Abstract
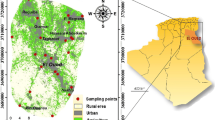
Groundwater resources are often exposed to multiple sources of pollution, which may make them unfit for human consumption. As a result, comprehensive geochemical studies on groundwater status and evolution are required for a sustainable management of water resources. In the present study, 38 water samples from hand-dug wells were collected in a peri-urban area, and their physico-chemical parameters, viz. pH, electrical conductivity (EC), turbidity, dissolved oxygen (DO), total dissolved solids (TDS), major ions (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, NO3−, Cl−, HCO3− and SO42−) and heavy metals (Cd, Cu, total Fe, Ni and Zn) were measured. Because of the short residence time of the groundwater and already advanced weathering stage of the aquifer materials, major ion concentrations, EC and TDS were low and within the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended guideline values for drinking water. However, turbidity, Cd, Ni and, to a lesser degree, total Fe had concentrations greater than the WHO acceptable limits. Piper and Durov diagrams showed that the aquifer is vulnerable to anthropogenic activities, as the groundwater is dominated by a mixed Ca–Mg–Cl–SO4-type water. Bivariate diagrams, correlation and factor analyses indicated that glauconite weathering during water–rock interactions within the aquifer contributed to Ca2+, Mg2+ and SO42− loadings into the groundwater. In contrast, K+ and Na+ can be derived from both chemical weathering and anthropogenic sources such as agricultural activities and landfill leachate. Anthropogenic environmental pollution was mainly associated with turbidity, NO3−, Cd, Ni and Zn. Under the current pH and potential redox conditions, Cu was naturally removed from the water column through adsorption onto Fe-oxydroxides; whereas, Cd, Ni and Zn were remained in their free ionic states. This study showed that hydrogeochemical characterization can be a robust tool in assessing groundwater evolution and its pollution status under the influence of multiple anthropogenic sources.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman G, Seidhom SH, Talaat AM, Some L (2008) Water requirements of some crops in Bobo Dioulasso, western region of Burkina Faso. J Appl Sci Res 4:1658–1666
Abdu N, Abdulkadir A, Agbenin J, Buerkert A (2011) Vertical distribution of heavy metals in wastewater irrigated vegetable garden soils of three West African cities. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 89:387–397
Abdulkadir A, Dossa LH, Lompo DJP, Abdu N, Van Keulen H (2012) Characterization of urban and peri-urban agroecosystems in three West African cities. Int J Agric Sustain 10:289–314
Ahoulé D, Lalanne F, Mendret J, Brosillon S, Maïga A (2015) Arsenic in African waters: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:1–13
Alloway BJ, Jackson AP (1991) The behavior of heavy-metals in sewage sludge-amended soils. Sci Total Environ 100:151–176
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA, AWWA and WEF, Washington
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1993) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Balkerma, Rotterdam
Baker A (2003) Land use and water quality. Hydrol Process 17:2499–2501
Barbier B, Dembelé Y, Compaoré L (2006) L’eau au Burkina Faso: usages actuels et perspectives. Sud Sci Technol 14:20–29
Barry B, Obuobie E, Andreini M, Andah W, Pluquet M (2005) Comprehensive assessment of water management in agriculture (comparative study of river basin development and management). International Water Management Institute.
