Abstract
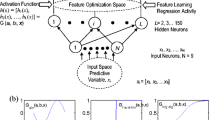
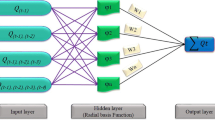
Water temperature impacts many processes in rivers, and it is determined by various environmental factors. This study proposed an extreme learning machine (ELM)-based model to predict daily water temperature for rivers. Air temperature (Ta), discharge (Q) and the day of the year (DOY) were used as predictors. Three rivers characterized by different hydrological conditions were investigated to test the modeling performances and the model results were compared with multilayer perceptron neural network (MLPNN) and simple multiple linear regression (MLR) models. Results showed that inclusion of three inputs as predictors (Ta, Q and the DOY) yielded the best modeling accuracy for all the developed models. It was also found that Q played a minor role and Ta and DOY are the most important explanatory variables for river water temperature predictions. Additionally, sigmoidal and radial basis activation functions within the ELM model performed the best for river water temperature forecasting. ELM and MLPNN models outperformed MLR model, and ELM model with sigmoidal and radial basis activation functions performed comparably to MLPNN model. Overall, results indicated that the ELM model developed in this study can be effectively used for river water temperature predictions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi-Nedushan B, St Hilaire A, Ouarda TBMJ, Bilodeau L, Robichaud É, Thiémonge N, Bobée B (2007) Predicting river water temperatures using stochastic models: case study of the Moisie River Quebec, Canada. Hydrol Process 21:21–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6353
Atkinson PM, Tatnall ARL (1997) Introduction neural networks in remote sensing. Int J Remote Sens 18(4):699–709. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311697218700
Benyahya L, Caissie D, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda TBMJ, Bobée B (2007) A review of statistical water temperature models. Can Water Resour J 32:179–192. https://doi.org/10.4296/cwrj3203179
Cha Y, Cho KH, Lee H, Kang T, Kim JH (2017) The relative importance of water temperature and residence time in predicting cyanobacteria abundance in regulated rivers. Water Res 124:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.040
Chaves P, Kojiri T (2007) Conceptual fuzzy neural network model for water quality simulation. Hydrol Process 21:634–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp
Cole JC, Maloney KO, Schmid M, McKenna JE (2014) Developing and testing temperature models for regulated systems: a case study on the Upper Delaware River. J Hydrol 519:588–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.07.058
Deo RC, Samui P, Kim D (2016) Estimation of monthly evaporative loss using relevance vector machine, extreme learning machine and multivariate adaptive regression spline models. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30:1769–1784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1153-y
Deo RC, Ghorbani MA, Samadianfard S, Maraseni T, Bilgili M, Biazar M (2018) Multi-layer perceptron hybrid model integrated with the firefly optimizer algorithm for wind speed prediction of target site using a limited set of neighboring reference station data. Renew Energy 116:309–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.09.078
DeWeber JT, Wagner T (2014) A regional neural network ensemble for predicting mean daily river water temperature. J Hydrol 517:187–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.05.035
Du X, Shrestha NK, Wang J (2019) Assessing climate change impacts on stream temperature in the Athabasca River Basin using SWAT equilibrium temperature model and its potential impacts on stream ecosystem. Sci Total Environ 650:1872–1881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.344
Gallice A, Schaefli B, Lehning M, Parlange MB, Huwald H (2015) Stream temperature prediction in ungauged basins: review of recent approaches and description of a new physics-derived statistical model. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:3727–3753. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-3727-2015
Garner G, Malcolm IA, Sadler JP, Hannah DM (2017) The role of riparian vegetation density, channel orientation and water velocity in determining river temperature dynamics. J Hydrol 553:471–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.03.024
Ghiassi M, Nangoy S (2009) A dynamic artificial neural network model for forecasting nonlinear processes. Comput Ind Eng 57:287–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2008.11.027
Ghorbani MA, Deo RC, Yaseen ZM, Kashani MH, Mohammadi B (2018a) Pan evaporation prediction using a hybrid multilayer perceptron-firefly algorithm (MLP-FFA) model: case study in North Iran. Theoret Appl Climatol 133:1119–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2244-0
Ghorbani MA, Deo RC, Karimi V, Yaseen ZM, Terzi O (2018b) Implementation of a hybrid MLP-FFA model for water level prediction of Lake Egirdir, Turkey. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 32:1683–1697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-017-1474-0
Ghorbani MA, Deo RC, Kashani MH, Shahabi M, Ghorbani S (2019) Artificial intelligence-based fast and efficient hybrid approach for spatial modelling of soil electrical conductivity. Soil Tillage Res 186:152–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.09.012
