Abstract
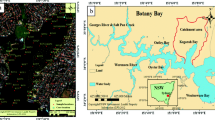
Brunei Bay, Borneo is a unique water ecosystem which has been conserved a wide range of wildlife. Hitherto, the rapidly increase of human activities has been denoted surround and within the bay ecosystem. Four sediment cores has been collected within Brunei Bay with the purpose of assessing metal’s pollution level and geochemical characteristics of the cores. Metals total concentration, sediment physico-chemical characteristic, and sediment sequential extraction analysis were determined in each layer of the sediment cores. Generally, all metals showed different pattern of enrichment or depletion in each core. Sediment core of station LB recorded the highest average of metals compared to other sediment cores. Brunei Bay sediment cores are dominant by silt with low total organic carbon (TOC) content. However, both parameters are not affecting the concentration of metals in the bay sediment. Largely, all metals in all sediment cores are classiffied as uncontaminated-to-moderately contaminated except for lead (Pb). During the period of 1980’s, Pb was moderately-to-strongly contaminated at station LB. It is most probably caused by the high usage of local boat and Labuan Port activities. The risk assessment code analysis has exhibited that only copper (Cu) has low risk on the benthic health in Brunei Bay sediment especially for station B5 and B7. In overall, Brunei Bay sediment shows no significant pollution caused by the metals; however, metal enrichment behavior in the sediment will increased the pollution risk on the bay ecosystem in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo P, Arienzo M, Imperato M, Naimo D, Nardi G, Stanzione D (2005) Distribution and partition of heavy metals in surface and sub-surface sediments of Naples city port. Chemosphere 61(6):800–809
Adiana G, Shazili NAM, Ariffin MM (2011) Cadmium, manganese and lead distribution in the South China Sea off the South Terengganu coast, Malaysia during post-monsoon and pre-monsoon. J Sustain Sci Manage 6(2):181–192
Adiana G, Shazili NAM, Joseph B, Hasrizal S (2016) The spatial distribution of Al, Fe, Cu, Cd and Pb in the surface sediment of Brunei Bay, Borneo during the Southwest and Northeast monsoons. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management Special Issue 1: The International Seminar on the Straits of Malacca and the South China Sea 93–106
Adiana G, Juahir H, Joseph B, Shazili NAM (2017) Tracing the sources of lead (Pb) in Brunei Bay, Borneo by using integrated spectrometry ICP-MS and chemometric techniques. Mar Pollut Bull 123:232–240
Ahdy HHH, Khaled A (2009) Heavy metals contamination in sediments of the western part of Egyptian Mediterranean Sea. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3(4):3330–3336
Aminti P, Billi P (1984) An investigation of the effect of the breakwaters on beach sediment characteristics. CATENA 11:391–400
Appleby PG, Oldfield F (1978) The calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. CATENA 5:1–8
Ayçik GA, Çetaku D, Erten HN, Salihoglu I (2004) Dating of Black sea sediments from Romanian coast using natural 210Pb and fallout 137Cs. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 259(1):177–180
Bidai J, Adiana G, Shazili NAM (2016) Particle sizes effect of the elements in the South China Sea sediment off Pahang coastal during the Northeast monsoon (pre-) and the Southwest monsoon (post-) periods. Environ Earth Sci 75(7):614
Censi P, Spoto SE, Saiano F, Spovieri M, Mazzola S, Nardone G, Di Geronimo SI, Punturo R, Ottonello D (2006) Heavy metals in coastal water systems. A case study from the northwestern Gulf of Thailand. Chemosphere 64(7):1167–1176
Chatterjee M, Silva Filho E, Sarkar SK, Sella SM, Bhattacharya A, Satpathy KK, Prasad MVR, Chakraborty S, Bhattacharya BD (2007) Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance. Environ Int 33(3):346–356
Chen CW, Kao CM, Chen CF, Dong CD (2007) Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 66:1431–1440
Chen CF, Dong CD, Chen CW (2013) Evaluation of sediment toxicity in Kaohsiung harbor, Taiwan. Soil Sediment Contam 22(3):301–314
Cho J, Hyun S, Han JH, Kim S, Shin DH (2015) Historical trend in heavy metal pollution in core sediments from the Masan Bay, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 95(1):427–432
Copaja SV, Molinam X, Tessada R (2014) Determination of heavy metals in Choapa River sediments using BCR sequential extraction procedure. J Chil Chem Soc 59(1):2353–2358
Daskalakis KD, O’Connor TP (1995) Normalization and elemental sediment contamination in the Coastal United States. Environ Sci Technol 29(2):470–477
