Abstract
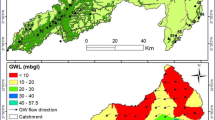
Increasing demand of the irrigation water led to improper surface water irrigation policies resulting in water logging problems in southwest Punjab coupled with apprehension of saline zones formation by salinity ingression towards central Punjab due to excessive groundwater abstraction. A network of piezometers exploring 4 upper aquifers was constructed at 6 sites in Sri Muktsar Sahib district of south-west Punjab. Groundwater samples were collected from these piezometers, TDS was measured and analysed for stable isotopes (ẟ18O and ẟD). Based on isotope characterization 4 zones were identified as: (1) zone A: source as fresh water or precipitation (2) zone B evaporation either during precipitation or infiltration (3) zone C intermediate of evaporated and recycled water (4) recycled water. This study can be useful in proper management of the water resources in this region by identifying the fresh water and saline groundwater zones in the area.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2005) Geochemistry groundwater and pollution. Balkema, Rotterdam, p 649
Argamasilla M, Barberà JA, Andreo B (2017) Factors controlling groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in coastal aquifers from southern Spain. Sci Total Environ 580(50–68):15
Bartarya SK (1993) Hydrochemistry and rock weathering in a subtropical lesser Himalayan river basin in Kumaun, India. J Hydrol 146:149–174
Bennetts DA, Webb JA, Stoneb DJM, Hill DM (2006) Understanding the salinisation process for groundwater in an area of southeastern Australia, using hydrochemical and isotopic evidence. J Hydrol 323(1–4):178–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.08.023
CGWB Report (2013) Unpublished report on ground water information Booklet Muktsar District, Punjab
Chen C-H, Wang C-H, Wen S, Yeh T-K, Lin C-H, Liu J-Y, Yen H-Y, Lin C, Rau R-J, Lin T-W (2013) Anomalous frequency characteristics of groundwater level before major earthquakes in Taiwan. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:1693–1703
Chopra RPS, Krishan G (2014) Analysis of aquifer characteristics and groundwater quality in southwest Punjab, India. J Earth Sci Eng 4(10):597–604
Custodio E (1993) Coastal aquifer salinization as a consequence of aridity: the case of Amurga phonolitic massif, Gran Canaria Island. Study and modelling of saltwater intrusion. CIMNEUPC, Barcelona, pp 81–98
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Guan H, Zhang X, Skrzypek G, Sun Z, Xu X (2013) Deuterium excess variations of rainfall events in a coastal area of South Australia and its relationship with synoptic weather systems and atmospheric moisture sources. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:1123–1138
Jouzel J et al (2013) Water isotopes as tools to document oceanic sources of precipitation. Water Resour Res 49:7469–7486
Kim G, Lee KK, Park KS, Hwang DW, Yang HS (2003) Large submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) from a volcanic island. Eophys Res Lett 30:21
Krishan G (2019) Groundwater salinity. Curr World Environ 14(2):186–188
Krishan G, Bisht M, Ghosh NC, Prasad G (2020a) Groundwater salinity in north west of India: a critical appraisal. In: Singh R, Shukla P, Singh P (eds) Environmental processes and management. Water Science and Technology Library, vol 91. Springer, Cham
Krishan G, Ghosh NC, Kumar CP, Sharma LM, Yadav B, Kansal ML, Singh S, Verma SK, Prasad G (2020b) Understanding stable isotope systematics of salinity affected groundwater in Mewat, Haryana India. J Earth Syst Sci 129:109
Krishan G, Kumar CP, Prasad G, Kansal ML, Yadav B, Verma SK (2020c) Stable isotopes and inland salinity evidences for mixing and exchange. In: Proceedings of Roorkee Water Conclave (RWC-2020) during 26–28 February, 2020 at IIT Roorkee
Krishan G, Prasad G, Anajli KCP, Patidar N, Yadav B, Kansal ML, Singh S, Sharma LM, Bardley A, Verma SK (2020) Identifying the seasonal variability in source of groundwater salinization using deuterium excess—a case study from Mewat, Haryana, India. J Hydrol Reg Stud 31:100724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2020.100724
MacDonald A, Bonsor H et al (2016) Groundwater depletion and quality in the Indo-Gangetic Basin mapped from in situ observations. Nat Geosci 9:762–766
Masson-Delmotte V et al (2008) A review of Antarctic surface snow isotopic composition: observations, atmospheric circulation, and isotopic modeling. J Clim 21:3359–3387
Matthess G (1982) The properties of groundwater. Wiley, New York, p 498
Rao MS, Krishan G, Kumar CP, Purushotmanan P, Sudhir K (2017) Observing changes in groundwater resource using hydro-chemical and isotopic parameters: a case study from Bist Doab, Punjab. Environ Earth Sci 76:175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6492-1
Schuh WM, Klinekebiel DL, Gardner JC, Meyar RF (1997) Tracer and nitrate movements to groundwater in the Norruem Great Plains. J Environ Qual 26:1335–1347
Toth J (1984) The role of regional gravity flow in the chemical and thermal evolution of groundwater. In: Proceedings of the first Canadian/American conference on hydrogeology, Banff, Alta, June, 1984
Wang Y, Jiao JJ (2012) Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in the confined Quaternary aquifer of the Pearl River Delta China. J Hydrol 438–439:112–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.008
Zhu L, Fan M, Hough B, Li L (2018) Spatiotemporal distribution of river water stable isotope compositions and variability of lapse rate in the central Rocky Mountains: controlling factors and implications for paleoelevation reconstruction. Earth Planet Sci Lett 496(2018):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2018.05.047
Acknowledgements
Funding received from Department of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Punjab is duly acknowledged and is a part of CDP study awarded to the NIH by the department.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishan, G., Vashisht, R., Sudarsan, N. et al. Groundwater salinity and isotope characterization: a case study from South-West Punjab, India. Environ Earth Sci 80, 169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09419-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09419-7