Abstract
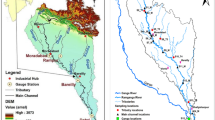
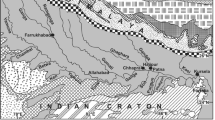
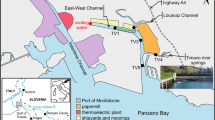
This study investigated the temporal variations of major and trace element contents and controlling factors in the upper reaches of the Xijiang River, SW China. The results showed the major ions principally derived from the weathering of carbonate and silicate rocks, with a seasonal variation impacted by the monsoonal climate. The contents of dissolved trace elements also varied seasonally in the two main tributaries: the Nanpan and Beipan rivers. Most dissolved trace elements such as Mn, Zn and Pb being affected by anthropogenic contributions displayed a large seasonal variability, from onefold to hundred-fold, while V, Rb and U show a relative stable trend uncorrelated with the different seasons, suggesting a natural origin by rock weathering. Suspended particle matter in the Nanpan and Beipan rivers was depleted in Ca, Mg, Na, K and Sr, but enriched in Al, Fe and Sb compared to the upper crust (UC) values. A binary mixture of silicate-rich and carbonate-rich sources dominates the behavior of elements such as Ca and Sr in riverine sediments, while a third end-member with an anthropogenic signature influenced the content of trace elements like Mn, Sb, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cr and Cu. The enrichments of Sb relative to the UC would be related to the mining activity in the studied area. The study highlights the importance of investigating temporal variations of major and trace element contents of rivers controlled by the monsoon climate and impacted by human activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchez J, Gaillardet J, France-Lanord C, Maurice L, Dutra-Maia P (2011) Grain size control of river suspended sediment geochemistry: clues from Amazon River depth profiles. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 12:Q03008. doi:10.1029/2010GC003380
Chen GY, Zou JB, Tan H, Fan YM (2008) The metallogenic regulation of lead–zinc deposit in Northwest Guizhou. Geol Guizhou 25(2):86–94
Chen JB, Gaillardet J, Louvat P, Huon S (2009) Zn isotopes in the suspended load of the Seine River, France: isotopic variations and source determination. Geochim Cosmochi Acta 73:4060–4076
Chen JB, Gaillardet J, Bouches J, Louvat P, Wang YN (2014) Anthropophile elements in river sediments: Overview from the Seine River, France. Geochem Geophy Geosy 101002/214GC005516: 4526-4546
Chetelat B, Liu CQ, Wang QL, Zhang GP (2013) Assessing the influence of lithology on weathering indices of Changjiang river sediments. Chem Geol 359:108–115
Cortecci G, Boschetti T, Dinelli E, Cidu R, Podda F, Doveri M (2009) Geochemistry of trace elements in surface waters of the Arno River Basin. Appl Geochem 24:1005–1022
Das A, Krishnaswami S (2007) Elemental geochemistry of river sediments from the Deccan Traps, India: implications to sources of elements and their mobility during basalt–water interaction. Chem Geol 242:232–254
Davide V, Pardos M, Diserens J, Ugazio G, Thomas R, Dominik J (2003) Characterisation of bed sediments and suspension of the river of Po (Italy) during normal and high flow conditions. Water Res 37:2847–2864
Dellinger M, Gaillardet J, Bouchez J, Calmels D, Galy V, Hilton RG, Louvat P, France-Lanord C (2014) Lithium isotopes in large rivers reveal the cannibalistic nature of modern continental weathering and erosion. Earth Planet Sci Lett 401:359–372
Dupré B, Gaillardet J, Rousseau D, Allègre CJ (1996) Major and trace elements of river-borne material: the Congo Basin. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:1301–1321
Elbaz-Poulichet F, Seyler P, Maurice-Bourgoin L, Guyot JL, Dupuy C (1999) Trace element geochemistry in the upper Amazon drainage basin. Chem Geol 157:319–334
Gaillardet J, Dupré B, Louvat P, Allègre CJ (1999) Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem Geol 159:3–30
Gaillardet J, Viers J, Dupré B (2005) Trace element in river waters: treatise on geochemistry. In: Drever JJ, Holland HD (eds) Surface and ground water weathering and soils. Elsevier, Turekian, pp 25–272