Barrett MH, Hiscock KM, Pedley S, Lerner DN, Tellam JH, French MJ (1999) Marker species for identifying urban groundwater recharge sources—a review and case study in Nottingham UK. Water Res 33:3083–3097
Belkhiri L, Mouni L, Tiri A (2012) Water-rock interaction and geochemistry of groundwater from the Ain Azel aquifer. Algeria Environ Geochem Health 34:1–13
Bigalke M, Ulrich A, Rehmus A, Keller A (2017) Accumulation of cadmium and uranium in arable soils in Switzerland. Environ Pollut 221:85–93
Böhlke JK (2002) Groundwater recharge and agricultural contamination. Hydrogeol J 10:153–179
Bostick BC, Fendorf S, Fendorf M (2000) Disulfide disproportionation and CdS formation upon cadmium sorption on FeS2. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:247–255
Bretzler A, Stolze L, Nikiema J, Lalanne F, Ghadiri E, Brennwald MS, Rolle M, Schirmer M (2018) Hydrogeochemical and multi-tracer investigations of arsenic-affected aquifers in semi-arid West Africa. Geosci Front 1–17 (in press)
Bretzler A, Lalanne F, Nikiema J, Podgorski J, Pfenninger N, Berg M, Schirmer M (2017) Groundwater arsenic contamination in Burkina Faso, West Africa: predicting and verifying regions at risk. Sci Total Environ 584–585:958–970
Bronner G, Roussel J, Trompette RA (1980) Genesis and geodynamic evolution of the Taoudeni Cratonic Basin (Upper Precambrian and Paleozoic), Western Africa, in dynamics of plate interior. Geodyn Ser Am Geophys Union 1:81–90
Brown CJ, Barlow JRB, Cravotta CA III, Lindsey BD (2019) The occurrence of lead and manganese in untreated drinking water from Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain aquifers, eastern United States-dissolved oxygen and pH framework for evaluating risk of elevated concentrations. Appl Geochem 101:88–102
Burkart MR, Kolpin DW (1993) Hydrogeologic and land-use factors associated with herbicide and nitrate occurrence in near-surface aquifers. Environ Qual J 22:646–656
Chapman MJ, Cravotta III CA, Szabo Z, Lindsey BD (2013) Naturally occurring contaminants in the Piedmont and Blue Ridge crystalline-rock aquifers and Piedmont Early Mesozoic basin siliciclastic-rock aquifers, eastern United States, 1994–2008: U.S. Geological Survey scientific investigations report 2013-5072, p 74
Chapman SW, Parker BL (2005) Plume persistence due to aquitard back diffusion following dense nonaqueous phase liquid source removal or isolation. Water Resour Res 41:1–16
Choi B, Yun S, Yu S, Lee P, Park S, Chae G, Mayer B (2005) Hydrochemistry of urban groundwater in Seoul, South Korea: effects of land use and pollutant recharge. Environ Geol 48:979–990
Compaore E, Namema LS, Bonkougou S, Sedogo MP (2010) Evaluation de la qualité de composts de déchets urbains solides de la ville de Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso pour une utilisation efficiente en agriculture. J Appl Biosci 33:2076–2083
Compaore E, Namema LS (2010) Compostage et qualité du compost de déchets urbains solides de la ville de Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso. Tropicultura 26:232–237
DeForest DK, Brix KV, Adams WJ (2007) Assessing metal bioaccumulation in aquatic environments: the inverse relationship between bioaccumulation factors, trophic transfer factors and exposure concentrations. Aquat Toxicol 84:236–246
Dieter HH, Bayer TA, Multhaup G (2005) Environmental copper and manganese in the pathophysiology of neurologic diseases (Alzheimer's disease and manganism). Actahydrochim Hydrobiol 33:72–78
Dippong T, Mihali C, Hoaghia MA, Cical E, Cosma A (2019) Chemical modeling of groundwater quality in the aquifer of Seini town+ Someş Plain, Northwestern Romania. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:88–101
Durov SA (1948) Natural waters and graphic representation of their composition. Dok Akad Nauk SSSR 59:87–90
