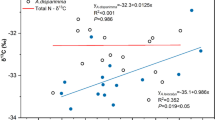
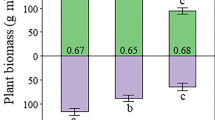
Abstract
Atmospheric deposition and mineral weathering are important sources of base cations in vegetated ecosystems. To assess plant preferences for weathering-fed versus atmospheric-fed mineral nutrition during different growth stages (sapling to mature), we have studied 87Sr/86Sr isotope ratios, and Ca and Sr concentrations in the vegetation, litter, organic matter and mineral soils from five functionally different species: Korean red pine, Korean chestnut, black locust, annual fleabane, and silvergrass. Isotope values of vegetations (0.7124–0.7162) closely matched with that of litter (0.7143–0.7161), soil (0.7126–0.7165), and parent material (0.7161). Plant height (as a proxy for maturity) and plant functional forms did not show discriminating effect on the variation in the Sr isotope ratio. An assessment of the relative contribution of the in-situ weathering input versus the ex-situ atmospheric input using a mixing equation suggests that vegetation, irrespective of maturity, is dependent on the weathering supplied elements as a primary source of nutrients. At all the sites, the 87Sr/86Sr ratio of organic layers and mineral soil were similar to the isotopic values of the vegetation, suggesting an active recycling pool and suggesting that vegetation in the region conservatively extracts nutrients from weathered parent materials, which are then internally recycled via organic layers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åberg G, Jacks G, Wickman T, Hamilton PJ (1990) Strontium isotopes in trees as an indicator for calcium availability. CATENA 17:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0341-8162(90)90011-2
Bailey SW, Hornbeck JW, Driscoll CT, Gaudette HE (1996) Calcium inputs and transport in a base-poor forest ecosystem as interpreted by Sr isotopes. Water Resour Res 32:707–719. https://doi.org/10.1029/95WR03642
Bedel L, Poszwa A, Van Der Heijden G, Legout A, Aquilina L, Ranger J (2016) Unexpected calcium sources in deep soil layers in low-fertility forest soils identified by strontium isotopes (Lorraine plateau, eastern France). Geoderma 264:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.09.020
Bélanger N, Holmden C (2010) Influence of landscape on the apportionment of Ca nutrition in a Boreal shield forest of Saskatchewan Canada using 87Sr/86Sr as a tracer. Can J Soil Sci 90:267–288. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJSS09079
Blum JD, Dasch AA, Hamburg SP, Yanai RD, Arthur MA (2008) Use of foliar Ca/Sr discrimination and 87Sr/86Sr ratios to determine soil Ca sources to sugar maple foliage in a northern hardwood forest. Biogeochemistry 87:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-008-9184-9
Bullen TD, Bailey SW (2005) Identifying calcium sources at an acid deposition–impacted spruce forest: a strontium isotope, alkaline earth element multi–tracer approach. Biogeochemistry 74:63–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-2619-z
Capo RC, Stewart BW, Chadwick OA (1998) Strontium isotopes as tracers of ecosystem processes: theory and methods. Geoderma 82:197–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(97)00102-X
Chadwick OA, Derry LA, Vitousek PM, Huebert BJ, Hedin LO (1999) Changing sources of nutrients during four million years of ecosystem development. Nature 397:491–497. https://doi.org/10.1038/17276
Dasch AA, Blum JD, Eagar C, Fahey TJ, Driscoll CT, Siccama TG (2006) The relative uptake of Ca and Sr into tree foliage using a whole–watershed calcium addition. Biogeochemistry 80:21–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-6008-z
Dijkstra FA, Van Breemen N, Jongmans AG, Davies GR, Likens GE (2003) Calcium weathering in forested soils and the effect of different tree species. Biogeochemistry 62:253–275. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021132132199
Drouet Th, Herbauts J, Gruber W, Demaiffe D (2005) Strontium isotope composition as a tracer of calcium sources in two forest ecosystems in Belgium. Geoderma 126:203–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.09.010
Elias RW, Hirao Y, Patterson CC (1982) The circumvention of the natural biopurification of calcium along nutrient pathways by atmospheric inputs of industrial lead. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:2561–2580. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(82)90378-7
Gautam MK, Lee KS (2016) Application of stable isotopes in ecosystem research. Current Sci 110:1288–1306. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v110/i7/1288-1306
Graustein WC (1989) 87Sr/86Sr ratios measure the sources and flow of strontium in terrestrial ecosystems. Stable isotopes in ecological research. Springer, New York, pp 491–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-3498-2_28
Green GP, Bestland EA, Walker GS (2004) Distinguishing sources of base cations in irrigated and natural soils: evidence from strontium isotopes. Biogeochemistry 68:199–225. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOG.0000025743.34079.d3
