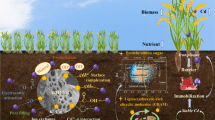
Abstract
Benzimidazole-based fungicide methyl-2-benzimidazole carbamate (MBC) has been assessed for its adsorptive pattern in seven soils of variable composition via batch equilibrium process. Adsorbed MBC expressed variable affinity towards the soil with linear adsorption coefficient (Kd) ranging between 11 and 59 µg mL−1 and Freundlich adsorption coefficient (Kf) ranging between 2.55 and 6.22 µg mL−1. Weaker bonding between MBC and selected soils was reflected via negative values of ∆G. Furthermore, statistical evaluation exhibited that soil organic matter and adsorption varied in a direct proportionality (R2 = 0.75) while pH of the soils and adsorption expressed an inverse relationship for all soils (R2 = − 0.81 and p = 0.02). MBC-adsorbed soils were further remediated in a cost-effective assay through the utilization of concentrated sulphuric acid-activated Saccharum officinarum biomass. Remediation assays showed 51% and 68% of MBC removal achieved with 5 and 7.5 ppm. Furthermore, microbial communities were also utilized for biodegradation of MBC in which A. niger and P. chrysogenum succeeded all microbes in removing MBC in water samples (89%). One way analysis of variance (ANOVA) confirmed the significance of the results. Current investigation presents a complete account of MBC surficial behaviour in soils, its sustainable management at macro scale and MBC biodegradation at microscale. This investigation can be further extended to the metabolite exploration and use of current managerial modes for those metabolites’ removal.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad KS (2017a) Green electrokinetic remediation of Thiabendazole adsorbed soils via mineralization. Agrochimica 61(3):190–205
Ahmad KS (2017b) Determination of Rimsulfuron sorption parameters in eight Pakistani soils. Agrochimica 61(2):140–153
Ahmad KS (2017c) Pedospheric sorption investigation of sulfonyl urea herbicide Triasulfuron via regression correlation analysis in selected soils. J S Afr Chem 70(1):163–170
Ahmad KS (2018a) Evaluating the adsorption potential of alachlor and its subsequent removal from soils via activated carbon. Soil Sediment Contam 16:1–8
Ahmad KS (2018b) Sorption and Juglans regia-derived activated carbon-mediated removal of aniline-based herbicide Alachlor from contaminated soils. Environ Earth Sci 77(12):437
Ahmad KS, Rashid N, Tazaiyen S, Zakria M (2011) Sorption-desorption characteristics of benzimidazole based fungicide 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole on physicochemical properties of selected Pakistani soils. J Chem Soc Pak 36(6):1189–1195
Ahmad KS, Rashid N, Nazar MF, Tazaiyen S (2013) Adsorption and desorption characteristic of benzimidazole based fungicide carbendazim in Pakistani soils. J Chem Soc Pak 35(3):1017–1024
Ahmad KS, Rashid N, Zakria M (2015) Adsorption and desorption characteristic of metsulfuron-methyl in Pakistani soils. J Chem Soc Pak 37(2):380–389
Arthur JD, Mark NW, Taylor S, Šimunek J, Brusseau ML, Dontsova KM (2017) Batch soil adsorption and column transport studies of 2, 4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) in soils. J Contam Hydrol 199:14–23
Bourguet D, Guillemaud T (2016) The hidden and external costs of pesticide use. In: Sustainable agriculture reviews. Springer, pp 35–120
Cai S, Cai T, Liu S, Yang Q, He J, Chen L, Hu J (2014) Biodegradation of N-methylpyrrolidone by Paracoccus sp. NMD-4 and its degradation pathway. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 93:70–77
Cao L, Xu J, Li M, Wu G, Wang J, Guan Y, He J, Li S, Hong Q (2013) Characterization and analysis of three newly isolated hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-degrading strains. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:407–412
Chen M, Xu P, Zeng G, Yang C, Huang D, Zhang J (2015) Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol Adv 33(6):745–755
Chen KL, Liu LC, Chen WR (2017) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics in high organic content soils. Envir Pollut 231:1163–1171
Cheng Z, Li C, Kennes C, Ye J, Chen D, Zhang S, Chen J, Yu J (2017) Improved biodegradation potential of chlorobenzene by a mixed fungal-bacterial consortium. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 123:276–285
Condron L, Stark C, O’Callaghan M, Clinton P, Huang Z (2010) The role of microbial communities in the formation and decomposition of soil organic matter. In: Soil microbiology and sustainable crop production. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 81–118
Cycoń M, Mrozik A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2017) Bioaugmentation as a strategy for the remediation of pesticide-polluted soil: a review. Chemosphere 172:52–71
Dhanya MS (2014) Advances in microbial biodegradation of chlorpyrifos. J Envir Res Dev 9(1):232–238
Garba A, Basri H, Nasri NS, Isma’il R (2016) Synthesis and characterization of porous carbon from biomass using KOH and K2CO3 chemical activation. ARPN J Eng Appl Sci 11:1613–1617