Dzombak DA, Morel FMM (1990) Surface complexation modelling: hydrous ferric oxide. Wiley, New York
Edmunds WM, Darling WG, Kinniburgh DG (1988) Solute profile techniques for recharge estimation in semi-arid and arid terrain. In: Simmers I (ed) Estimation of natural groundwater recharge. Proceeding NATO advanced research workshop, Reidel, pp 139–157
Eillas JA (1980) Convenient parameter for tracing leachate from sanitary landfills. Water Res 14:1283–1287
Elango L, Kannan R (2007) Rock–water interaction and its control on chemical composition of groundwater. In: Sarkar D, Datta R, Hannigna R (eds) Development in environmental science, vol 5, , pp 229–243
Freeze AR, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall Inc, Englewood cliffs, p 604
Gad M, Dahab K, Ibrahim H (2016) Impact of iron concentration as a result of groundwater exploitation on the Nubian sandstone aquifer in El Kharga Oasis, western desert, Egypt. NRIAG J Astron Geophys 5:216–237
Gaillardet J, Dupré B, Louvat P, Allègre CJ (1999) Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem Geol 159:3–30
Gombert P (1998) Synthèse sur la géologie et hydrogéologie de série sédimentaire du sud-est du Burkina Faso. Rapport technique, Programme RESO, ATG, IWACO, Ouagadougou
Grant CA (2011) Influence of phosphate fertilizer on cadmium in agricultural soils and crops. Pedologist 3:143–155
Groen J, Schuchmann JB, Geinaert W (1988) The occurrence of high nitrate concentrations in groundwater in villages in northwestern Burkina Faso. J Afr Earth Sci 7:999–1009
Gwebu TD (2003) Environmental problems among low income urban residents: an empirical analysis of old Naledi-Gaborone. Botswana Habitat Int 27:407–427
Hajeb P, Sloth JJ, Shakibazadeh S, Mahyudin NA, Afsah-Hejri L (2014) Toxic elements in food: occurrence, binding, and reduction approaches. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 13:457–472
Hao Y, Cao B, Chen X, Yin J, Sun R, Yeh T-CJ (2012) A piecewise grey system model for study the effects of anthropogenic activities on karst hydrological processes. Water Resour Manag 27(5):1207–1220
Hasan MR, Khan MZH, Khan M, Aktar S, Rahman M, Hossain F, Hasan ASMM (2016) Heavy metals distribution and contamination in surface water of the Bay of Bengal coast. Cogent Environ Sci 2:1–12
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, 3rd edn. In: U.S. Geological Survey water-supply paper, vol 2254, p 263, 3 pls
Houben GJ, Sitnikova MA, Post VEA (2017) Terrestrial sedimentary pyrites as a potential source of trace metal release to groundwater—a case study from the Emsland, Germany. Appl Geochem 76:99–111
Hrudey SE, Hrudey EJ (2004) Safe drinking water—lessons from recent outbreaks in affluent nations. IWA Publishing, London
Huneau F, Dakouré D, Celle-Jeanton H, Vitvar J, Ito M, Traoré S, Compaoré NF, Jirakova H, Le Coustumer P (2011) Flow pattern and residence time of groundwater within the south-eastern Taoudeni sedimentary basin (Burkina Faso, Mali). J Hydrol 409:423–439
IAEA; International Atomic Energy Agency (2017) Integrated and sustainable management of shared aquifer systems and basins of the Sahel regions, Taoudeni Basin, p 126
INSD; Institut National de la Statistique et de la Démographie (2007) Résultants préliminaires du recensement général de la population et de l’habitation (RGPH) de 2006, Burkina Faso, p 51
Jalali M (2005) Nitrate leaching from agricultural land in Hamadan, western Iran. Agricult Ecosyst Environ 110:210–218
Jiao JJ, Wang XS, Nandy S (2006) Preliminary assessment of the impacts of deep foundations and land reclamation on groundwater flow in a coastal area in Hong Kong, China. Hydrogeol J 14(1–2):100–114
Kiba DI, Lompo F, Compaore E, Randriamantsoa L, Sedogo PM, Frossard E (2012) A decade of non-sorted solid urban wastes inputs safely increases sorghum yield in periurban areas of Burkina Faso. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 62:59–69