Hadzima-Nyarko M, Rabi A, Šperac M (2014) Implementation of artificial neural networks in modeling the water-air temperature relationship of the River Drava. Water Resour Manage 28:1379–1394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0557-7
Haykin S (1999) Neural networks a comprehensive foundation. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Heddam S, Kisi O (2017) Extreme learning machines: a new approach for modeling dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration with and without water quality variables as predictors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9283-z
Heddam S, Kisi O (2018) Modelling daily dissolved oxygen concentration using least square support vector machine, multivariate adaptive regression splines and M5 model tree. J Hydrol 559:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.02.061
Hornik K (1991) Approximation capabilities of multilayer Feedforward networks. Neural Netw 4(2):251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/0893-6080(91)90009-T
Hornik K, Stinchcombe M, White H (1989) Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw 2(89):359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/0893-6080 90020–8
Huang GB, Chen L (2008) Enhanced random search based incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 71:3460–3468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2007.10.008
Huang GB, Chen L, Siew CK (2006a) Universal approximation using incremental constructive feedforward networks with random hidden nodes. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(4):879–892. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2006.875977
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006b) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Huang G, Huang GB, Song S, You K (2015) Trends in extreme learning machines: a review. Neural Netw 61:32–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.10.001
Humphrey GB, Gibbs MS, Dandy GC, Maier HR (2016) A hybrid approach to monthly streamflow forecasting: integrating hydrological model outputs into a Bayesian artificial neural network. J Hydrol 540:623–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.06.026
Isaak DJ, Luce CH, Horan DL, Chandler GL, Wollrab SP, Nagel DE (2018) Global Warming of Salmon and Trout Rivers in the Northwestern U.S.: road to ruin or path through purgatory? Trans Am Fish Soc 147: 566–585. https://doi.org/10.1002/tafs.10059
Karami F, Dariane AB (2017) Optimizing signal decomposition techniques in artificial neural network-based rainfall-runoff model. Int J River Basin Manag 15:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2016.1203331
Kędra M, Wiejaczka Ł (2018) Climatic and dam-induced impacts on river water temperature: assessment and management implications. Sci Total Environ 626:1474–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.044
Khatibi R, Ghorbani MA, Pourhosseini FA (2017) Stream flow predictions using nature-inspired firefly algorithms and a multiple model strategy-directions of innovation towards next generation practices. Adv Eng Inform 34:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2017.10.002
Kim JS, Seo IW, Lyu S, Kwak S (2018a) Modeling water temperature effect in diatom (Stephanodiscus hantzschii) prediction in eutrophic rivers using a 2D contaminant transport model. J Hydro Environ Res 19:41–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2018.01.003
Kim S, Seo Y, Rezaie-Balf M, Kisi O, Ghorbani MA, Singh VP (2018b) Evaluation of daily solar radiation flux using soft computing approaches based on different meteorological information: peninsula vs continent. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2627-x
Krider LA, Magner JA, Perry J, Vondracek B, Ferrington LC (2013) Air-water temperature relationships in the trout streams of southeastern Minnesota’s carbonate-sandstone landscape. J Am Water Resour Assoc 49:896–907. https://doi.org/10.1111/jawr.12046
Kwak J, St-Hilaire A, Chebana F (2017) A comparative study for water temperature modelling in a small basin, the Fourchue River, Quebec, Canada. Hydrol Sci J 62:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2016.1174334
Liang NY, Huang GB, Rong HJ, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2006) A fast and accurate on-line sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17:1411–1423. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2006.880583
Marcé R, Armengol J (2010) Modelling river water temperature using deterministic, empirical, and hybrid formulations in a Mediterranean stream. Hydrol Process 22:3418–3430. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6955
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas imminent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478259
Piccolroaz S, Calamita E, Majone B, Gallice A, Siviglia A, Toffolon M (2016) Prediction of river water temperature: a comparison between a new family of hybrid models and statistical approaches. Hydrol Process 30:3901–3917. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10913
Piotrowski AP, Napiorkowski JJ (2018) Performance of the air2stream model that relates air and stream water temperatures depends on the calibration method. J Hydrol 561:395–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.016