Gao QZ, Wang Z (2015) Dissolved inorganic carbon in the Xijiang River: concentration and stable isotopic composition. Environ Earth Sci 73:253–266
Gao QZ, Tao Z, Huang XK, Nan L, Yu KF, Wang ZG (2009) Chemical weathering and CO2 consumption in the Xijiang River basin, South China. Geomorphology 106(3):324–332
Garzanti E, Ando S, France-Lanord C, Vezzoli G, Censi P, Galy V, Najman Y (2010) Mineralogical and chemical variability of fluvial sediments 1 Bedload sand (Ganga-Brahmaputra, Bangladesh). Earth Planet Sci Lett 299:368–381
Han GL, Liu C-Q (2004) Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: a study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province China. Chem Geol 204:1–21
Han GL, Liu C-Q (2006) Strontium isotope and major ion chemistry of the rainwaters from Guiyang, Guizhou Province, China. Sci Total Environ 364:165–174
Houhou J, Lartiges BS, Montarges-Pelletier E, Sieliechi J, Ghanbaja J, Kohler A (2009) Sources, nature, and fate of heavy metal-bearing particles in the sewer system. Sci Total Environ 407:6052–6062
Hu ZC, Gao S (2008) Upper crustal abundances of trace elements: a revision and update. Cheml Geol 253:205–221
Li SL, Calmels D, Han GL, Gaillardet J, Liu C-Q (2008) Sulfuric acid as an agent of carbonate weathering constrained by δ13CDIC: examples from Southwest China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 270:189–199
Li SL, Liu CQ, Li J, Lang YC, Li LB (2010) Geochemistry of dissolved inorganic carbon and carbonate weathering in a small typical karstic catchment of Southwest China: isotopic and chemical constraints. Chem Geol 277:301–309
Li SL, Chetelat B, Yue FJ, Zhao ZQ, Liu C-Q (2014) Chemical weathering processes in the Yalong River draining the eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. J Asian Earth Sci 88:74–84
Liu C-Q (2007) Biogeochemical processes and cycling of nutrients in the earth’s surface: chemical erosion and nutrient cycling in karstic catchments, Southwest China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Millot R, Allègre CJ, Gaillardet J, Roy S (2004) Lead isotopic systematic of major river sediments: a new estimate of the Pb isotopic composition of the Upper Continental Crust. Chem Geol 203:75–90
Morris JM, Farag AM, Nimick DA, Meyer JS (2006) Light-mediated Zn uptake in photosynthetic biofilm. Hydrobiologia 571:361–371
Négrel P, Allègre CJ, Dupré B, Lewin E (1993) Erosion sources determined by inversion of major and trace element ratios in river water: the Congo Basin Case. Earth Planet Sci Lett 120:59–76
Nimick DA, Gammons CH, Parker SR (2011) Diel biogeochemical processes and their effect on the aqueous chemistry of streams: a review. Chem Geol 283:3–17
Nriagu JO, Pacyna JM (1988) Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace-metal. Nature 333:134–139
Palmer MR, Edmond JM (1993) Uranium in river water. Geochem Cos Acta 57:4947–4955
Pekka L, Ingri J, Widerlund A, Mokrotovarova O, Riabtseva M, Öhlander B (2004) Geochemistry of the Kola River, northwestern Russia. Appl Geochem 19:1975–1995
Picouet C, Dupré B, Orange D, Valladon M (2002) Major and trace element geochemistry in the upper Niger river (Mali): physical and chemical weathering rates and CO2 consumption. Chem Geol 185:93–124
Pontér C, Ingri J, Bonström K (1992) Geochemistry of manganese in the Kalix river, northern Sweden. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:1485–1494
Qi CY, Yang YB (2011) The geology and prospecting potentiality of Lida Sb deposit in Funing. Yunan. Geology of Yunan of China 30(3):294–298
Qing WQ, He MF, Chen YP (2008) Improvement of flotation behavior of Mengzi lead–zinc ore by pulp potential control flotation. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 18:949–954
Rai SK, Singh SK, Krishnaswami S (2010) Chemical weathering in the plain and peninsular sub-basins of the Ganga: impact on major ion chemistry and elemental fluxes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74(8):2340–2355
Roy S, Gaillardet J, Allègre CJ (1999) Geochemistry of dissolved and suspended load of the Seine river, France: anthropogenic impact, carbonate and silicate weathering. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1277–1292
