Abstract
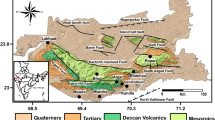
Nuclear power plants are designed to prevent the hazardous effects of the earthquakes and any external events to keep the safety of the plant. Ninety-one shallow seismic refraction profiles were performed to determine shear wave velocity of the engineering layers at the site of El Dabaa area that is situated to the northern coastline of Egypt for seismic hazard microzonation evaluation according to hazard index values. A microzonation is a procedure of delineating an area into individual zones having different ranks of numerous seismic hazards. This will aid in classifying areas of high seismic risk which is vigorous for industrial design of nuclear structures. The site response analysis requires the characterization of subsurface materials considering local subsurface profiles of the site. Site classification of the area under investigation was undertaken using P- and S-waves and available borehole data. The studied nuclear power plant site has been characterized as per NEHRP site classification using an average velocity of transverse wave (V 30s ) of depth 30 m which acquired from seismic survey. This site was categorized into two site classes: the major one is “site class B,” and the minor one is “site class A.” The attenuation coefficient, the damping ratio and the liquefaction potential are geotechnical parameters which were derived from P- and S-waves, and have their major effects on the seismic hazard contribution. 1D ground response analysis was carried out in the places of seismic profiles inside the site for estimating the amount of ground quaking using peak ground acceleration (PGA), site amplification, predominant frequency and spectral accelerations on the surface of ground by the DEEPSOIL software package. Seven factors (criteria) deliberated to assess the earthquake hazard index map are: (1) the peak ground acceleration at the bedrock, (2) the amplification of the site, (3) the liquefaction potential, (4) the main frequency of the earthquake signal, (5) the average V s of the first 30 m from the ground surface, (6) the depth to the groundwater and (7) the depth to the bedrock. These features were exemplified in normalized maps after uniting them to 0–1 scores according to some criteria by the minimum and maximum values as linear scaling points. Multi-criteria evaluation is an application of multi-criteria decision analysis theory that used for developing a seismic hazard index map for a nuclear power plant site at El Dabaa area in ArcGIS 10.1 software. Two models of decision making were used in this work for seismic hazard microzonation. The analytic hierarchy process model was applied to conduct the relative weights of the criteria by pairwise comparison using Expert Choice Software. An earthquake hazard index map was combined using Weighted Linear Combination model of the raster weighted overlay tool of ArcGIS 10.1. The results indicated that most of the study site of the nuclear power plant is a region of low to moderate hazard; its values are ranging between 0.2 and 0.4.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu El Ella (1987) Geological and hydrogeological studies for El-Dabaa Nuclear Power Plant Station, Northwestern Desert, Egypt. M.Sc. thesis, Cairo University, Egypt
Abu El Ella (1992) Influence of the geological factors on the radioactive contamination of the groundwater at El-Dabaa Nuclear Power Plant Northwestern Desert, Egypt., Ph.D thesis Cairo University, Egypt
Abudeif AM, Abdel Moneim AA, Farrag AF (2015) Multicriteria decision analysis based on analytic hierarchy process in GIS environment for siting nuclear power plant in Egypt. Ann Nucl Energy 75:682–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anucene.2014.09.024
Adham K, El-Hemamy S (2006) Modeling of seismic hazard for El-Dabaa area. Bull Eng Geol Env 65:273–279
Albert R, Kebeasy R (1986) Seismicity survey at El Dabaa area. In: Northern western desert. Egypt: Proc. lsl Sc. Gen Meetings, NARIG, Egypt, vol B, pp 1–23,1986
Allam A, El Khashab H, Maamoun M, Ibrahim E, Abuel Ata A (1979) Studies on seismicity in the area of El Dabaa, Zaafarana and South Safaga nuclear power plant sites. NRIAG J Astron Geophys Cairo, Egypt 186:1–83
Anbazhagan P, Sitharam T (2008) Seismic microzonation of Bangalore. India J Earth Syst Sci 117:833–852
Azab AMA (2013) Seismic microzonation studies of El Dabaa area. Menufiya University, Egypt, Egypt
Beresnev IA, Atkinson GM (1998) Stochastic finite-fault modeling of ground motions from the 1994 Northridge, California, earthquake. I. Validation on rock sites. Bull Seismol Soc Am 88:1392–1401
Bielak J, Xu J, Ghattas O (1999) Earthquake ground motion and structural response in alluvial valleys. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 125:413–423
Boominathan A, Rao PK, Pillai CS, Hari S Measurement of dynamic properties and evaluation of liquefaction potential of a 500 mw prototype fast breeder reactor site located in South of India. In: Proceedings of the 12th world conference on earthquake engineering, 2000. Auckland:[sn], pp 964–970
Boore DM (1983) Stochastic simulation of high-frequency ground motions based on seismological models of the radiated spectra. Bull Seismol Soc Am 73:1865–1894
BSSC (2004) NEHRP recommended provisions for seismic regulations for new buildings and other structures. 2003 edition, report no FEMA 450-1., Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington, D.C
Chung-Chun FF, Win-Shan-Guo, Kuen Yu (1990) Site INVESTIGATION OF THE Maanshan nuclear power plant in Taiwan. Paper presented at the 6th South East Asian conference on soil engineering, 19–23 May
Council BSS (2004) NEHRP recommended provisions for seismic regulations for new buildings and other structures (FEMA 450): provisions/prepared by the Building Seismic Safety Council. Building Seismic Safety Council, National Institute of Building Sciences
Eastman J (1997) Idrisi for Windows, user’s guide, version 2.0, Clark Labs for Cartographic Technology and Geographic Analysis Clark University, Worcester
Farrag AF (2015) Engineering and environmental applications of geophysical methods for studying the nuclear power plant site, northwestern coast. Sohag University, Egypt, Egypt.