Kinané ML, Tougouma A, Ouédraogo D, Sanou M (2008) Urban farmers’ irrigation practices in Burkina Faso. Urban Agric Mag 20:25–26
Koh DC, Ko KS, Kim Y, Lee SG, Chang HW (2007) Effect of agricultural land use on the chemistry of groundwater from basaltic aquifers, Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrogeol J 15:727–743
Koterba MT, Wilde FD, Lapham WW (1995) Groundwater data-collection protocols and procedures for the National Water-Quality Assessment Program—collection and documentation of water-quality samples and related data. U.S. Geological Survey open-file report 95-399, p 114
Kubier A, Pichler T (2019) Cadmium in groundwater—a synopsis based on a large hydrogeochemical data set. Sci Total Environ (in press)
Kumar M, Kumari K, Ramamathan AL (2007) A comparative evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in two intensively cultivated districts. Environ Geol 53:553–574
Lee SM, Min KD, Woo NC, Kim YJ, Ahn CH (2003) Statistical assessment of nitrate contamination in urban groundwater using GIS. Environ Geol 44:210–221
Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Upper Han River, China. J Hazard Mater 181:1051–1058
Leckie JO, Pacey JG, Halvadakis C (1975) Accelerated refuse stabilization through controlled moisture application. In: Presented in 2nd annual national conference on environmental engineering research device design, Gainesville, July 1975 (unpublished)
Leung CM, Jiao JJ, Malpas J, Chan WT, Wang YX (2005) Factors affecting the groundwater chemistry in a highly urbanized coastal area in Hong Kong: an example from the mid-levels area. Environ Geol 48(4–5):480–495
Ma B, Jin M, Liang X, Li J (2018) Groundwater mixing and mineralization processes in a mountain–oasis–desert basin, northwest China: hydrogeochemistry and environmental tracer indicators. Hydrogeol J 26:233–250
Macpherson GI (2009) CO2 distribution in groundwater and the impact of groundwater extraction on the global C cycle. Chem Geol 264:328–336
Mahlknecht J, Steinich B, De Leon IN (2004) Groundwater chemistry and mass transfers in the Independence aquifer, central Mexico, by using multivariate statistics and mass-balance models. Environ Geol 45:781–795
Mann AG, Tam CC, Higgins CD, Rodrigues LC (2007) The association between drinking water turbidity and gastrointestinal illness: a systematic review. BMC Publ Health 7:256
Martinez JD, Johnson KS, Neal JT (1998) Sinkholes in evaporite rocks. Am Sci 86:38–51
Mapanda F, Mangwayana EN, Nyaman-gara J, Giller KE (2005) The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agric Eco-Syst Environ 107:151–165
Maya AL, Loucks MD (1995) Solute and isotopic geochemistry and groundwater flow in the Central Wasatch Range, Utah. J Hydrol 172:31–59
McMahon PB, Chapelle FH (2008) Redox processes and water quality of selected principal aquifer systems. Ground Water 46(259–271):38–51
Melegy AA, Shaban AM, Hassaan MM, Salman SA (2014) Geochemical mobilization of some heavy metals in water resources and their impact on human health in Sohag governorate. Egypt Arab J Geosci 7:4541–4552
Mirlean N, Roisenberg A (2006) The effect of emissions of fertilizer production on the environment contamination by cadmium and arsenic in southern Brazil. Environ Pollut 143:335–340
Moeck C, Affolter A, Radny D, Dressmann H, Auckenthaler A, Huggenberger P, Schirmer M (2017) Improved water resource management for a highly complex environment using three-dimensional groundwater modeling. Hydrogeol J 26:133–146
Morris BL, Lawrence AR, Chilton PJC, Adams B, Calow RC, Klinck BA (2003) A global assessment of problem and options for management. United Nations Environment Program Groundwater, Nairobi, p 140