Piotrowski AP, Osuch M, Napiorkowski MJ, Rowinski PM, Napiorkowski JJ (2014) Comparing large number of metaheuristics for artificial neural networks training to predict water temperature in a natural river. Comput Geosci 64:136–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.12.013
Piotrowski AP, Napiorkowski MJ, Napiorkowski JJ, Osuch M (2015) Comparing various artificial neural network types for water temperature prediction in rivers. J Hydrol 529:302–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.07.044
Pohle I, Helliwell R, Aube C, Gibbs S, Spencer M, Spezia L (2018) Citizen science evidence from the past century shows that Scottish rivers are warming. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.325
Rabi A, Hadzima-Nyarko M, Sperac M (2015) Modelling river temperature from air temperature in the River Drava (Croatia). Hydrol Sci J 60:1490–1507. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.914215
Rezaie-Balf M, Kisi O (2017) New formulation for forecasting streamflow: evolutionary polynomial regression vs. extreme learning machine. Hydrol Res 49:939–953. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2017.283
Sahoo GB, Schladow SG, Reuter JE (2009) Forecasting stream water temperature using regression analysis, artificial neural network, and chaotic non-linear dynamic models. J Hydrol 378:325–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.09.037
Samadianfard S, Ghorbani MA, Mohammadi B (2018) Forecasting soil temperature at multiple-depth with a hybrid artificial neural network model coupled-hybrid firefly optimizer algorithm. Inform Process Agric 5:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2018.06.005
Šiljić Tomić A, Antanasijević D, Ristić M, Perić-Grujić A, Pocajt V (2018a) A linear and non-linear polynomial neural network modeling of dissolved oxygen content in surface water: inter- and extrapolation performance with inputs significance analysis. Sci Total Environ 610–611:1038–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.192
Šiljić Tomić A, Antanasijević D, Ristić M, Perić-Grujić A, Pocajt V (2018b) Application of experimental design for the optimization of artificial neural network-based water quality model: a case study of dissolved oxygen prediction. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:9360–9370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1246-5
Temizyurek M, Dadasercelik F (2018) Modelling the effects of meteorological parameters on water temperature using artificial neural networks. Water Sci Technol 77:1724–1733. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.058
Toffolon M, Piccolroaz S (2015) A hybrid model for river water temperature as a function of air temperature and discharge. Environ Res Lett 10:114011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/11/114011
Trichakis IC, Nikolos IK, Karatzas GP (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) based modeling for Karstic groundwater level simulation. Water Resour Manage 25:1143–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9628-6
Van Vliet MTH, Ludwig F, Zwolsman JJG, Weedon GP, Kabat P (2011) Global river temperatures and sensitivity to atmospheric warming and changes in river flow. Water Resour Res 47:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010WR009198
Van Vliet MTH, Yearsley JR, Franssen WHP, Ludwig F, Haddeland I, Lettenmaier DP, Kabat P (2012) Coupled daily streamflow and water temperature modeling in large river basins. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:4303–4321. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-4303-2012
Vasu NN, Lee SR (2016) A hybrid feature selection algorithm integrating an extreme learning machine for landslide susceptibility modeling of Mt. Woomyeon, South Korea. Geomorphology 263:50–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.03.023
Webb BW, Clack PD, Walling DE (2003) Water-air temperature relationships in a Devon river system and the role of flow. Hydrol Process 17:3069–3084. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1280
Williamson RJ, Entwistle NS, Collins DN (2018) Meltwater temperature in streams draining Alpine glaciers. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.215
Yaseen ZM, Jaafar O, Deo RC, Kisi O, Adamowski J, Quilty J, El-Shafie A (2016) Stream-flow forecasting using extreme learning machines: a case study in a semi-arid region in Iraq. J Hydrol 542:603–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.09.035
Zhu S, Nyarko EK, Nyarko MH (2018a) Modelling daily water temperature from air temperature for the Missouri River. Peer J 6:e4894. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4894
Zhu S, Heddam S, Nyarko EK, Hadzima-Nyarko M, Piccolroaz S, Wu S (2018b) Modeling daily water temperature for rivers: comparison between adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems and artificial neural networks models. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3650-2
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0407200), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M640499), and the research project from Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute (Y118009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Heddam, S., Wu, S. et al. Extreme learning machine-based prediction of daily water temperature for rivers. Environ Earth Sci 78, 202 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8202-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8202-7