Abstract
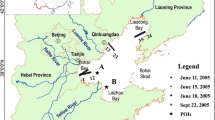
Concentrations of suspended solids in lakes can affect the latter’s primary productivity and reflect changes in sediment deposition. Determining the temporal and spatial distribution of suspended solid concentrations has important significance in lake water environmental management; this is particularly urgent for Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. In this study, suspended solid concentration inversion models for Poyang Lake were created using a semi-empirical method with regression analysis between continuously measured suspended solid concentration data and multi-band moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer images for spring, summer, autumn, and winter from 2009 to 2012. The coefficient of determination (R2) is from 0.6 to 0.9 and the average relative error for the accuracy verification was between 10 and 30%. The seasonal distributions of suspended solid concentrations in Poyang Lake from 2000 to 2013 were then obtained using optimal reversal models. The results showed that the seasonal variation in suspended solid concentrations had a “W” shape in which high spring and autumn and low summer and winter values. The suspended solid concentrations increased annually from 2000 to 2013 and were mainly distributed in the northern and central portions of the lake, with lower values along the shorelines. Further analysis indicated that the large difference in water level between the wet and dry seasons is an important factor in explaining these seasonal variations. Moreover, the suspended solid concentrations were poorly correlated with water temperature and chlorophyll-a concentration but more highly correlated with the deferred chlorophyll-a concentration.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown OB, Jacobs MM (1975) Computed relationships between the inherent and apparent optical properties of a flat homogenous ocean. Appl Opt 14(2):417–427
Chen J (2009) The research of scaling effect and accuracy assessments of quantitative model for suspended sediment concentration of case II waters: a case study on Taihu Lake. China University of Geosciences, Beijing
Chen X, Wu Y, Tian L (2007) Inversion model for dynamic monitoring of suspended sediment: a case study on Poyang Lake. Sci Technol Rev 25(06):19–22
Chen J, Quan W, Wen Z (2013a) An improved three-band semi-analytical algorithm for estimating chlorophyll-a concentration in highly turbid coastal waters: a case study of the Yellow River estuary, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(8):2709–2719
Chen J, Zhang X, Quan W (2013b) Retrieval chlorophyll-a concentration from coastal waters: three-band semi-analytical algorithms comparison and development. Opt Express 21(7):9024–9042
Chen F, Xiao D, Li Z (2016) Developing water quality retrieval models with in situ hyperspectral data in Poyang Lake, China. Geo-spat Inf Sci 19(4):255–266
Cohen WB, Maiersperger TK, Gower ST (2003) An improved strategy for regression of biophysical variables and Landsat ETM+ data. Remote Sens Environ 84(4):561–571
Cui L, Qiu Y, Fei T, Liu Y, Wu G (2013) Using remotely sensed suspended sediment concentration variation to improve management of Poyang Lake, China. Lake Reserv Manag 29:1,47–60
Dai Z, Zhang W, Chan X et al (2013) Monitoring TSM by HJ CCD imagery index in Poyang Lake. Geomat Inf Sci Wuhan Univ 38(11):1303–1307
Dekker A, Vos R, Peters S (2001) Comparison of remote sensing data, model results and in situ data for total suspended matter (TSM) in the southern Frisian lakes. Sci Total Environ 268(1):197–214
Gartner JW (2004) Estimating suspended solids concentrations from backscatter intensity measured by acoustic Doppler current profiler in San Francisco Bay, California. Mar Geol 211(3–4):169–187
Haldna M, Milius A, Laugaste R, Kangur K (2008) Nutrients and phytoplankton in Lake Peipsi during two periods that differed in water level and temperature. Hydrobiologia 599(1):3–11
Hu C (2009) A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens Environ 113(10):2118–2129
Huang H, Peng X, Kong F (2014) Evaluation of ecological economy index in the poyang lake ecological economic zone. Acta Ecol Sin 34(11):3107–3114
Jiang H, Liu Y (2011) Monitoring of TSS concentration in Poyang Lake based on MODIS data. Yangtze River 42(17):87–90
Lai X, Shankman D, Huber C et al (2014) Sand mining and increasing Poyang Lake’s discharge ability: a reassessment of causes for lake decline in China[J]. J Hydrol 519:1698–1706
