Abstract
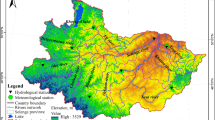
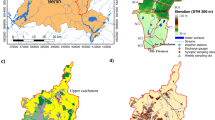
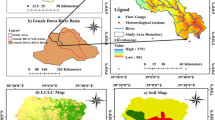
This research addressed the separate and combined impacts of climate and land use change on streamflow, suspended sediment and water quality in the Kor River Basin, Southwest of Iran, using (BASINS–WinHSPF) model. The model was calibrated and validated for hydrology, sediment and water quality for the period 2003–2012. The model was run under two climate changes, two land use changes and four combined change scenarios for near-future period (2020–2049). The results revealed that projected climate change impacts include an increase in streamflow (maximum increases of 52% under RCP 2.6 in December and 170% under RCP 8.5). Projected sediment concentrations under climate change scenarios showed a monthly average decrease of 10%. For land use change scenarios, agricultural development scenario indicated an opposite direction of changes in orthophosphate (increases in all months with an average increase of 6% under agricultural development scenario), leading to the conclusion that land use change is the dominant factor in nutrient concentration changes. Combined impacts results indicated that streamflows in late fall and winter months increased while in summer and early fall decreased. Suspended sediment and orthophosphate concentrations were decreased in all months except for increases in suspended sediment concentrations in September and October and orthophosphate concentrations in late winter and early spring due to the impact of land use change scenarios.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour KC, Faramarzi M, Ghasemi SS, Yang H (2009) Assessing the impact of climate change on water resources in Iran. Water Resour Res 45:1–16. doi:10.1029/2008WR007615
Albek M, Albek E (2003) Predicting the effects of climate change on the sediment yield of watersheds. In: Diffuse pollution conference dublin 2003 3G: Agriculture, pp 137–142
Astaraie-Imani M, Kapelan Z, Fu G, Butler D (2012) Assessing the combined effects of urbanisation and climate change on the river water quality in an integrated urban wastewater system in the UK. J Environ Manag 112:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.06.039
Bicknell BR, Imhoff JC, Kittle Jr JL, Jobes TH, Donigian Jr AS (2001) Hydrological simulation program—FORTRAN (HSPF) Version 12, User’s Manual, 2001
Cox BA, Whitehead PG (2009) Impacts of climate change scenarios on dissolved oxygen in the River Thames, UK. Hydrol Res 40:138. doi:10.2166/nh.2009.096
Crossman J, Futter MN, Oni SK, Whitehead PG, Jin L, Butterfield D, Baulch HM, Dillon PJ (2013) Impacts of climate change on hydrology and water quality: future proofing management strategies in the Lake Simcoe watershed, Canada. J Great Lakes Res 39:19–32. doi:10.1016/j.jglr.2012.11.003
Dixon B, Earls J (2012) Effects of urbanization on streamflow using SWAT with real and simulated meteorological data. Appl Geogr 35:174–190. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2012.06.010
Duda PB, Hummel PR, Donigian ASJ, Imhoff JC (2012) Basins/Hspf: model use, calibration, and validation. Trans Asabe 55:1523–1547. doi:10.13031/2013.42261
El-Khoury A, Seidou O, Lapen DRL, Que Z, Mohammadian M, Sunohara M, Bahram D (2015) Combined impacts of future climate and land use changes on discharge, nitrogen and phosphorus loads for a Canadian river basin. J Environ Manag 151:76–86. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.12.012
Etemadi H, Samadi SZ, Sharifikia M (2012) Stastistical downscaling of climate variables in Shadegan Wetland, Iran. Sci Rep 1:1–9. doi:10.4172/scientificrep
Fakhraei H (2009) Determination of self assimilating capacity of Kor and Sivand Rivers and total maximum daily load allocation (TMDL) of their pollution sources. Shiraz University, Shiraz
Fan M, Shibata H (2015) Simulation of watershed hydrology and stream water quality under land use and climate change scenarios in Teshio River watershed, northern Japan. Ecol Indic 50:79–89. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.003
Fernandes MR, Segurado P, Jauch E, Ferreira MT (2016) Riparian responses to extreme climate and land-use change scenarios. Sci Total Environ 569–570:145–158. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.099
Ficklin DL, Stewart IT, Maurer EP (2013) Effects of climate change on stream temperature, dissolved oxygen, and sediment concentration in the Sierra Nevada in California. Water Resour Res 49:2765–2782. doi:10.1002/wrcr.20248
Hadjikakou M, Whitehead PG, Jin L, Futter M, Hadjinicolaou P, Shahgedanova M (2011) Modelling nitrogen in the Yeilirmak River catchment in Northern Turkey: impacts of future climate and environmental change and implications for nutrient management. Sci Total Environ 409:2404–2418
Hamon RW (1961) Estimating potential evapotranspiration. J Hydraul Div 87(HY3):107–120
Jin L, Whitehead PG, Futter MN, Lu Z (2012) Modelling the impacts of climate change on flow and nitrate in the River Thames: assessing potential adaptation strategies. Hydrol Res 43:902–916. doi:10.2166/nh.2011.080
Jones PD, Hulme M (1996) Calculating regional climatic time series for temperature and precipitation: methods and illustrations. Int J Climatol 16:361–377. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(199604)16:4<361:AID-JOC53>3.0.CO;2-F
Kim SM, Benham BL, Brannan KM, Zeckoski RW, Doherty J (2007) Comparison of hydrologic calibration of HSPF using automatic and manual methods. Water Resour Res. doi:10.1029/2006WR004883
Kim J, Choi J, Choi C, Park S (2013) Impacts of changes in climate and land use/land cover under IPCC RCP scenarios on streamflow in the Hoeya River Basin, Korea. Sci Total Environ 452–453:181–195. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.005
