Abstract
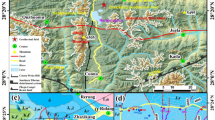
Niutuozhen geothermal field is located in the Jizhong graben, belonging to the northern part of Bohai Bay Basin in North China. Chemical and isotopic analyses were carried out on 14 samples of the geothermal fluids discharged from Neogene Minghuazhen (Nm), Guantao (Ng), and Jixianian Wumishan (Jxw) formations. The δ2H and δ18O in water, δ13C in CH4, δ13C in CO2, and 3He/4He ratio in the gases were analyzed in combination with chemical analyses on the fluids in the Niutuozhen geothermal field. The chemical and isotopic compositions indicate a meteoric origin of the thermal waters. The reservoir temperatures estimated by chemical geothermometry are in the range between 60 and 108 °C. The results show that the gases are made up mainly by N2 (18.20–97.42 vol%), CH4 (0.02–60.95 vol%), and CO2 (0.17–25.14 vol%), with relatively high He composition (up to 0.52 vol%). The chemical and isotopic compositions of the gas samples suggest the meteoric origin of N2, predominant crustal origins of CH4, CO2, and He. The mantle-derived He contributions are calculated to be from 5 to 8% based on a crust–mantle binary mixing model. The deep temperatures in the Jxw reservoir were evaluated based on gas isotope geothermometry to be in the range from 141 to 165 °C. The mantle-derived heat fraction in the surface heat flow is estimated to be in the range of 48–51% based on 3He/4He ratios.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews J (1985) The isotopic composition of radiogenic helium and its use to study groundwater movements in confined aquifers. Chem Geol 49:339–351
Arnorsson S (1986) The chemistry of gases associated with geothermal activity and volcanism in Iceland. J Geophys Res 91(12):261–268
Arnorsson S (1991) Geochemistry and geothermal resources in Iceland. In: Applications of geochemistry in geothermal reservoir development. UNITAR publication, Rome, pp 145–196
Arnorsson S, Fridriksson T, Gunnarsson I (1998) Gas chemistry of the Krafla geothermal field, Iceland. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on water–rock interaction, Auckland, New Zealand, pp 613–616
Bergfeld D, Goff F, Janik CJ (2001) Carbon isotope systematic and CO2 sources in the geyers-clear lake region, northern California, USA. Geothermics 30:303–331
Bottinga Y (1969) Calculated fractionation factors for carbon and hydrogen isotope exchange in the system calcite-carbon dioxide graphite, methane-hydrogen-water vapor. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 33(1):49–64
Caliro S (2015) Gas geochemistry of hydrothermal fluids of the S. Miguel and Terceira Islands, Azores. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 168:43–57
Chen M (1988) Geothermal resources in North China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chen J, Wang HN (2004) Geothermical introduction. Science Press, Beijing, pp 106–137 (in Chinese)
Cinti D, Tassi F, Procesi M, Bonini M, Capecchiacci F, Voltattorni N, Vaselli O, Quattrocchi F (2014) Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry in the unexploited geothermal field of the Vicano–Cimino Volcanic District (Central Italy). Chem Geol 371:96–114
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrology. Lewis Pubishers, New York
Craig H (1963) The isotopic geochemistry of water and carbon in geothermal areas. In: Tongiorgi E (ed) Nuclear geology on geothermal areas. Consiglio Nazionale delle Richerche. Laboratorio di Geologia Nucleare, Pisa
Craig H, Lupton JE, Horibe Y (1978) A mantle helium component in circum pacific volcanic glasses: Hakone, the Marianas and Mt Lassen. In: Alexander E, Ozima M (eds) Terrestrial rare gases. Japan Science Society Press, Tokyo
D’Amore F, Arnorsson S (2000) Geothermometry. In: Arnorsson S (ed) Isotopic and chemical techniques in geothermal exploration, development and use. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 152–178
de Leeuw GAM, Hilton DR, Gulec N, Mutlu H (2010) Regional and temporal variations in CO2/3He, 3He/4He and δ13C along the North Anatolian Fault Zone, Turkey. Appl Geochem 25:524–539
Fischer TP, Giggenbach WF, Sano Y, Williams SN (1998) Fluxes and sources of volatiles discharged from Kudryavy, a subduction zone volcano, Kurile Islands. Earth Planet Sci Lett 160:81–96
Fournier R (1977) Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems. Geothermics 5:41–50
Fournier R, Potter R (1982) A revised and expanded silica (quartz) geothermometer. Geotherm Resour Counc Bull 11:3–12
Fournier R, Truesdell A (1973a) An empirical Na–K–Ca geothermometer for natural waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37:1255–1275
Fournier R, Truesdell A (1973b) An empirical Na–K–Ca geothermometer for natural waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37:1255–1275
Gherardi F, Panichi C (2000) Water and gas geochemistry of the Euganean and Berician thermal district (Italy). Appl Geochem 2000:455–474
Giggenbach W (1982) The chemical and isotopic composition of gas discharges from New Zealand andesitic volcanoes. Bull Volcanol 45(3):253–255