Harasim P, Filipek T (2015) Nickel in the environment. J Element 20(2):525–534
Jacquet P, Daudé D, Bzdrenga J, Masson P, Elias M, Chabrière E (2016) Current and emerging strategies for organophosphate decontamination: special focus on hyperstable enzymes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(9):8200–8218
Kalderis D, Koutoulakis D, Paraskeva P, Diamadopoulos E, Otal E, del Valle JO, Fernández-Pereira C (2008) Adsorption of polluting substances on activated carbons prepared from rice husk and sugarcane bagasse. J Chem Eng 144(1):42–50
Khodaei K, Nassery HR, Asadi MM, Mohammadzadeh H, Mahmoodlu MG (2017) BTEX biodegradation in contaminated groundwater using a novel strain (Pseudomonas sp. BTEX-30). Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 116:234–242
Kumar A, Trefault N, Olaniran AO (2016) Microbial degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid: insight into the enzymes and catabolic genes involved, their regulation and biotechnological implications. Crit Rev Microbiol 42(2):194–208
Li Y, Dong F, Liu X, Xu J, Li J, Kong Z, Chen X, Zheng Y (2012) Environmental behavior of the chiral triazole fungicide fenbuconazole and its chiral metabolites: enantioselective transformation and degradation in soils. Envir Sci Technol 46(5):2675–2683
Liu X, Wu H, Hu T, Chen X, Ding X (2018) Adsorption and leaching of novel fungicide pyraoxystrobin on soils by 14C tracing method. Environ Monit Assess 190(2):86–90
Maznah Z, Halimah M, Ismail BS (2018) Evaluation of the persistence and leaching behaviour of thiram fungicide in soil, water and oil palm leaves. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100(5):677–682
Morillo E, Villaverde J (2017) Advanced technologies for the remediation of pesticide-contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 586:576–597
Muhamad H, Ai TY, Sahid I, Mat N (2010) Downward movement of chlorpyrifos in the soil of an oil palm plantation in Sepang, Selangor, Malaysia. J Oil Palm Res 22:721–728
Muhamad SG, Shareef KM, Smail HA (2011) Thermal adsorption and catalytic photodegradation studies of carbendazim fungicide in natural soil and water. J Int Chem 3(2):218–222
OECD (2000) Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Adsorption-desorption using a batch equilibrium method
Panadés R, Ibarz A, Esplugas S (2000) Photodecomposition of carbendazim in aqueous solutions. Water Res 34(11):2951–2954
Parameswaran B (2009) Sugarcane Bagasse. In: Pandey P A. (eds) Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilisation Singh nee’ Nigam. Springer, Dordrecht
Park MK, Liu KH, Lim Y, Lee YH (2013) Biotransformation of a Fungicide Ethaboxam by Soil Fungus CunninghameUa. J Microbiol Biotechnol 13(1):43–49
Perveen S, Malik Z, Nazif W (2010) Fertility status of vegetable growing areas of Peshawar, Pakistan. Pak J Bot 42(3):1871–1880
Rajamanickam R, Kaliyamoorthi K, Ramachandran N, Baskaran D, Krishnan J (2017) Batch biodegradation of toluene by mixed microbial consortia and its kinetics. Int Biodeterior Biodeg 119:282–288
Rico A, Sabater C, Castillo M (2016) Lethal and sub-lethal effects of five pesticides used in rice farming on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 127:222–229
Saien J, Khezrianjoo S (2008) Degradation of the fungicide carbendazim in aqueous solutions with UV/TiO2 process: optimization, kinetics and toxicity studies. J Hazard Mater 157(2–3):269–276
Santhi T, Manonmani S, Smitha T (2010) Kinetics and isotherm studies on cationic dyes adsorption onto Annona squmosa seed activated carbon. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2(3):287–295
Shan J, Jiang B, Yu B, Li C, Sun Y, Guo H, Wu J, Klumpp E, Schäffer A, Ji R (2011) Isomer-specific degradation of branched and linear 4-nonylphenol isomers in an oxic soil. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8283–8289
Shiva V (2016) The violence of the green revolution: third world agriculture, ecology, and politics. University Press of Kentucky
Thangadurai P, Suresh S (2014) Biodegradation of endosulfan by soil bacterial cultures. Int Biodeterior Biodeg 94:38–47
Zhang L, Qiao X, Ma L (2009) Influence of environmental factors on degradation of carbendazim by Bacillus pumilus strain NY97-1. J Int Envir Poll 38(3):309–317
Zhang H, Zhang Y, Hou Z, Wang X, Wang J, Lu Z, Zhao X, Sun F, Pan H (2016) Biodegradation potential of deltamethrin by the Bacillus cereus strain Y1 in both culture and contaminated soil. Int Biodeterior Biodeg 106:53–59
Zhang S, Yang Q, Yang X, Wang W, Li Z, Zhang L, Wang C, Wang Z (2017) A zeolitic imidazolate framework based nanoporous carbon as a novel fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction of pyrethroid pesticides. Talanta 166:46–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, K.S. Carbendazole lithospheric adsorption, Saccharum officinarum-based remediation and microbial degradation in heterogeneously composed soils. Environ Earth Sci 78, 31 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-8000-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-8000-7