Li Z, Huang G, Wang X, Han J, Fan Y (2016) Impacts of future climate change on river discharge based on hydrological inference: a case study of the Grand River Watershed in Ontario, Canada. Sci Total Environ 548–549:198–210. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.002
Mehdi B, Ludwig R, Lehner B (2015) Evaluating the impacts of climate change and crop land use change on streamflow, nitrates and phosphorus: a modeling study in Bavaria. J Hydrol Reg Stud 4:60–90. doi:10.1016/j.ejrh.2015.04.009
Mitsova D (2014) Coupling land use change modeling with climate projections to estimate seasonal variability in runoff from an urbanizing catchment near Cincinnati, Ohio. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 3:1256–1277. doi:10.3390/ijgi3041256
Mohsenipour M, Shahid S, Nazemosadat MJ (2013) Effects of El Nino-Southern oscillation on the discharge of Kor River in Iran. Adv Meteorol 2013:1–4. doi:10.1155/2013/846397
Mukundan R, Pradhanang SM, Schneiderman EM, Pierson DC, Anandhi A, Zion MS, Matonse AH, Lounsbury DG, Steenhuis TS (2013) Suspended sediment source areas and future climate impact on soil erosion and sediment yield in a New York City water supply watershed, USA. Geomorphology 183:110–119. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.06.021
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Pervez MS, Henebry GM (2015) Assessing the impacts of climate and land use and land cover change on the freshwater availability in the Brahmaputra River basin. J Hydrol Reg Stud 3:285–311. doi:10.1016/j.ejrh.2014.09.003
Praskievicz S (2016) Impacts of projected climate changes on streamflow and sediment transport for three snowmelt-dominated rivers in the interior Pacific Northwest. River Res Appl 32:4–17. doi:10.1002/rra.2841
Praskievicz S, Chang H (2009) A review of hydrological modelling of basin-scale climate change and urban development impacts. Prog Phys Geogr 33:650–671. doi:10.1177/0309133309348098
Praskievicz S, Chang H (2011) Impacts of climate change and urban development on water resources in the Tualatin River Basin, Oregon. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 101:249–271. doi:10.1080/00045608.2010.544934
Rehana S, Mujumdar PP (2011) River water quality response under hypothetical climate change scenarios in Tunga–Bhadra river, India. Hydrol Process 25:3373–3386. doi:10.1002/hyp.8057
Rodriguez-Lloveras X, Buytaert W, Benito G (2016) Land use can offset climate change induced increases in erosion in Mediterranean watersheds. CATENA 143:244–255. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2016.04.012
Ruiter A (2012) Delta-change approach for CMIP5 GCMs. Utrecht
Shrestha B, Babel MS, Maskey S, Van Griensven A, Uhlenbrook S, Green A, Akkharath I (2013) Impact of climate change on sediment yield in the Mekong River basin: a case study of the Nam Ou basin, Lao PDR. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:1–20. doi:10.5194/hess-17-1-2013
Taylor KE, Stouffer RJ, Meehl GA (2012) An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 93:485–498. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1
Thodsen H, Hasholt B, Kjærsgaard JH (2008) The influence of climate change on suspended sediment transport in Danish rivers. Hydrol Process 22:764–774. doi:10.1002/hyp.6652
Tong STY, Sun Y, Ranatunga T, He J, Yang YJ (2012) Predicting plausible impacts of sets of climate and land use change scenarios on water resources. Appl Geogr 32:477–489. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2011.06.014
Tu J (2009) Combined impact of climate and land use changes on streamflow and water quality in eastern Massachusetts, USA. J Hydrol 379:268–283. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.009
Tu J, Xia Z (2008) Examining spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality using geographically weighted regression I: model design and evaluation. Sci Total Environ 407(1):358–378. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.09.031
Ward PJ, van Balen RT, Verstraeten G, Renssen H, Vandenberghe J (2009) The impact of land use and climate change on late Holocene and future suspended sediment yield of the Meuse catchment. Geomorphology 103:389–400. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.07.006
Whitehead PG, Johnes PJ, Butterfield D (2002) Steady state and dynamic modelling of nitrogen in the River Kennet: impacts of land use change since the 1930s. Sci Total Environ 282–283:417–434. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00927-5
Whitehead PG, Wilby RL, Butterfield D, Wade AJ (2006) Impacts of climate change on in-stream nitrogen in a lowland chalk stream: an appraisal of adaptation strategies. Sci Total Environ 365:260–273. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.02.040
Whitehead PG, Sarkar S, Jin L, Futter MN, Caesar J, Barbour E, Butterfield D, Sinha R, Nicholls R, Hutton C, Leckie HD (2015) Dynamic modeling of the Ganga river system: impacts of future climate and socio-economic change on flows and nitrogen fluxes in India and Bangladesh. Environ Sci Impacts 17:1082–1097. doi:10.1039/c4em00616j
Wilson CO, Weng Q (2011) Simulating the impacts of future land use and climate changes on surface water quality in the Des Plaines River watershed, Chicago Metropolitan Statistical Area, Illinois. Sci Total Environ 409:4387–4405. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaighan, A.A., Talebbeydokhti, N. & Bavani, A.M. Assessing the impacts of climate and land use change on streamflow, water quality and suspended sediment in the Kor River Basin, Southwest of Iran. Environ Earth Sci 76, 543 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6880-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6880-6