Giggenbach W (1988) Geothermal mineral equilibria. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:393–410
Giggenbach WF (1991) Chemical techniques in geothermal exploration. Application of geochemistry in geothermal reservoir development. UNDP Centre on Small Energy Resources, Rome, pp 119–144
Giggenbach W (1993) Isotopic composition of helium and CO2, CH4 contents in gases produced along the New Zealand part of a convergent plate boundary. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 57:3427–3455
Giggenbach WF (1995) Variations in the chemical and isotopic composition of fluids discharged from the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 68:89–116
Giovanni C, Maria LC, Francesco F (2006) Carbon dioxide degassing at Latera caldera (Italy): evidence of geothermal reservoir and evaluation of its potential energy. J Geophys Res 112:B12204
He L, Hu S, Wang J (2001) The characteristics of heat structure of lithosphere in mainland of eastern China. J Prog Nat Sci 11:966–969 (in Chinese)
Heaton THE, Vogel JC (1981) Excess air in groundwater. J Hydrol 50:201–208
Hilton DR, Fischer TP, Marty B (2002) Noble gases and volatile recycling at subduction zones. Rev Mineral Geochem 47:319–370
Horita J (2001) Carbon isotope exchange in the system CO2–CH4 at elevated temperatures. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65(12):1907–1919
Hu AP, Dai JX, Yang C (2009) Geochemical characteristics and distribution of CO2 gas fields in Bohai Bay Basin. Petrol Explor Dev 36:181–189 (in Chinese)
Karakuş H (2015) Helium and carbon isotope composition of gas discharges in the Simav Geothermal Field, Turkey: implications for the heat source. Geothermics 57:213–223
Kawagucci S, Ueno Y, Takai K, Toki T, Ito M, Inoue K, Makabe A, Yoshida N, Muramatsu Y, Takahata N, Sano Y, Narita T, Teranishi G, Obata H, Nakagawa S, Nunoura T, Gamo T (2013) Geochemical origin of hydrothermal fluid methane in sediment-associated fields and its relevance to the geographical distribution of whole hydrothermal circulation. Chem Geol 339:213–225
Kharaka Y, Hanor J (2003) Deep fluids in the continents: I. Sedimentary basins. In: Drever JI (ed), Holland HD, Turekian, KK (executive editors) Treatise on geochemistry, vol 5, p 605. Elsevier, Amsterdam. pp 499–540. ISBN 0-08-043751-6
Kong Y, Pang Z, Shao H, Hu S, Kolditz O (2014) Recent studies on hydrothermal systems in China: a review. Geotherm Energy 2:19
Kong Y, Pang Z, Pang J, Luo L, Luo J, Shao H, Kolditz O (2015) Deep groundwater cycle in Xiongxian geothermal field. In: Proceedings world geothermal congress 2015, Melbourne, 19–25 April
Li WW, Rao S, Tang XY, Jiang GZ, Hu SB (2014) Borehole temperature logging and temperature field in the Xiongxian geothermal field, Hebei Province. Chin J Geol 49(3):850–863
Liang HB, Xiang SQ, Yang GR, Dan WN, Wang WY (2002) The study of natural gas in the northern part of the Jizhong depress. China Petrol Explor 7(1):17–33 (in Chinese)
Mamyrin BA, Tolstikhin IN (1984) Helium isotopes in Nature. Developments in Geochemistry, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Marty B, Jambon A (1987) C/3He in volatile fluxes from the solid Earth: implications for carbon geodynamics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 83:16–26
Marty B, O’Nions RK, Oxburgh ER, Martel D, Lombardi S (1992) Helium isotopes in Alphine regions. Tectonophysics 206:71–78
Mayo AL, Muller AB (1997) Low temperature diagenetic–metamorphic and magmatic contributions of external CO2 gas to a shallow ground water system. J Hydrol 194:286–304
Minissale A, Vaselli O, Chandrasekharam D, Magro G, Tassi F, Casiglia A (2000) Origin and evolution of ‘intracratonic’ thermal fluids from central-western peninsular India. Earth Planet Sci Lett 181:377–394
Moore JN, Norman DJ, Kennedy BM (2001) Fluid inclusion gas compositions from an active magmatic-hydrothermal system: a case study of the Geysers geothermal field. Chem Geol 173:3–30
Mutlu H, Gulec N, Hilton DR (2008) Helium–carbon relationships in geothermal fluids of western Anatolia, Turkey. Chem Geol 247:305–321
Nicholson K (2012) Geothermal fluids: chemistry and exploration techniques. Springer, Berlin
O’Nions RK, Oxburgh ER (1988) Helium, volatile fluxes and the development of continental crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 90:331–347
Oxburgh ER, O’Nions RK (1987) Helium loss, tectonics and the terrestrial heat budget. Science 237:1583–1588
Pang Z, Reed M (1998) Theoretical chemical thermometry on geothermal waters: problems and methods. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:1083–1091
Pang Z, Yang F, Huang T, Duan Z (2010) Genesis analysis of geothermal system in Guanzhong Basin of China with implications on sustainable geothermal resources development. In: Proceedings world geothermal congress 2010, Bali, Indonesia, 25–29 April 2010
