Abstract
The paper presents distribution of radionuclide elements for different samples of igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks in the south of Mugla city, Turkey. The composite image maps for each of radioelement ratios (eU, eTh and K), radiogenic heat-producing map (RHP) and absorbed dose rate of these radionuclides in air were calculated and generated anomaly maps. The obtained results were compared with geological units of the study area. It has been observed that western side of the study area (the Bodrum Peninsula) is mainly characterized volcanic rocks that display high radioactivity concentrations (for U, Th, and K, 120.2 Bq/kg, 101.60 Bq/kg, and 690.1 Bq/kg, respectively). The latite–andesite association causes higher Th concentrations (varying between 1.5 and 101.6 Bq/kg). Higher U and Th anomalies are close relation with the mineral compositions of the volcanic rocks and their silica contents. Due to K-bearing minerals such as K-feldspar (orthoclase, sanidine, biotite) higher K concentrations are determined. On the other hand, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks is dominant in the eastern side of the study area. The sedimentary units have the lowest radioactive concentrations (for U, Th, and K, 8, 0.20, and 24 Bq/kg, respectively), whereas marble and cherty marbles has higher U and K concentrations. It has been also seen that schist and calc-schists exhibit important thorium enrichment (80–100 Bq/kg).


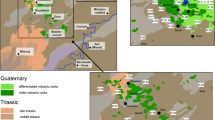
(Modified from1/500,000 digital geological maps database of Mineral Research and Exploration General Directorate). Red circles show the measurement points, b maximized geological map of Bodrum Peninsula





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Trabulsy HA, Khater AEM, Habbani FI (2011) Radioactivity levels and radiological hazard indices at the Saudi coastline of the Gulf of Aqaba. Radiat Phys Chem 80:343–348
Chiozzi P, Pasquale V, Verdoya M (1998) Ground radiometric survey of U, Th and K on the Lipari Island, Italy. J Appl Geophys 38:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9851(97)00035-9
Chiozzi P, De Felice P, Pasquale V (1999) Field γ-ray spectrometry on the Vulcano island (Aeolian Arc, Italy). Appl Radiat Isot 51:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8043(98)00181-X
Chiozzi P, Pasquale V, Verdoya M, Minato S (2001) Natural gamma-radiation in the Aeolian volcanic arc. Appl Radiat Isot 55:737–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8043(01)00127-0
Doretti L, Ferrar D, Barison G, Gerbasi R, Battiston G (1992) Natural radionuclides in the muds and waters used in thermal therapy in Abano Terme, Italy. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 45(1):175–178
Duval JS (1983) Composite colour images of aerial gamma-ray spectrometry data. Geophysics 48:722–735
Ebaid YY, El-Tahawy MS, El-Lakany et al (2000) Environmental radioactivity measurements of Egyptian soils. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 243:543–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2014.07.232
Eggeling L, Genter A, Kölbel T, Münch W (2013) Impact of natural radionuclides on geothermal exploitation in the Upper Rhine Graben. Geothermics 47:80–88
Ercan T, Günay E, Turkecan A (1984) Petrology of the igneous rocks of the Bodrum Peninsula and their genetic implication. Bull Geol Soc Turk 27:85–98
Erees FS, Akozcan S, Parlak Y, Cam S (2006) Assessment of dose rates around Manisa (Turkey). Radiat Meas 41:598–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.11.004
Florou H, Kriditis P (1992) Gamma radiation measurements and dose rate in the coastal areas of a volcanic island, Aegan Sea, Greece. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 45:277–279
Genc SC, Karacık Z, Altunkaynak S, Yılmaz Y (2001) Geology of a magmatic complex in the Bodrum peninsula, SW Turkey. International Earth Sciences Colloquium on the Aegean Region, I˙zmir, pp 63–68
Haenel R, Rybach L, Stegena L (1988) Handbook of terrestrial heat-flow density determination. Solid Earth Sciences Library, vol 4, Springer, Netherlands, p 486. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-2847-3
Hurley WB, (2009) Natural Radioactivity in the Geologic Environment. National Nuclear Security Administration, Nevada Site Office
IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency (1989) Construction and use of calibration facilities for radiometric field equipment. In: Proceedings of IAEA technical reports series 309, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, p 123
IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency (1991) Airborne gamma ray spectrometer surveying. In: Proceedings of IAEA technical reports series 323, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, p 116
IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency (2003) Guidelines for radioelement mapping using gamma ray spectrometry data. In: Proceedings of IAEA technical reports series 1363, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, p 179
Jaupart C, Mareschal JC (2013) Constraints on crustal heat production from heat flow data. Treatise Geochem Second Ed 4:53–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00302-8
Kalyoncuoglu UY (2015) In situ gamma source radioactivity measurement in Isparta plain. Turk Environ Earth Sci 73:3159–3175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3610-1
Karagianni EE, Papazachos CB (2007) Shear velocity structure in the Aegean region obtained by joint inversion of Rayleigh and Love waves. In: Taymaz T, Yilmaz Y, Dilek Y (eds) The geodynamics of the Aegean and Anatolia, vol 291. Geological Society London Special Publication, London, pp 159–181
Karahan G, Bayulken A (2000) Assessment of gamma dose rates around Istanbul. Turk Environ Radioact 47:213–221