Ghosh A (2006) Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis for a site. Nuclear Eng Des 236:1192–1200
Haase AB, Stewart RR (2004) Attenuation (Q) from VSP and log data: Ross Lake, Saskatchewan, CSEG National Convention
Hartzell SH (1978) Earthquake aftershocks as Green’s functions. Geophys Res Lett 5:1–4
Hashash YMA, Groholski DR, Phillips CA, Park D, Musgrove M (2012) DEEPSOIL 5.1, user manual and tutorial, 107
IAEA (2003) Site evaluation for nuclear installations. IAEA safety standard series no. NS-R-3, Vienna, Austria
IAEA (2010) Evaluation of seismic hazard for nuclear power plants. Safety guide, IAEA safety standards series, Vienna, No NS-G-33
IAEA (2012) Managing siting activities for nuclear installations. Nuclear energy series IAEA, Vienna Austria no. NG-T-3.7
Imai T, Fumoto H, Yokota K (1976) P-and S-wave velocities in subsurface layers of ground in Japan Oyo technical note, TN-14. Urawa Research Institute, Japan
Irikura K (1983) Semi-empirical estimation of strong ground motions during large earthquakes. Bull Disas Prev Res Inst 33:63–104
Ishita RP, Khandaker S (2010) Application of analytical hierarchical process and GIS in earthquake vulnerability assessment: case study of ward 37 and 69 in Dhaka City. J Bangladesh Inst Plan ISSN 2075:9363
James N, Sitharam T, Padmanabhan G, Pillai C (2014) Seismic microzonation of a nuclear power plant site with detailed geotechnical, geophysical and site effect studies. Nat Hazards 71:419–462
Keeney RL (1987) An analysis of the portfolio of sites to characterize for selecting a nuclear repository. Risk Anal 7:195–218
Kramer SL (1996) Geotechnical earthquake engineering, vol 80. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Longley PA, Goodchild MF, Maguire DJ, Rhind DW (2001) Geographic information system and science England. Wiley, Hoboken
Mohanty WK, Verma AK (2013) Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis for Kakrapar atomic power station, Gujarat, India. Nat Hazards 69:919–952
Nath SK, Thingbaijam KKS, Raj A (2008) Earthquake hazard in northeast India—a seismic microzonation approach with typical case studies from Sikkim Himalaya and Guwahati city. J Earth Syst Sci 117:809–831
Raghu Kanth STG, Iyengar RN (2007) Estimation of seismic spectral acceleration in Peninsular India. J Earth Sys Sci 116(3):199–214
Reynolds JM (2011) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Riahi M, Tabatabaei S, Beytollahi A, Ghalandarzadeh A, Talebian M, Fattahi M (2012) Seismic refraction and downhole survey for characterization of shallow depth materials of Bam city, southeast of Iran. J Earth Space Phys 37:41–58
Roshan A, Basu P (2010) Application of PSHA in low seismic region: a case study on NPP site in peninsular India. Nucl Eng Des 240:3443–3454
Saaty T (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resources allocation. McGraw, New York
Saaty T (2008) Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Serv Sci 1:83–98
Salman AAB (1995) Proposed geologic studies for minimising earthquakes hazards in El Dabaa nuclear power plant site. West Alexandria, Egypt. Paper presented at the proceedings of the international conference. 30 years Cooper
Schnabel PB (1972) SHAKE a computer program for earthquake response analysisi of horizontally layered sites EERC report:72-12
Seed HB, Idriss IM (1969) Influence of soil conditions on ground motions during earthquakes. University of California, Institute of Transportation and Traffic Engineering, Soil Mechanics Laboratory
Sheehan JR, Doll WE, Mandell WA (2005) An evaluation of methods and available software for seismic refraction tomography analysis. J Environ Eng Geophys 10:21–34
Smethurst M (2005) A software tool to rotate spatial data on the surface of the sphere (Earth) for Geosoft’s Oasis Montaj NGU report
Toksöz MN, Johnston DH (eds) (1981) Preface. In: Seismic wave attenuation. Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Tulsa, OK, pp v–vi
Udias A (1999) Principles of seismology, vol 260. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Underwood D (2007) Introduction to SeisImager/SW. Geometrics Inc, San Jose
USNRC (2003) Site investigations for foundations of nuclear power plants. Regulatory guide no 1132 USA
Voogd H (1983) Multicriteria evaluation for urban and regional planning. Pion Ltd, Amsterdam
Waters KH (1978) Reflection seismology, vol 203. Wiley, Hoboken
Acknowledgments
This study was mainly performed in the years of 2013 and 2014. The data were processed and interpreted by corporation between the Geophysical Lab at Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Sohag University and the Siting Department, Nuclear Power Plants Authority, Cairo, Egypt; the authors would like to thank all the colleagues and technicians who participated in the completion of their mission. The authors are grateful to the reviewers and the editor for the time and effort they put into their detailed comments that helped improve this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abudeif, A.M., Abdelmoneim, A.A. & Farrag, A.F. GIS-based multi-criteria earthquake hazards evaluation using analytic hierarchy process for a nuclear power plant site, west Alexandria, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 76, 796 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7148-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7148-x