Moussine-Pouchkine A, Bertrand-Sarfati J (1997) Tectonosedimentary subdivisions in the Neoproterozoic to Early Cambrian cover of the Taoudenni Basin (Algeria–Mauritania–Mali). J Afr Earth Sci 24:425–443
Nagarajan R, Rajmohan N, Mahendran U, Senthamikumar S (2010) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Thanjavur city, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 171:289–308
Nies DH (1999) Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:730–750
Obuobie E, Barry B (2012) Burkina Faso, in groundwater availability and use in sub Saharan Africa; a review of fifteen countries. In: Pavelic P et al (eds) International Water Management Institute, Sri Lanka
Ouédraogo C (2006) Synthèse Géologique de la Région Ouest du Burkina Faso. Programme VREO, SOFRECO-SAWES, Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso
Pan JL, Plant JA, Voulvoulis N, Oates CJ, Ihlenfeld C (2010) Cadmium levels in Europe: implications for human health. Environ Geochem Health 32:1–12
Pawar NJ, Shaikh IJ (1995) Nitrate pollution of groundwaters from shallow basaltic aquifers, Deccan trap hydrologic province, India. Environ Geol 25:197–204
Piper AM (1944) A graphical procedure in the chemical interpretation of groundwater analysis. Trans Am Geo Union 25:914–928
Prasanna MV, Chidambaram S, Srinivasamoorthy K, Anandhan P, John P (2006) A study on hydrogeochemisty along the groundwater flow path is different litho units in Gadilam river basin, Tamilnadu (India). J Ultra Chem 2:2157–17210
Puigdomenech IH (2001) Medusa, hydra-medusa: make equilibrium diagrams using sophisticated algorithms. Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm
Rajmohan N, Elango L (2005) Nutrient chemistry of groundwater in an intensively irrigated region of southern India. Environ Geol 47:820–830
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ravikumar B, Bai G, Li X (2018) Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediments, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 191:626–638
Ren W, Zhong Y, Meligrana J, Anderson B, Watt WE, Chen J, Leung H-L (2003) Urbanization, land use, and water quality in Shanghai, 1947–1996. Environ Int 29:649–659
Rosen M, Jones S (1998) Controls on the chemical composition of groundwater from alluvial aquifers in the Wanaka and Wakatipu basins, Central Otago, New Zealand. Hydrogeol J 6(2):264–281
Sako A, Yaro JM, Bamba O (2018a) Impacts of hydrogeochemical processes and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in the Upper Precambrian Sedimentary aquifer of northwestern Burkina Faso. Appl Water Sci 88:1–14
Sako A, Swadogo S, Yoni M, Nimi M, Zongo O, Bamba O (2018b) Hydrogeochemical characterization of dug well water and its suitability for domestic water supply in the village of Passakongo, Dedougou municipality, Burkina Faso. Environ Nat Resour Res 8:126–137
Sako A, Bamba O, Gordio A (2016) Hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater quality around Bomboré gold mineralized zone, Central Burkina Faso. J Geochem Explor 170:58–71
Sangare CK, Compaore E, Buerkert A, Vanclooster M, Sedogo MP, Bielders CL (2012) Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 92:207–224
Satarug S, Garrett SH, Sens A, Sens DA (2010) Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ Health Perspect 118:182–190
Schecher WD, McAvoy DC (2003) MINEQL+ chemical equilibrium modeling system, version 4.5 for Windows, user's manual. Environmental Research Software
Sidibé-Anago AG, Ouedraogo GA, Kanwé AB, Ledin I (2009) Foliage yield, chemical composition and intake characteristics of three mucuna varieties. Trop Subtrop Agroecosyst 10:75–84
Seddique AA, Ahmed KM, Shamsudduha M, Aziz Z, Hoque MA (2004) Heavy Metal pollution in groundwater in and around Narayanganj town, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Geol 23:1–12