Deepulal PM, Gireesh Kumar TR, Sujatha CH, Rejomon G (2012) Chemometric study on the trace metal accumulation in the sediments of the Cochin Estuary – Southwest coast of India. Environ Monit Assess 184:6161–6279
Dickinson W, Dunbar G, McLeod H (1996) Heavy metal history from cores in Wellington Harbour, New Zealand. Environ Geol 27:59–69
Domínguez C, Sarkar SK, Bhattacharya A, Chatterjee M, Bhattacharya BD, Jover E, Albaiges J, Bayona JM, Alam MA, Satpathy KK (2010) Quantification and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in core sediments from Sundarban Mangrove Wetland, India. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59(1):49–61
Ellis J, Stone GW (2006) Numerical simulation of net longshore sediment transport and granulometry of surficial sediments along Charideleur Island, Lousiana, U.S.A. J Mar Geol 232:115–129
Fernandes LL, Nayak GN (2014) Characterizing metal levels and their speciation in intertidal sediments along Mumbai coast, India. Mar Pollut Bull 79(1–2):371–378
Filella M, Belzile N, Chen Y-W (2002) Antimony in the environment: a review focused on natural waters: I. Occurrence. Earth Sci Rev 57(1–2):125–176
Gajghate DG, Bhanarkar AD (2005) Characterisation of particulate matter for toxic metals in ambient air of Kochi city, India. Environ Monit Assess 102(1–3):119–129
Ghrefat H, Yusuf N (2006) Assessing Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, and Cd pollution in bottom sediments of Wadi Al-Arab Dam, Jordan. Chemosphere 65:2114–2121
Haghani S, Leroy SAG, Wesselingh FP, Rose NL (2016) Rapid evolution of coastal lagoons in response to human interference under rapid sea level change: a south Caspian Sea case study. Quatern Int 408:93–112
Harikumar PS, Nasir UP (2010) Ecotoxicological impact assessment of heavy metals in core sediments of a tropical estuary. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(7):1742–1747
Herreros MA, Iñigo-Nuñez S, Sanchez-Perez E, Encinas T, Gonzalez-Bulnes A (2008) Contribution of fish consumption to heavy metals exposure in women of childbearing age from a Mediterranean country (Spain). Food Chem Toxicol 46(5):1591–1595
Hirao Y, Mabuchi H, Fukada E, Tanaka H, Imamura T, Todoroki H, Kimura K, Matsumoto E (1986) Lead isotope ratios in Tokyo Bay sediments and their implications in the lead consumption of Japanese industries. Geochem J 20(1):1–15
Holzhacker R, Agussalim D (2019) Sustainable development goals in Southeast Asia and ASEAN: national and regional approaches. BRILL, Netherlands, pp 291–292
Hornung H, Krom MD, Cohen Y (1989) Trace metal distribution in sediments and benthic fauna of Haifa Bay, Israel. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 29(1):43–56
Hoshika A, Shiozawa T, Kawana K, Tanimoto T (1991) Heavy metal pollution in sediment from the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Mar Pollut Bull 23:101–105
Hosono T, Su C-C, Siringan F, Amano A, Onodera S-I (2010) Effects of environmental regulations on heavy metal pollution decline in core sediments from Manila Bay. Mar Pollut Bull 60:780–785
Hosono T, Su C-C, Delinom R, Umezawa Y, Toyota T, Kaneko S, Taniguchi M (2011) Decline in heavy metal contamination in marine sediments in Jakarta Bay, Indonesia due to increasing environmental regulations. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 92:297–306
Jain CK, Gupta H, Chakrapani GJ (2008) Enrichment and fractionation of heavy metals in bed sediments of River Narmada, India. Environ Monit Assess 141(1–3):35–47
Jiang Y, Kirkman H, Hua A (2001) Megacity development: managing impacts on marine environments. Ocean Coast Manag 44(5–6):293–318
Joseph B, Adiana G, Shazili NAM, Ong MC, Juahir H, Shaari H, Yii MW, Kamarudin MKA, Gasim MB, Maulud KNA, Islam MS (2018) The evaluation of Brunei Bay sediment cores sedimentation rate using 210Pb radiometric dating technique. Int J Eng Technol 7(3.14):107–114
Kumar A, Ramanathan AL (2015) Speciation of selected trace metals (Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn) with depth in the sediments of Sundarban mangroves: India and Bangladesh. J Soils Sediments 15(12):2476–2486
Leonardo DR, Vizzini S, Bellanca A, Mazolla A (2009) Sedimentary record of anthropogenic contaminants (trace metals and PAHs) and organic matter in a Mediterranean coastal area (Gulf of Palermo, Italy). J Mar Syst 78(1):136–145
Moore F, Nematollahi MJ, Keshavarzi B (2015) Heavy metals fractionation in surface sediments of Gowatr bay-Iran. Environ Monit Assess 187(1):4117
Morelli G, Gasparon M, Fierro D, Hu WP, Zawadzki A (2012) Historical trends in trace metal and sediment accumulation in intertidal sediments of Moreton Bay, southeast Queensland, Australia. Chem Geol 300–301:152–164
Moukhchan F, March JG, Cerda V (2013) Distribution of trace metals in marine sediments of the Bay of Palma de Mallorca (Mallorca Island, Spain). Environ Monit Assess 185(1):695–706