Kathren RL (1998) NORM sources and their origins. Appl Radiat Isot 49(3):149–168
Kukkonen IT, Lahtinen R (2001) Variation of radiogenic heat production rate in 2.8–1.8 Ga old rocks in the Central Fennoscandian shield. Phys Earth Planet Interiors 126:279–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9201(01)00261-8
Kumar PS, Reddy GK (2004) Radioelements and heat production of an exposed Archaean crustal cross-section, Dharwar craton, south India. Earth Planet Sci Lett 224:309–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.05.032
Kumar PS, Menon R, Reddy GK (2007) The role of radiogenic heat production in the thermal evolution of a Proterozoic granulite-facies orogenic belt: Eastern Ghats, Indian Shield. Earth Planet Sci Lett 254:39–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2006.11.018
Maden N, Akaryali E (2015) A review for genesis of continental arc magmas: U, Th, K and radiogenic heat production data from the Gümüşhane Pluton in the Eastern Pontides (NE Türkiye). Tectonophysics 664:225–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.09.023
Marchalland CP, Fairbridge RW (1999) Encyclopedia of geochemistry. Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht
Mareschal JC, Jaupart C, Gariépy C, Cheng LZ, Guillou-Frottier L, Bienfait G, Lapointe R (2000) Heat flow and deep thermal structure near the southeastern edge of the Canadian Shield. Can J Earth Sci 37:399–414. https://doi.org/10.1139/e98-106
Narayana Y, Somashekarappa HM, Karunakara N, Avadhani DN, Mahesh HM, Siddappa K (2001) Natural Radioactivity in the soil samples of coastal Karnataka of South India. Health Phys 80:24–33
Narayana Y, Shetty PK, Siddappa K (2005) Enrichment of natural radionuclides in monazite areas of coastal Kerala. Int Congr Ser 1276:333–334
Perry HKC, Jaupart C, Mareschal J, Bienfait G (2006) Crustal heat production in the Superior Province and in North America inferred from heat flow data. Can Shield 111:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB003893
Ramasamy V, Paramasivam K, Suresh G, Jose MT (2014) Role of sediment characteristics on natural radiation level of the Vaigai river sediment, Tamil Nadu, India. J Environ Radioact 127:64–74
Ramola RC, Manjulata Y, Gusain GS (2014) Distribution of natural radionuclide along Main Central Thrust in Garhwal Himalaya. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:614–619
Ray L, Roy S, Srinivasan R (2008) High radiogenic heat production in the Kerala Khondalite Block, Southern Granulite Province. India. Int J Earth Sci 97:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-007-0278-8
Rosner G, Bunzl K, Hötzl H, Winkler R (1984) Low level measurements of natural radionuclides in soil samples around a coal-fired power plant. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res 223:585–589
Rybach L (1988) Determination of the heat production rate. In: Haenel R, Rybach L, Stegena L (eds) Handbook of Terrestrial Heat-Flow Density Determination. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 125–142
Saqan SA, Kullab MK, Ismail AM (2001) Radionuclides in hot mineral spring waters in Jordan. J Environ Radioact 52:99–107
Saunders P, Priestley K, Taymaz T (1998) Variations in the crustal structure beneath western Turkey. Geophys J Int 134:373–389
Sayın N (2013) Radioactive element contents of some granites used as building materials: insights into the radiological hazards. Bull Eng Geol Environ 72:579–587
Selvasekarapandian S, Sivakumar R, Manikandan NM, Meenakshisundaram V, Raghunath VM, Gajenndran V (2000) Natural radionuclide distribution in soils of Gudalore, India. Appl Radiat Isot 52:299–306
Tan G, Li C, Li M, (1991) Investigation of environment natural penetrating radiation level in Guangdong Province. Radiat Prot (in Chinese with English abstract) 11:47–57
Telford W, Sheriff R (1990) Applied Geophysics. Cambridge University Press, p 770. ISBN:9781139635691
Tezel T, Erduran M, Alptekin O (2007) Crustal shear wave velocity structure of Turkey by surface wave dispersion analysis. Ann Geophys 50:177–190
UNSCEAR United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (2000) Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, United Nations, New York
Van Schmus WR (1995) Natural radioactivity of the crust and mantle. A Handbook of Physical Constants (AGU Reference Shelf 1), Global Earth Physics, pp 283–291. https://doi.org/10.1029/RF001p0283
Wang Q, Song J, Li X, Yuan H, Li N, Cao L (2016) Environmental evolution records reflected by radionuclides in the sediment of coastal wetlands: a case study in the Yellow River Estuary wetland. J Environ Radioact 162–163:87–96
Youssef MAS, Elkhodary ST (2013) Utilization of airborne gamma ray spectrometric data for geological mapping, radioactive mineral exploration and environmental monitoring of southeastern Aswan city, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Geophys J Int 195:1689–1700. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt375
Zhu L, Mitchell BJ, Akyol N, Cemen I, Kekovali K (2006) Crustal thickness variations in the agean region and implications fot the extension of continental crust, Journal of. Geophys Res 111:B01301
Acknowledgements
This work is primarily supported by Suleyman Demirel University (Project No. 05283-DR-14). The authors greatly appreciate constructive and thoughtful comments from an anonymous reviewers and Dr. James W. LaMoreaux (Editor).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erbek, E., Dolmaz, M.N. In situ measurements of radionuclide concentrations in south of Mugla city, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 77, 377 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7562-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7562-8