Abstract
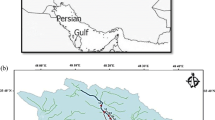
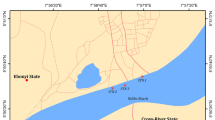
River heavy metal contamination (HM) is a serious growing concern across the globe. In Iran, particularly, rivers serve as the most important freshwater resource and underlie the majority of water-demanding activities, resulting in highly polluted rivers. In central Iran, the Ghareh-Aghaj River supports many industrial, municipal, and agricultural land-uses along its path to the Persian Gulf. Although there may be reciprocal HM effects, no study has yet provided supporting scientific evidence on the river’s sediment HM content that might affect the sensitive biodiversity of the river and the Persian Gulf. This study measured the concentrations of five HMs at 11 susceptible and accessible locations along the river as follows: Arsenic (41.83 mg/kg) > Nickel (38.08 mg/kg) > Zinc (24.46 mg/kg) > Copper (18.86 mg/kg) > Lead (4.97 mg/kg). The HM distributions were uniform due to insignificant correlations and high coefficient of variations. According to the results, the river was not polluted with Cu, Zn, and Pb, partly with Ni, and highly with As. The concentration of As exceeded natural values in the river midstream zone and the seawardmost station where the river is exposed to intense agriculture and extensive use of arsenical pesticides and herbicides. This study highlighted the Ghareh-Aghaj River as worthy of further HM investigation, particularly As and urged implementation of HM elimination and monitoring measures to ensure their health and well-functioning.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim G (2005) Holocene sediments of Tamaki Estuary: characterisation and impact of recent human activity on an urban estuary in Auckland, New Zealand. ResearchSpace@ Auckland
Alahabadi A, Malvandi H (2018) Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloids in surface sediments of the Tajan River, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull 133:741–749
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA Washington DC, USA
Ashraf S et al (2019) Compounding effects of human activities and climatic changes on surface water availability in Iran. Clim Change 152:379–391
Bagheri H, Alinejad S, DarvishBastami K (2011) Heavy metals (Co, Cr, Cd, Ni, Pb and Zn) in sediment of Gorganrud River, Iran. Res J Environ Toxicol 5:147–151
Bahrami M, Rahimi A (2009) Calculation of the transpotation of the total sediment yield of Ghareh-Aghaj River at Karar Dam site using hydraulic methods. Iran J ApplGeol 5:220–229
Barkett MO, Akün E (2018) Heavy metal contents of contaminated soils and ecological risk assessment in abandoned copper mine harbor in Yedidalga, Northern Cyprus. Environ Earth Sci 77:378
Black CA, Evans D, White J, Ensminger L, Clarke F (1965) Methods of soil analysis. American Society of Agronomy. Madison, Wisconsin, part I, pp 1–770
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils 1. Agron J 54:464–465
Bowen HJM (1979) Environmental chemistry of the elements. Academic Press, Cambridge
Buat-Ménard P (1979) Influence de la retombée atmosphérique sur la chimie des métaux en trace dans la matière en suspension de l’Atlantique Nord. Thèse de Doctorat d'Etat, Sciences, Paris 7
Chapman HD (1965) Cation exchange capacity. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp. 891–901
Charkhabi AH, Sakizadeh M, Rafiee G (2005) Seasonal fluctuation in heavy metal pollution in Iran s Siahroud River-a preliminary study (7 pp). Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:264–270
Diagomanolin V, Farhang M, Ghazi-Khansari M, Jafarzadeh N (2004) Heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu) in the karoon waterway river, Iran. ToxicolLett 151:63–67
Dou Y, Li J, Zhao J, Hu B, Yang S (2013) Distribution, enrichment and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of the eastern Beibu Bay, South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 67:137–145
Fadaei A, Dehghani MH, Nasseri S, Mahvi AH, Rastkari N, Shayeghi M (2012) Organophosphorous pesticides in surface water of Iran. Bull Environ ContamToxicol 88:867–869
Fattahi M, Jahangiri H (2012) The relations between the fractal properties of the river networks and the river flow time series. Int J Geol Environ Eng 6:111–116
Goorzadi M, Vahabzadeh G, Ghanbarpour M, Karbassi A (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in Tilehbon River sediments, Iran. J ApplSci 9:1190–1193
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach . Water Res 14:975–1001
Jafarabadi AR, Bakhtiyari AR, Toosi AS, Jadot C (2017) Spatial distribution, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in marine surface sediments and coastal seawaters of fringing coral reefs of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Chemosphere 185:1090–1111
Kabata-Pendias A (2010) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
Karimian S, Chamani A, Shams M (2020) Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the Zayandeh-Rud River as the only permanent river in the central plateau of Iran. Environ Monit Assess 192:316–316
Kazemi M, Chamani A, Agh N (2018) The ssessment of arsenic contamination in Urmia lake sediments and its effect on human health. J Environ Stud 45:485–497
Kumar V, Parihar RD, Sharma A, Bakshi P, Singh Sidhu GP, Bali AS, Karaouzas I, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK, Gyasi-Agyei Y, Rodrigo-Comino J (2019) Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: a meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 236:124364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124364