Sivakumar MVK, Gnoumou F (1987) Agroclimatology of Africa of the West: Burkina Faso. In: Bulletin of information no. 23. ICRISAT, Pantcheru
Smedley PL, Knudsen J, Maiga D (2007) Arsenic in groundwater from mineralised Proterozoic basement rocks of Burkina Faso. Appl Geochem 22:1074–1092
Sogreah Ingénierie (1993) Notice explicative de la carte hydrogéologique 1:50000 de la région de Bobo-Dioulasso. Etude des ressources en eau souterraine de la zone sédimentaire de la région de Bobo-Dioulasso, Ministère de l'Eau, Direction Régionale de l'Eau des Hauts Bassins, Bobo Dioulasso, Burkina Faso
Sprynskyy M, Kowalkowski T, Tutu H, Cozmuta LM, Cukrowska EM, Buszewski B (2011) The adsorption properties of agricultural and forest soils towards heavy metal ions (Ni, Cu, Zn, and Cd). Soil Sediment Contam 20:12–29
Sunkari ED, Zango MS, Korboe HM (2018) Comparative analysis of fluoride concentrations in groundwaters in northern and southern Ghana: implications for the contaminant sources. Earth Syst Environ 2:103–117
Taylor RG, Scanlon B, Doll P, Rodell M, van Beek R, Wada Y, Treidel H (2012) Ground water and climate change. Nat Clim Change 3:322–329
Tirogo J, Jost A, Biaou A, Valdes-Lao D, Koussoubé Y, Ribstein P (2016) Climate variability and groundwater response: a case study in Burkina Faso (West Africa). Water 8:1–20
Traoré F (2007) Méthodes d’estimation de l’évapotranspiration réelle à l’échelle du bassin versant du Kou au Burkina Faso. Université de Liège, Mémoire de DEA en Sciences de Gestion de l’Environnement
UNEP (2010) Final review of scientific information on cadmium. United Nations Environment Programme
WHO (2008) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wallens J, Compaoré NF (2003) Renforcement de la Capacité de Gestion des Ressources en eau dans l’Agriculture Moyennant des Outils de Suivi-Évaluation—GEeau; Rapport Annuel N1 (Décembre 2001–Novembre 2002); Direction Régionale de l’Agriculture, de l’Hydraulique et des Ressources Halieutiques des Hauts Bassins: Bobo Dioulasso, Burkina Faso
Walvoord MA, Phillips FM, Stonestrom DA, Evans RD, Hartsough PC, Newman BD, Striegl RG (2003) A reservoir of nitrate beneath desert soils. Science 302:1021–1024
Wright A (1999) Groundwater contamination as a result of developing urban settlements. Water Research Commission report 514/1/99. Water Research Commission, Pretoria
Yaméogo S, Savadogo AN (2002) Les Ouverages de Captage de la ville de Ouagadougou et Leur Vulnérabilité à la Pollution. In Maiga AH, Pereira LS, Musy A (eds) Sustainable water resources management: health and productivity
Yashoda T, Reddy B, Ramana CV (2014) Pre- and post-monsoon variation in physico chemical characteristics in groundwater quality of Mindi industrial area, Visakhapatnam, India. Int J Environ Sci 4:746–753
Yidana SM, Banoeng-Yakubo B, Akabzaa TM (2010) Analysis of groundwater quality using multivariate and spatial analyses in the Keta basin, Ghana. J Afr Earth Sci 58:220–234
Zhang WJ, Jiang FB, Ou JF (2011) Global pesticide consumption and pollution: with China as a focus. Proc Int Acad Ecol Environ Sci 1:125–144
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their gratitude to Nestor Fiacre Compoaré, a water engineer from the Direction Régionale de l’Eau et de l’Assainissement des Hauts Bassins, Bobo-Dioulasso, for providing sampling and logistic support. The authors would also like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions which have greatly improved the early version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sako, A., Sawadogo, S., Nimi, M. et al. Hydrogeochemical and pollution characterization of a shallow glauconitic sandstone aquifer in a peri-urban setting of Bobo-Dioulasso, southwestern Burkina Faso. Environ Earth Sci 79, 296 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09041-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09041-z