measuring the Pozzolanic activity of both ashes throughout physical and chemical tests. It was found out that increasing amount of FDS reduced specific gravity of AG1 and AG2, while increasing amount SSA in the mix improved the surface texture and increased the specific gravity of both AG1 and AG2. Results also indicated that both SSA1 and SSA2 have Pozzolanic properties based in all tests performed. Therefore, using sewage sludge produced from the NWWTP in Nicosia as a sustainable construction material is potential and this could extend the disposal route of the sludge and resolve the accumulation problem in Nicosia.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreoli CV, Von SM, Fernandes F, Ronteltap M (2007) Sludge treatment and disposal. IWA Publishing, London
ASTM C125 (2013) Standard Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0125-13
ASTM C127 (2007) Standard Test Method for Density, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), and Absorption of Coarse Aggregate. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0127-07
ASTM C311/C311M (2016) Standard Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Fly Ash or Natural Pozzolans for Use in Portland-Cement Concrete. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0311_C0311M-16
ASTM C618 (2015) Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.https://doi.org/10.1520/C0618-15
Behbahaninia A, Mirbagheri S, Nouri J (2010) Effects of sludge from wastewater treatment plants on heavy metals transport to soils and groundwater. J Environ Heal Sci Eng 7:401–406
Bengtsson M, Tillman A-M (2004) Actors and interpretations in an environmental controversy: the Swedish debate on sewage sludge use in agriculture. Resour Conserv Recycl 42:65–82
Bhatty JI, Reid KJ (1989) Lightweight aggregates from incinerated sludge ash. Waste Manag Res 7:363–376
Blair S, Rossmiller B, Abu-Awwad A, Meserlian M (2012) Bi-communal reuse of treated effluent in Cyprus. J Water Reuse Desalin 2:218–226
Bresters AR, Coulomb I, Deak B et al (1998) Sludge Treatment and disposal: management approaches and experiences. In: Office for official publications of the European communities, European Environment Agency
BS EN 196-2 (2005) Methods of Testing Cement-Part 2: Chemical Analysis of Cement. British Standards Institution, London, UK
BS EN 196-5 (2011) Methods of Testing Cement-Part 5: Pozzolanicity Test for Pozzolanic Cements. British Standards Institution, London, UK
Celik T, Bayasi Z (1995) Comparison of clay-blended sludge aggregate with normal weight crushed rock and lightweight shale. Concr Int 17:63–65
Chen M, Blanc D, Gautier M et al (2013) Environmental and technical assessments of the potential utilization of sewage sludge ashes (SSAs) as secondary raw materials in construction. Waste Manag 33:1268–1275
Chen Z, Li JS, Poon CS (2018) Combined use of sewage sludge ash and recycled glass cullet for the production of concrete blocks. J Clean Prod 171:1447–1459
Chen Z, Poon CS (2017) Comparative studies on the effects of sewage sludge ash and fly ash on cement hydration and properties of cement mortars. Constr Build Mater 154:791–803
Chiou J, Wang K-S, Chen C-H, Lin Y-T (2006) Lightweight aggregate made from sewage sludge and incinerated ash. Waste Manag 26:1453–1461
Cieślik BM, Namieśnik J, Konieczka P (2015) Review of sewage sludge management: standards, regulations and analytical methods. J Clean Prod 90:1–15
Cyr M, Coutand M, Clastres P (2007) Technological and environmental behavior of sewage sludge ash (SSA) in cement-based materials. Cem Concr Res 37:1278–1289
de Luxán MP, Madruga F, Saavedra J (1989) Rapid evaluation of pozzolanic activity of natural products by conductivity measurement. Cem Concr Res 19:63–68
Donatello S, Freeman-Pask A, Tyrer M, Cheeseman CR (2010a) Effect of milling and acid washing on the pozzolanic activity of incinerator sewage sludge ash. Cem Concr Compos 32:54–61
Donatello S, Tyrer M, Cheeseman CR (2010b) Comparison of test methods to assess pozzolanic activity. Cem Concr Compos 32:121–127
Donatello S, Tyrer M, Cheeseman CR (2010c) EU landfill waste acceptance criteria and EU Hazardous Waste Directive compliance testing of incinerated sewage sludge ash. Waste Manag 30:63–71
Elkins BV, Wilson GE, Gersberg RM (1985) Complete reclamation of wastewater and sludge. Water Sci Technol 17:1453–1454
European Commission-DG Environment (2001a) Disposal and recycling routes for sewage sludge. In: Part 1: sludge use acceptance report. Luxembourg
European Commission-DG Environment (2001b) Disposal and recycling routes for sewage sludge. In: Part 2: regulatory report. Luxembourg
European Commission-DG Environment (2001c) Disposal and recycling routes for sewage sludge. In: Part 3: scientific and technical report. Luxembourg
Fytili D, Zabaniotou A (2008) Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 12:116–140