Li Y, Zhou Q, Ren B, Luo J, Yuan J, Ding X, Bian H (2019) Trends and health risks of dissolved heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water from 1970 to 2017. Rev Environ ContamToxicol 251:1–24
Long ER, Macdonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manag 19:81–97
Luo W, Lu Y, Wang T, Hu W, Jiao W, Naile J, Khim JS, Giesy J (2010) Ecological risk assessment of arsenic and metals in sediments of coastal areas of northern Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Ambio 39:367–375
Madani K (2014) Water management in Iran: what is causing the looming crisis? J Environ Stud Sci 4:315–328
Madani K, AghaKouchak A, Mirchi A (2016) Iran’s socio-economic drought: challenges of a water-bankrupt nation. Iran Stud 49:997–1016
Malvandi H (2017) Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the Zarrin-Gol River sediments, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull 117:547–553
Memoli V, Esposito F, Panico SC, De Marco A, Barile R, Maisto G (2019) Evaluation of tourism impact on soil metal accumulation through single and integrated indices. Sci Total Environ 682:685–691
MirzaeeMahmoodabadi R (2019) Evaluation of water quality and bed load sediment contamination of Qareaqhaj River to heavy metals, Kahfr Watershed, Fars province. J Environ Sci Stud 4(3):1696–1706
Mombeni HA, Rezaei S, Nadarajah S, Emami M (2013) Estimation of water demand in Iran based on SARIMA models. Environ Model Assess 18:559–565
Muller G (1979) Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veran-derngrenseitt 1971. Umschan 79:778–783
Nafchi MA, Chamani A (2019) Physiochemical factors and heavy metal pollution, affecting the population abundance of Coenobitascaevola. Mar Pollut Bull 149:110494
Nasrabadi T, Bidhendi GN, Karbassi A, Mehrdadi N (2010) Evaluating the efficiency of sediment metal pollution indices in interpreting the pollution of Haraz River sediments, southern Caspian Sea basin. Environ Monit Assess 171:395–410
Nazarpour A, Watts MJ, Madhani A, Elahi S (2019) Source spatial distribution and pollution assessment of Pb, Zn, Cu, and Pb, isotopes in urban soils of Ahvaz City, a semi-arid metropolis in southwest Iran. Sci Rep 9:1–11
Noorbakhsh S, Sahraiian H, Soroosh MJ, Rezaii V, Fotoohi A (2011) Inventory of important pests, diseases, and weeds of the major agricultural crops: pesicides and recommended methods of application (in Persian). Ministry of Agriculture, Plant Protection Organization. p 197
Nourouzi M, Chamani A, Shirani M, Malekpouri P, Chuah A (2018) Effect of Cd and Pb pollutions on physiological growth: wavelet neural network (WNN) as a new approach on age determination of Coenobita scaevola. Bull Environ ContamToxicol 101:320–325
Office of Planning and Economy (2015) Agricultural statistics of Fars province. Publication of Fars Agricultural Organization, 197 pages
Ra K et al (2014) Assessment of pollution and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Ulsan Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci J 49:279–289
Saeedi M, Hosseinzadeh M, Rajabzadeh M (2011) Competitive heavy metals adsorption on natural bed sediments of Jajrood River, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 62:519–527
Salati S, Moore F (2010) Assessment of heavy metal concentration in the Khoshk River water and sediment, Shiraz, Southwest Iran. Environ Monit Assess 164:677–689
Sanayei Y, Ismail N, Talebi S (2009) Determination of heavy metals in Zayandeh Rood river, Isfahan-Iran. World ApplSci J 6:1209–1214
Sayadi M, Sayyed M, Kumar S (2010) Short-term accumulative signatures of heavy metals in river bed sediments in the industrial area, Tehran, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 162:465–473
Shanbehzadeh S, Vahid Dastjerdi M, Hassanzadeh A, Kiyanizadeh T (2014) Heavy metals in water and sediment: a case study of Tembi River. J Environ Public Health 2014:858720
Sheykhi V, Moore F (2013) Evaluation of potentially toxic metals pollution in the sediments of the Kor river, southwest Iran. Environ Monit Assess 185:3219–3232
Simpson S, Batley G (2016) Sediment quality assessment: a practical guide. Csiro Publishing, Clayton
Tomlinson D, Wilson J, Harris C, Jeffrey D (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländermeeresuntersuchungen 33:566
Vahid HD, Noori M, Heydari M, Sheikhi M (2016) An investigation into the qualitative and quantitative effects of climate change on rivers in Iran. Int J Rev Life Sci 6:6–13
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Yazdanpak A, Ostovan H, Hesami S, Gheibi M (2020) Determination of residue levels of pesticides (acetamipride, diazinon, imidacloprid, primicarb) in greenhouse tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) var. Izmir in Fars. J Anim Environ 11(4):289–296
Zhang M, He P, Qiao G, Huang J, Yuan X, Li Q (2019) Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the Subei Shoal, China: spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk. Chemosphere 223:211–222
Zhou Q, Yang N, Li Y, Ren B, Ding X, Bian H (2020) Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob EcolConserv 22:9–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahradnia, H., Chamani, A., Zamanpoore, M. et al. Heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of Ghareh-Aghaj River, one of the longest perennial rivers in Iran. Environ Earth Sci 80, 91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09384-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09384-1