Müller G (1979) Heavy metals in the sediment of Rhines – Changes seity. Umschau in Wissenschaft und Technik 79:778–783
Nazneen S, Patel P (2016) Distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chilika lagoon, east coast of India. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 10(6):63–71
Pempkowiase J, Sikora A, Biemacka E (1999) Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments vs their bioaccumulation by Mussels. Chemosphere 39(2):313–321
Perin G, Craboledda L, Lucchese M, Cirillo R, Dotta L, Zanetta ML, Oro AA (1985) Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of northern Adriatic Sea. A new approach for environmental toxicity determination. In: Lakkas TD (ed) Heavy metals in the environment. CEP Consultants, Edinburgh, pp 454–456
Ruiz-Fernández AC, Hillaire-Marcel C, Páez-Osuna F, Ghaleb B, Soto-Jiménez FM (2003) Historical trends of metal pollution recorded in the sediments of Culiacan river estuary Northwestern Mexico. Appl Geochem 18(4):577–588
Salomons W, Förstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer-Verlag, New York
Saraee KRE (2010) Elemental Assessments of South China Sea Marine Sediments along the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Dissertation. Universiti Putra Malaysia, Malaysia
Sarkar SK, Binelli A, Chatterjee M, Bhattacharya BD, Parolini M, Riva C, Jonathan MP (2012) Distribution and ecosystem risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in core sediments of Sundarban mangrove wetland, India. Polycyclic Aromat Compd 32(1):1–26
Sekabira K, Origa OH, Basamba TA, Mutumba G, Kakudidi E (2010) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the urban stream sediments and its tributaries. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(3):435–446
Selvam AP, Priya SL, Banerjee K, Hariharan G, Purvaja R, Ramesh R (2012) Heavy metal assessment using geochemical and statistical tools in the surface sediments of Vembanad Lake, southwest coast of India. Environ Monit Assess 184(10):5899–5915
Shelton D, Kiss A (2005) Judicial handbook on environmental law. United Nations Environment Programme, United Kingdom
Shi Q, Leipe T, Rueckert P, Zhou D, Harff J (2010) Geochemical sources, deposition and enrichment of heavy metals in short sediment cores from the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. J Mar Syst 82:S28–S42
Singh S, Raju NJ, Nazneen S (2015) Environmental risk of heavy metal pollution and contamination sources using multivariate analysis in the soils of Varanasi environs, India. Environ Monit Assess 187(6):345
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedures for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51(7):844–851
Tranchina L, Basile S, Brai M, Caruso A, Cosentino C, Miccichè S (2008) Distribution of heavy metals in marine sediments of Palermo Gulf (Sicily, Italy). Water Air Soil Pollut 191(1–4):245–256
Usman A, Alkredaa RS, Al-Wabel MI (2013) Heavy metal contamination in sediments and mangroves from the coast of Red Sea: Avicennia marina as potential metal bioaccumulator. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 97:263–270
Veerasingam S, Vethamony P, Mani Murali R, Fernandes B (2015) Depositional record of trace metals and degree of contamination in core sediments from the Mandovi estuarine mangrove ecosystem, west coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull 91(1):362–367
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wang S, Jia Y, Wang S, Wang X, Wang H, Zhao Z, Liu B (2010) Fractionation of heavy metals in shallow marine sediments from Jinzhou Bay, China. J Environ Sci 22(1):23–31
Wang Y, Hu J, Xiong K, Huang X, Duan S (2012) Distribution of heavy metals in core sediments from Baihua Lake. Procedia Environ Sci 16:51–58
Wedepohl KH (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59(7):1217–1232
Yusof ZA, Bhattasali D (2008) Economic growth and development in Malaysia: policy making and leadership. The World Bank Group, Washington
Zhang J, Liu CL (2002) Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54(6):1051–1070
Acknowledgements
The Ministry of Education Malaysia (MOE) funded this research through the Higher Institution Centre of Excellent (HiCoE) in a Marine Science research grant (Grant Numbers: 66928). The authors would like to thank MOE for the research grant and the Institute of Oceanography and Environment for the assistance given during sampling and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, B., Adiana, G., Ong, M.C. et al. Scrutinizing the anthropogenic metals in the Brunei Bay sediment cores off the Malaysian waters. Environ Earth Sci 79, 452 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09203-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09203-z