Abstract
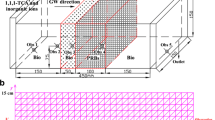
Dense non-aqueous-phase liquids (DNAPLs) are difficult to be removed from the highly heterogeneity aquifer. In situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) is one of the main DNAPL remediation technologies, but when using permanganate as oxidant to remediate the DNAPL in groundwater, the permeability within the DNAPL source area can be reduced due to the MnO2 solid-phase formation. Hence, the study of the complex dynamic change in the DNAPL source zone is meaningful for improvement in the ISCO efficiency. A developed one-dimensional column experiment was used in this study. The columns used in the experiments were parallel-connected. Limited time interval and low-concentration permanganate flushing were applied in the experiments to mimic real field condition. It was found that the permeability within the DNAPL source zone was reduced only for short time due to the precipitation and flocculation of MnO2 formed. The flow flux and mass flux within the DNAPL source zone decreased during permanganate oxidation while rebounded again after the oxidation. The experiment results illustrated that low concentration of permanganate oxidation can activate the DNAPL source area. Based on this phenomenon, an effective ISCO could be developed to remediate the source zone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brusseau ML, DiFilippo EL, Marble JC, Oostrom M (2008) Mass–removal and mass-flux-reduction behavior for idealized source zones with hydraulically poorly-accessible immiscible liquid. Chemosphere 71:1511–1521
Chen HL, Park E, Kim YK, Kim KJ (2011) DNAPL mass flux assessment of in-situ chemical oxidation using quasi-multidimensional experiments. In: 5th international conference on bioinformatics and biomedical Engineering, doi:10.1109/icbbe.2011.5780740
Chokejaroenrat C, Comfort S, Sakulthaew C, Dvorak B (2014) Improving the treatment of non-aqueous phase TCE in low permeability zones with permanganate. J Hazard Mater 268:177–184
Difilippo EL, Brusseau ML (2008) Relationship between mass-flux reduction and source-zone mass removal: analysis of field data. J Contam Hydrol 98:22–35
Erning K, Grandel S, Dahmke A, Schafer D (2012) Simulation of DNAPL infiltration and spreading behaviour in the saturated zone at varying flow velocities and alternating subsurface geometries. Environ Earth Sci 65:1119–1131
Heiderscheidt JL, Siegrist RL, Illangasekare TH (2008) Intermediate-scale 2D experimental investigation of in situ chemical oxidation using potassium permanganate for remediation of complex DNAPL source zones. J Contam Hydrol 102:3–16
Henderson TH, Mayer KU, Parker BL, Al TA (2009) Three-dimensional density-dependent flow and multicomponent reactive transport modeling of chlorinated solvent oxidation by potassium permanganate. J Contam Hydrol 106:195–211
Hood E (2000) Permanganate flushing of DNAPL source zones: experimental and numerical investigation. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Waterloo, Waterloo. pp 243–243
Huang KC, Hoag GE, Chheda P, Dobbs GM (2002a) Kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of tetrachloroethylene with permanganate. Chemosphere 46(6):815–825
Huang KC, Hoag GE, Chheda P, Dobbs GM (2002b) Chemical oxidation of trichloroethylene with potassium permanganate in a porous medium. Adv Environ Res 7(1):217–229
Kram ML, Keller AA, Rossabi J, Everett LG (2001) DNAPL characterization methods and approaches, part 1: performance comparisons. Ground Water Monit Rev, Fall:109–123. http://www.esm.ucsb.edu/facstaff/fac/keller/papers/Abstract37.pdf
Lee ES, Seol Y, Fang YC, Schwartz FW (2003) Destruction efficiencies and dynamics of reaction fronts associated with the permanganate oxidation of trichloroethylene. Environ Sci Technol 37(11):2540–2546
Li XD, Schwartz FW (2000) Efficiency problems related to permanganate oxidation schemes. In: Wickramanayake GB, Gavaskar AR, Chen ASC (eds) Chemical oxidation and reactive barriers. Battelle Press, Columbus, pp 41–48
Li XD, Schwartz FW (2004) DNAPL mass transfer and permeability reduction during in situ chemical oxidation with permanganate. Geophys Res Lett 31:L06504. doi:10.1029/2003GL019218
Liang SH, Chen KF, Wu CS, Lin YH, Kao CM (2014) Development of KMnO4-releasing composites for in situ chemical oxidation of TCE-contaminated. Water Res 54:149–158
Park E, Parker JC (2007) Effects of mass reduction, flow reduction and enhanced biodecay of DNAPL source zones. Transp Porous Med 73:95–108
Randhawa J (2001) Manganese dioxide induced permeability reduction of porous media during permanganate oxidation of chlorinated alkenes. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Windsor, Windsor, Ontario, Canada, pp 13–44
Rao PSC, Jawitz JW (2003) Comment on “Steady state mass-transfer from single-component dense nonaqueous phase liquids in uniform flow fields” by. T.C. Sale and D.B. McWhorter. Water Resour Res 39:1068–1070
Schroth MH, Oostrom M, Wietsma TW, Istok JD (2001) In situ oxidation of trichloroethene by permanganate: effects on porous medium hydraulic properties. J Contam Hydrol 50(1–2):79–98
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41401539) and Science Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars (State Education Ministry of China, [2015] No.1098) for supporting this study. Special thanks go to the anonymous reviewers and editor for their critical comments which improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Park, E. Reduction in contaminant mass flux with induced oxide mineral precipitation in quasi-multidimensional systems. Environ Earth Sci 76, 475 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6807-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6807-2