Abstract
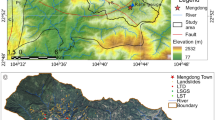
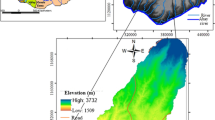
The major limitation in planning water harvesting is the lack of knowledge in the estimation of surface area and storage volume at any depth of dam reservoir. The area–volume–elevation (AVE) curve of a reservoir plays a key role in estimating the most suitable depth, optimum surface area and highest capacity of reservoir storage. The existing methods to estimate the AVE curve are costly and time-consuming and require laborious work. This study attempts to develop a method to optimize the AVE curve for earth dams, using the digital elevation model generated by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) data, and integrate it with the geographic information system (GIS), known as the GIS–SRTM. The proposed method was tested using field data in the Western Desert of Iraq, which is an arid environment. Three constructed small earth dams were selected for this study. The AVE curves were extracted for Horan 2 (H2), Al-gara 2 (G2) and Al-gara 4 (G4) earth dams. Comprehensive analyses have been carried out to evaluate the performance of the AVE curves using the proposed GIS–SRTM method and the field data. From the comparison, the proposed GIS–SRTM method was able to produce reliable AVE curves with a relative error less than 20%. Additionally, the proposed method was less time-consuming and the AVE curves can be visualized immediately. The proposed GIS–SRTM method is relatively supportive in analyzing spatial data to select the optimal site for rainwater harvesting and prevent excessive evaporation losses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Adamat R (2008) GIS as a decision support system for siting water harvesting ponds in the basalt aquifer/Ne Jordan. J Environ Assess Policy Manag 10:189–206. doi:10.1142/S1464333208003020
Al-Adamat R, Diabat A, Shatnawi G (2010) Combining GIS with multicriteria decision making for siting water harvesting ponds in Northern Jordan. J Arid Environ 74:1471–1477. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2010.07.001
Chowdary VM, Ramakrishnan D, Srivastava YK et al (2009) Integrated water resource development plan for sustainable management of Mayurakshi watershed, India using remote sensing and GIS. Water Resour Manag 23:1581–1602. doi:10.1007/s11269-008-9342-9
Crapper PF (1980) Errors incurred in estimating an area of uniform land cover using Landsat. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 46:1295–1301
Cross BK, Moore BC (2014) Lake and reservoir volume: hydroacoustic survey resolution and accuracy. Lake Reserv Manag 30:405–411. doi:10.1080/10402381.2014.960115
Cvar A (2014) GIS-based reservoir planning with limited data in developing nations: a case study of the lower Mekong River basin. Colorado State University, Fort Collins
Durga Rao KHV, Bhaumik MK (2003) Spatial expert support system in selecting suitable sites for water harvesting structures—a case study of song watershed, Uttaranchal, India. Geocarto Int 18:43–50. doi:10.1080/10106040308542288
Forzieri G, Gardenti M, Caparrini F, Castelli F (2008) A methodology for the pre-selection of suitable sites for surface and underground small dams in arid areas: a case study in the region of Kidal, Mali. Phys Chem Earth 33:74–85. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2007.04.014
Gupta KK, Deelstra J, Sharma KD (1997) Estimation of water harvesting potential for a semiarid area using GIS and remote sensing. In: Remote Sensing and geographic information systems for design and operation of water resources systems. Proceedings of Rabat symposium S3. IAHS Publications, 242(63):63
Haghiabi AH, Slamian SS, Mohammadzadeh-Habili J, Mousavi SF (2013) Derivation of reservoir’s area-capacity equations based on the shape factor. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 37:163–167
İrvem A (2011) Application of GIS to determine storage volume and surface area of reservoirs: the case study of Buyuk Karacay Dam. Int J Nat Eng Sci 5:39–43
Jasrotia AS, Majhi A, Singh S (2009) Water balance approach for rainwater harvesting using remote sensing and GIS techniques, Jammu Himalaya, India. Water Resour Manag 23:3035–3055. doi:10.1007/s11269-009-9422-5
Jha MK, Chowdhury A, Chowdary VM, Peiffer S (2007) Groundwater management and development by integrated remote sensing and geographic information systems: prospects and constraints. Water Resour Manag 21:427–467. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9024-4
Jha MK, Chowdary VM, Kulkarni Y, Mal BC (2014) Rainwater harvesting planning using geospatial techniques and multicriteria decision analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 83:96–111. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.12.003
Kahinda JM, Lillie ESB, Taigbenu AE et al (2008) Developing suitability maps for rainwater harvesting in South Africa. Phys Chem Earth 33:788–799. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2008.06.047
Linger H, Mekdaschi Studer R, Hauert C, Gurtner M (2011) Sustainable land management in practice: Guidelines and best practices for Sub-Saharan Africa. TerrAfrica, World Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies (WOCAT) and Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Rome
Mugabe FT, Hodnett MG, Senzanje A (2003) Opportunities for increasing productive water use from dam water: a case study from semi-arid Zimbabwe. Agric Water Manag 62:149–163. doi:10.1016/S0378-3774(03)00077-5
Ni-Bin C, Parvathinathan G (2008) Combining GIS with fuzzy multicriteria decision-making for landfill siting in a fast-growing urban region. J Environ Manag 87:139–153
Sattari M, Salmasi F, Öztürk F (2008) Sulama Amaçlı Hazne Kapasitesinin Belirlenmesinde Çeşitli Yöntemlerin Karşılaştırılması. Tarım Bilimleri Dergisi 14(1):1–7
Sawunyama T, Senzanje A, Mhizha A (2006) Estimation of small reservoir storage capacities in Limpopo River Basin using geographical information systems (GIS) and remotely sensed surface areas: case of Mzingwane catchment. Phys Chem Earth 31:935–943. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2006.08.008
Sayl KN, Muhammad NS, Yaseen ZM, El-shafie A (2016) Estimation the physical variables of rainwater harvesting system using integrated GIS-based remote sensing approach. Water Resour Manag 30:3299–3313. doi:10.1007/s11269-016-1350-6
Siegert K (1994) Introduction to water harvesting: some basic principles for planning, design and monitoring. In: Water harvesting for improved agricultural production. Proceedings of the FAO Expert Consultation, Cairo, Egypt, Nov 1993. FAO, Rome, Italy
Stephens T (2010) Manual on small earth dams: a guide to siting, design and construction. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Rome
Tsihrintzis VA, Hamid R, Fuentes HR (1996) Use of geographic information systems (GIS) in water resources: a review. Water Resour Manag 10:251–277. doi:10.1007/BF00508896
Vorhauer CF, Hamlett JM (1996) GIS: a tool for siting farm ponds. J Soil Water Conserv 51:434–438
Zhang S, Gao H, Naz BS (2014) Monitoring reservoir storage in South Asia from multisatellite remote sensing. Water Resour Res 50:8927–8943. doi:10.1002/2014WR015829
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayl, K.N., Muhammad, N.S. & El-Shafie, A. Optimization of area–volume–elevation curve using GIS–SRTM method for rainwater harvesting in arid areas. Environ Earth Sci 76, 368 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6699-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6699-1