Pang Z, Hu S, Wang S, Xu P, Wang G, Yang F (2015a) Geothermal systems and resources. In: Wang J (ed) Geothermic and its applications. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Pang Z, Pang J, Kong Y, Luo L, Duan Z, Yang F (2015b) Large karstic geothermal reservoirs in sedimentary basins in China: genesis, energy potential and optimal exploitation. In: Proceedings world geothermal congress 2015, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 April
Poreda RJ, Craig H (1989) Helium isotope ratios in circum-Pacific volcanic arcs. Nature 338:473–478
Rao S, Jiang GZ, Gao YJ, Hu SB, Wang JY (2016) The thermal structure of the lithosphere and heat source mechanism of geothermal field in Weihe Basin. Chin J Geophys 59:2176–2190 (in Chinese)
Reed M, Spycher N (1984) Calculation of pH and mineral equilibria in hydrothermal waters with application to geothermometry and studies of boiling and dilution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1479–1492
Reed M, Spycher N, Palandri J (2010) SOLVEQ-XPT: a computer program for computing aqueous-mineral-gas equilibria. University of Oregon, Department of Geological Sciences, Eugene, p 43
Richet P, Bottinga Y, Javoy M (1977) A review of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur and chlorine stable isotope fraction among the geous nolecure. Ann Reg Ength Planet 5:65–110
Sano Y, Marty B (1995) Origin of carbon in fumarolic gas from island arcs. Chem Geol 119:265–274
Sano Y, Wakita H (1985) Geographical distribution of 3He/4He ratios in Japan: implications for arc tectonics and incipient magmatism. J Geophys Res 90:8729–8741
Sano Y, Williams SN (1996) Fluxes of mantle and subducted carbon along convergent plate boundaries. Geophys Res Lett 23:2749–2752
Stefan A (2000) Isotopic and chemical techniques in geothermal exploration, development and use: sampling methods, data handling, interpretation. Int Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 152–178
Torgersen T, Habermehl MA, Clarke WB (1992) Crustal helium fluxes and heat flow in the Great Artesian Basin, Australia. Chem Geol 102:139–152
Wang Y (2000) Estimations of the ratio of crust/mantle heat flow using helium isotopic ratio of underground fluid. Chin J Geophys 43:762–770
Wang S (2011) Hydrothermal process tracing and simulation for the optimization of geothermal resources development: a case study of the Niutuozhen geothermal field in North China. Dissertation, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese)
Wang YC, Sun XR (1992) Seismogeological features of the dissolved CO2, H2 and He groundwater in Hebei province and its adjacent area. North China Earthq Sci 10(2):59–68 (in Chinese)
Wang S, Pang Z, Liu J, Liu S, Yin M (2013) Origin and evolution characteristics of geothermal water in the Niutuozhen Geothermal Field, North China Plain. J Earth Sci China 24:891–902
Whiticar MJ (1999) Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane. Chem Geol 161:291–314
Xu YC, Wang XB (1995) Helium isotope compositions in sedimentary basins in China. Appl Geochem 10:643–656
Yan DS, Yu YT (2000) Evaluation and utilization of geothermal resource in the oil zone of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Area. China University of Geosciences Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang J, Cai H, Liu C, Zhou A, Yan Z (2005) Characteristics of helium isotopes of groundwater in the Quaternary System in the Heibei Plain, North China. Earth Sci Front 12(suppl):112–116 (in Chinese)
Zhang LP, Wang AG, Jin ZJ (2011) Origins and fates of CO2 in the Dongying depression of the Bohai Bay Basin. Energy Explor Exploit 29(3):291–314
Zhang DZ, Liu ZG, Lv HL (2013) Geothermal resources in Hebei province. Geological Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang W, Du J, Zhou X, Wang F (2016) Mantle volatiles in spring gases in the Basin and Range Province on the west of Beijing, China: constraints from helium and carbon isotopes. J Volcanol Geoth Res 309:45–52
Zhao P, Xie E, Dor J, Jin J (2002) Geochemical characteristics of geothermal gases and their geological implications in Tibet. Acta Petrol Sin 18:539–550 (in Chinese)
Zhou RL, Liu QS, Zhang J, Yang LQ (1989) The geological features and exploitive prospects of the geothermal field of salient type of bed rock of Niutuozhen in the fault basin of north China. Bull 562 Compr Geol Brig Chin Acad Geol Sci 7:21–35 (in Chinese)
Zuo YH, Qiu NS, Chang J, Hao QQ (2016) Meso-cenozoic lithospheric thermal structure in the Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Geol Sin 87:145–153 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 41372257). Sincere thanks are due to Prof. Liwu Li and Prof. Zhongping Li for offering access to gas isotope test instruments. Thanks are also to Dr. Yiman Li and Dr. Tianming Huang for their suggestions on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Subsurface Energy Storage II,” guest edited by Zhonghe Pang, Yanlong Kong, Haibing Shao, and Olaf Kolditz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, J., Pang, Z., Lv, M. et al. Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of fluids in the Niutuozhen geothermal field, North China. Environ Earth Sci 77, 12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7171-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7171-y