Lei P (2012) The establishment and application of semi-analysis model on suspended sediment remote sensing inversion in Caofeidian Offshore water. Chang’an University, Xian
Li J (1986) A study on determination of concentration of suspended solids in water by remote sensing. Acta Sci Circum 6(2):166–173
Li X (1992) An united equation for remote sensing quantitative analysis of supended sediment and its application at Zhujiang River Estuary. Remote Sens Environ China 7(2):106–114
Li H, Chen X, Lu J et al (2016) Numerical simulation of suspended sediment concentration in Lake Poyang during flood season considering dredging activities. J Lake Sci 28(2):421–431
Liu Z, Ni Z (2015) The rules and the effects of varing river-lake relationships on the evolution of Poyang Lake. Acta Sci Circum 35(5):1265–1273
Liu Q, Rossiter DG (2008) Estimation on suspended sedimentation concentration of Poyang Lake using MODIS and hyperspectral data. Remote Sens Technol Appl 23(1):7–11
Liu Z, Li Y, Tan J (2012) Construction of semi-analytical model for inversing total suspended matter in Lake Taihu and Chaohu and assessment of its applicability. Environ Sci 33(09):3000–3008
Liu J, Zhang Q, Gu X (2015) Evaluation of ecological flow with considerations of hydrological alterations in the Poyang Lake basin. Acta Ecol Sin 35(16):5477–5485
Ma Y, Ma Y (2003) Protection and utilization of Poyang Lake Wetland. Territ Nat Resour Study 4:66–67
Ma R, Tang J (2009) Progress in lake water color remote sensing. J Lake Sci 21(2):143–158
Miller RL, McKee BA (2004) Using MODIS Terra 250 m imagery to map concentrations of total suspended matter in coastal waters. Remote Sens Environ 93(1):259–266
Min Q (1995) On the regularities of water level fluctuations in Poyang Lake. J Lake Sci 7(3):281–288
Shi K, Li Y, Liu Z (2011) Estimation of total suspended matter concentration based on semi-analysis algorithm in Inland turbid waters. Environ Sci 32(06):1571–1580
Thormann MN, Bayley SE, Szumigalski AR (1997) Effects of hydrologic charges on above ground production and surface water chemistry in two boreal peatlands in Alberia: implications for global warming. Hydrobiologia 362(1–3):171–183
Wan B, Jiang H (2011) Thoughts on national environmental monitoring in “12th five-year plan”. Environ Monit China 27(1):2–4
Wang X (2004) Assessment of wetland ecological system of Poyang Lake. Science Press, Beijing
Wang S (2016) Ecological security of Poyang Lake. Science Press, Beijing
Wang S, Dou H (1998) Chinese Journal of lakes. Science Press, Beijing
Wang J, Zhang Y, Yang F, Cao X (2015) Spatial and temporal variations of chlorophyll-a, concentration from 2009 to 2012 in Poyang Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 73(8):4063–4075
Yin Z, Zhang J (1987) The hydrological features of Poyang Lake (II). Oceanol Limnol Sin 18(2):22–27
Zhang Y (2013) Estimation of chlorophyll a concentration in Poyang Lake based on measured spectral analysis and MODIS data. China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing
Zhang W, Chen X, Tian L et al (2010) Suspended sediment monitoring in Poyang Lake using HJ-1-A/B CCD imagery. Geomat Inf Sci Wuhan Univ 35(12):1466–1469
Zhang R, Jiang Y, Wan J (2014) Effect of urbanization on the ecosystem of Poyang Lake. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 23(3):400–406
Zhou Y, Wang H, Yao L (2004) Analysis of the ecological environment in Poyang Lake area and comprehensive countermeasures. Environ Pollut Control 26(2):159
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Class A Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA19040501), National Science Foundation of China (41421001, 41501477), Science & Technology Basic Research Program of China (2013FY114600), Specific Informatization Scientific Research Science Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XXH13505-07), and the foundation of Chinese Academy of Forestry (CAFYBB2016QB021). Additional thanks are due to the Lake Poyang Laboratory for Wetland Ecosystem Research (PLWER) for providing long-term in situ measured data and to Junxiang Zhu and Yujie Zhou for their data preprocessing work. Special thanks are given to anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Chen, E., Li, G. et al. Spatial and temporal variations of suspended solid concentrations from 2000 to 2013 in Poyang Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 77, 590 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7773-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7773-z