Sauvé S, Hendershot W, Allen HE (2000) Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminating soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 34(7):1125–1131
Scott DT, McKnight DM, Voelker BM, Hrncir DC (2002) Redox processes controlling manganese fate and transport in a mountain stream. Environ Sci Technol 36:453–459
Sen IS, Peucker-Ehrenbrink B (2012) Anthropogenic disturbance of element cycles at the earth’s surface. Environ Sci Technol 46:8601–8609
Shiller AM (1997) Dissolved trace elements in Mississippi River: seasonal, interannual, and decadal variability. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:4321–4330
Shope CL, Xie Y, Gammons CH (2006) The influence if hydrous Mn–Zn oxides on diel cycling of Zn in an alkaline stream draining abandoned mine lands. Appl Geochem 21:476–491
Tao Y, Hu RZ, Zhu FL, Ma YS, Ye L, Cheng ZT (2010) Ore-forming age and the geodynamic background of the Hetaoping lead–zinc deposit in Baoshan, Yunnan. Acta Petrol Sin 26(6):1760–1772
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford
Thevenot DR, Moilleron R, Lestel L, Gromaire MC, Rocher V, Cambier P, Bonte P, Colin JL, de Ponteves C, Meybeck M (2007) Critical budget of metal sources and pathways in the Seine River basin (1994–2003) for Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb and Zn. Sci Total Environ 375:180–203
Tipper ET, Bickle MJ, Galy A, West AJ, Pomiès C, Chapman HJ (2006) The short term climatic sensitivity of carbonate and silicate weathering fluxes: insight from seasonal variations in river chemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:2737–2754
Viers J, Dupré B, Gaiilardet J (2009) Chemical composition of suspended sediments in World Rivers: new insights from a new database. Sci Total Environ 407:853–868
Wang JJ, Hu YZ, Han RS (2011) Geochemical characteristics and its implications of trace elements in Qinglong antimony deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Acta Mineral Sin 31(3):571–577
Wei GJ, Ma JL, Liu Y, Xie LH, Lu WJ, Deng WF, Ren ZY, Zeng T, Yang YH (2013) Seasonal changes in the radiogenic and stable strontium isotopic composition of Xijiang River water: implications for chemical weathering. Chem Geol 343:67–75
Xiao J, Jin ZD, Ding H, Wang J, Zhang F (2012) Geochemistry and solute sources of surface waters of the Tarim River Basin in the extreme arid region, NW Tibetan Plateau. J Asian Earth Sci 54–55:162–173
Xu ZF, Liu CQ (2007) Chemical weathering in the upper reaches of Xijiang River draining the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, Southwest China. Chem Geol 239:83–95
Yang SY, Wang ZB, Guo Y, Li CX, Cai JG (2009) Heavy mineral compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtza River) sediments and their provenance-tracing implication. J Asian Earth Sci 35:56–65
Yu XJ (2015) Environmental effects under China’s Western Development Strategy: a case study in the Beipan River basin, Guizhou. Int J Environ Stud 72(1):132–145
Yu S, Du W, Sun P, He S, Kuo Y, Yuan Y, Huan J (2015) Study on the hydrochemistry character and carbon sink in the middle and upper reaches of the Xijiang River basin, China. Environ Earth Sci 74:997–1005
Acknowledgements
Helpful discussions with Dr. Mostofa greatly improved many of the ideas in this manuscript. Dr. Mostofa is thanked for polishing English of this manuscript. The authors also thank the anonymous reviewer for the constructive comments, which improved an earlier version of this manuscript. This work is financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China through Grant Nos. 2013CB956700 and 2016YFA0601000, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41422303, 41130536 and U1301231) and Water Project of MEP (2012ZX07503003001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Li, SL., Chen, JB. et al. Temporal transport of major and trace elements in the upper reaches of the Xijiang River, SW China. Environ Earth Sci 76, 299 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6625-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6625-6