Garcés P, Carrión MP, García-Alcocel E et al (2008) Mechanical and physical properties of cement blended with sewage sludge ash. Waste Manag 28:2495–2502
Inglezakis VJ, Zorpas AA, Karagiannidis A et al (2014) European Union legislation on sewage sludge management. Fresenius Environ Bull 23:635–639
Kappel A, Ottosen LM, Kirkelund GM (2017) Colour, compressive strength and workability of mortars with an iron rich sewage sludge ash. Constr Build Mater 157:1199–1205
Kosmatka SH, Kerkhoff B, Panarese WC (2011) Design and control of concrete mixtures: the guide to applications, methods and materials, 15th edn. Portland Cement Association, Skokie, Illinois, USA
Laner D, Fellner J, Brunner PH (2009) Flooding of municipal solid waste landfills—an environmental hazard? Sci Total Environ 407:3674–3680
Lynn CJ, Dhir RK, Ghataora GS, West RP (2015) Sewage sludge ash characteristics and potential for use in concrete. Constr Build Mater 98:767–779
Naamane S, Rais Z, Taleb M (2016) The effectiveness of the incineration of sewage sludge on the evolution of physicochemical and mechanical properties of Portland cement. Constr Build Mater 112:783–789
Nair DG, Fraaij A, Klaassen AAK, Kentgens APM (2008) A structural investigation relating to the pozzolanic activity of rice husk ashes. Cem Concr Res 38:861–869
Newman J, Choo BS (2003) Advanced concrete technology 1: constituent materials. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Nourani V, Elkiran G, Abba SI (2018) Wastewater treatment plant performance analysis using artificial intelligence–an ensemble approach. Water Sci Technol 78:2064–2076
Pan S-C, Tseng D-H, Lee C-C, Lee C (2003) Influence of the fineness of sewage sludge ash on the mortar properties. Cem Concr Res 33:1749–1754
Pérez-Carrión M, Baeza-Brotons F, Payá J et al (2014) Potential use of sewage sludge ash (SSA) as a cement replacement in precast concrete blocks. Mater Constr 64:e002
Piasta W, Lukawska M (2016) The effect of sewage sludge ash on properties of cement composites. Procedia Eng 161:1018–1024
Raask E, Bhaskar MC (1975) Pozzolanic activity of pulverized fuel ash. Cem Concr Res 5:363–375
Ramezanianpour AA (2014) Cement replacement materials (properties, durability, sustainability), 1st edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Seco A, Ramirez F, Miqueleiz L et al (2012) Types of waste for the production of pozzolanic materials–a review. Ind waste 2012:141
Sewerage Department of Nicosia Turkish Municipality (2019) Problems Related to Disposing Sewage Sludge at Nicosia City, Northern Cyprus
Smol M, Kulczycka J, Henclik A et al (2015) The possible use of sewage sludge ash (SSA) in the construction industry as a way towards a circular economy. J Clean Prod 95:45–54
Tang Y, Chui SS-Y, Shih K, Zhang L (2011) Copper stabilization via spinel formation during the sintering of simulated copper-laden sludge with aluminum-rich ceramic precursors. Environ Sci Technol 45:3598–3604
Tang Y, Zheng X, Ma W, Wu P (2018) Residues from sewage sludge incineration for ceramic products with potential for zinc stabilization. Waste Manag 82:188–197
Tantawy MA, El-Roudi AM, Abdalla EM, Abdelzaher MA (2012) Evaluation of the pozzolanic activity of sewage sludge ash. ISRN Chem Eng 2012:5
Tironi A, Trezza MA, Scian AN, Irassar EF (2013) Assessment of pozzolanic activity of different calcined clays. Cem Concr Compos 37:319–327
Tironi A, Trezza MA, Scian AN, Irassar EF (2012) Kaolinitic calcined clays: factors affecting its performance as pozzolans. Constr Build Mater 28:276–281
Türker U, Okaygün M, Almaqadma SJ (2009) Impact of anaerobic lagoons on the performance of BOD and TSS removals at the Haspolat (Mia Milia) Wastewater Treatment Plant. Desalination 249:403–410
United Nations Development Programme in Cyprus (2014) Working together for the people of Nicosia
Weng C-H, Lin D-F, Chiang P-C (2003) Utilization of sludge as brick materials. Adv Environ Res 7:679–685
Wesche K (2014) Fly ash in concrete: properties and performance. CRC Press, Hoboken
Yu Q, Sawayama K, Sugita S et al (1999) The reaction between rice husk ash and Ca(OH)2 solution and the nature of its product. Cem Concr Res 29:37–43
Yusuf RO, Noor ZZ, Din MFM, Abba AH (2012) Use of sewage sludge ash (SSA) in the production of cement and concrete-a review. Int J Glob Environ Issues 12:214–228
Zongjin L (2011) Advanced concrete technology. Wiley, Hoboken
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of the Topical collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Water Problems in E. Mediterranean Countries” guest edited by H. Gökçekuş, D. Orhon, V. Nourania, and S. Sozen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alayish, O., Çelik, T. Extending disposal route of dewatered sewage sludge produced from the new wastewater treatment plant in Nicosia toward sustainable building materials. Environ Earth Sci 80, 146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09439-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09439-3