Guibourdenche L, Stevenson R, Pedneault K, Poirier A, Widory D (2020) Characterizing nutrient pathways in Quebec (Canada) vineyards: insight from stable and radiogenic strontium isotopes. Chem Geol 532:119375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119375
Jacks G, Åberg G, Hamilton PJ (1989) Calcium budgets for catchments as interpreted by strontium isotopes. Hydrol Res 20:85–96. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.1989.0007
Jeon SR, Chung JI (2005) The Sr and Pb isotopic and geochemical properties of the atmospheric bulk deposition of Jeonju Gunsan and Namweon areas. Econ Environ Geol 38:463–479
Kennedy MJ, Chadwick OA, Vitousek PM, Derry LA, Hendricks DM (1998) Changing sources of base cations during ecosystem development Hawaiian Islands. Geology 26:1015–1018. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<1015:CSOBCD>2.3.CO;2
Kennedy MJ, Hedin LO, Derry LA (2002) Decoupling of unpolluted temperate forests from rock nutrient sources revealed by natural 87Sr/86Sr and 84Sr tracer addition. PNAS 99:9639–9644. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.152045499
Lee D, Jin V, Choe JC, Son Y, Yoo S, Lee HY, Hong SK, Ihm BS (2002) Ecology of Korea. Bumwoo Publishing Company, Seoul, pp 243–250
Nakano T, Tanaka T (1997) Strontium isotope constraints on the seasonal variation of the provenance of base cations in rain water at Kawakami central Japan. Atmos Env 3:4237–4245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00229-X
Novak M, Holmden C, Farkaš J, Kram P, Hruska J, Curik J, Fottova D (2020) Calcium and strontium isotope dynamics in three polluted forest ecosystems of the Czech Republic, Central Europe. Chem Geol 536:119472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119472
Perakis SS, Maguire DA, Bullen TD, Cromack K, Waring RH, Boyle JR (2006) Coupled nitrogen and calcium cycles in forests of the Oregon Coast Range. Ecosystems 9:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-004-0039-5
Poszwa A, Dambrine E, Pollier B, Atteia O (2000) A comparison between Ca and Sr cycling in forest ecosystems. Plant Soil 225:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026570812307
Poszwa A, Dambrine E, Ferry B, Pollier B, Loubet M (2002) Do deep tree roots provide nutrients to the tropical rainforest? Biogeochemistry 60:97–118. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016548113624
Poszwa A, Ferry B, Dambrine E, Pollier B, Wickman T, Loubet M, Bishop K (2004) Variations of bioavailable Sr concentration and 87Sr/86Sr ratio in boreal forest ecosystems. Biogeochemistry 67:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOG.0000015162.12857.3e
Reynolds AC, Quade J, Betancourt JL (2012) Strontium isotopes and nutrient sourcing in a semi-arid woodland. Geoderma 189:574–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.06.029
Schmitt AD, Gangloff S, Labolle F, Chabaux F, Stille P (2017) Calcium biogeochemical cycle at the beech tree-soil solution interface from the Strengbach CZO (NE France): insights from stable Ca and radiogenic Sr isotopes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 213:91–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.06.039
Song BY, Gautam MK, Ryu JS, Lee D, Lee KS (2015) Effects of bedrock on the chemical and Sr isotopic compositions of plants. Environ Earth Sci 74:829–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4087-2
Swoboda S, Brunner M, Boulyga S, Galler P, Horacek M, Prohaska T (2008) Identification of Marchfeld asparagus using Sr isotope ratio measurements by MC–ICP–MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:487–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1582-7
Vitousek PM, Kennedy MJ, Derry LA, Chadwick OA (1999) Weathering versus atmospheric sources of strontium in ecosystems on young volcanic soils. Oecologia 121:255–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050927
Wiegand BA, Chadwick OA, Vitousek PM, Wooden JL (2005) Ca cycling and isotopic fluxes in forested ecosystems in Hawaii. Geophys Res Lett 32:L11404. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL022746
Witty JH, Graham RC, Hubbert KR, Doolittle JA, Wald JA (2003) Contributions of water supply from the weathered bedrock zone to forest soil quality. Geoderma 114:389–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00051-X
Zheng HY, Liu CQ, Wang ZL, Yang C, Chen S, Zhu SF (2008) Strontium isotopes as a tracer of plant nutrition element source in yellow soil region of Guizhou Province. J Beijing Univ 4:72–76
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Hyung-Seon Shin for providing laboratory facilities for the sample processing and isotopic analysis. This work was supported by the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST) Grant by the Government of Korea (MSIP) (No. CAP-17–05-KIGAM) and partly by KBSI Grant (C050200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gautam, M.K., Lee, KS. & Song, BY. Strontium isotope composition aided strontium and calcium sourcing in a cool temperate ecosystem, South Korea. Environ Earth Sci 79, 300 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09046-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09046-8