Abstract
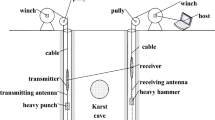
This paper studies karst cave and soil cavity development in the process of karst collapse as a means of disaster prevention and control. Using the karst area of the Shandong section of the Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway as a test area, a numerical simulation method is presented as well as the model test to study the characteristics of typical radar images of different types of karst caves and soil cavities. By combining theoretical analysis with field test results, the method and characteristic standards for nondestructive testing using ground-penetrating radar to determine the grouting effect on a karst roadbed are given. The radar spectrum characteristics are analyzed for a cave, water-filled cave, clay-filled cave, karst cave with dense grouting and karst cave with grouting that is not dense. Comprehensive analysis of the results of indoor model testing and numerical analysis, combined with the engineering practice of evaluating the effect of grouting treatment in the selected section of the Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway, clarifies the basic characteristics of map recognition of radar detection of karst grouting. The morphological characteristics of the karst caves in the geological radar images are usually composed of many hyperbolic strong reflection waves. Multiple-reflection wave groups of high amplitude, low frequency, and equal distance indicate the side wall of the cave. The bottom interface of the cave is not obvious, although when the bottom part of the cave is filled with water or clay, silt, sand and gravel material. The bottom of the reflection wave will be enhanced. When the cave is filled with material, the electromagnetic wave energy decays rapidly, the high-frequency part is absorbed, and the reflection is mostly low frequency wave. The characteristics of radar images of the slurry distribution area are obvious in the grouting zone. A horizontal direction results in arc-shaped distribution, and a vertical direction has more regular distribution. The results of the study are helpful in the exploration of karst caves and soil caves, and the evaluation of the effect of grouting treatment in mitigating karst collapse.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Z (2014) Model test on grouting quality detection of karst subgrade by high density resistivity method. Southwest Jiaotong University
Galve JP, Guerrero J, Alonso J, Diego I (2012) Optimizing the application of geosynthetics to roads in sinkhole-prone areas on the basis of hazard models and cost-benefit analyses. Geotext Geomembr 34:80–92
Guo M (2009) Technology research on real-time monitoring for treatment effect of karst geological conditions in Beijing-Shanghai High-speed Railway. Beijing Jiaotong University
Jiang X, Lei M, Gu W, Zhang M (2008) Soil cave monitoring and sinkhole prediction in linear engineering: summarization. Carsol Sin 2:172–176
Liu K, Liu H, Pei J (2011) GPR simulation analysis of karst collapse. Chin J Eng Geophys 8(3):334–338
Mingtang L, Xiaozhen J, Yu L, Zhou L (2000) The risk assessment of karst collapse in urban area—a case study in Liupanshui, Guizhou, China. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 4:26–30
Ren X (2012) Study on grouting detection method and assessment indicators of karst roadbed grouting effect in Nanning-Guangzhou Railway. Southwest Jiaotong University
Wang M (2007) Research on forward numerical simulation and indoor experiment of GPR in highway tunnel lining. Tongji University
Zheng X (2010) Research on genetic mechanism and risk evaluation of karst collapse in Guanghua Basin. Central South University
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 41672339).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of the Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on Karst Hydrogeology: Advances in Karst Collapse Studies, edited by Dr. Zhou Wanfang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, M., Chen, Y., Wang, C. et al. Radar spectral analysis and evaluation of the effect of grouting treatment in karst caves and soil caves. Environ Earth Sci 77, 795 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7980-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7980-7