Abstract
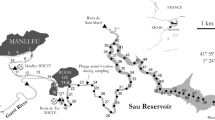
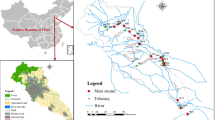
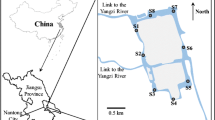
Both three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis were utilized to identify dissolved organic matter (DOM) components in sediments of thirty eutrophic shallow lakes in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Four distinct DOM components were identified: two main components regarding terrestrial humic-like materials (C1 and C2), one about terrestrial fulvic/humic-like materials (C3), and one related to autochthonous tryptophan-like materials (C4). The dominance of terrestrial fluorescence materials in DOM indicated that terrestrial inputs have critical effects on the surveyed lakes. The Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Canonical Corresponding Analysis (CCA) were applied to analyze DOM components and their relationship with the environmental variables. PCA graphs showed that there were spatial differences in DOM fluorophores among lakes with various environments. Components C1, C2, and C4 were correlated positively with PC1 axis (factor 1), while C3 was opposite. Component C1 and C3 showed positive correlations with PC2 axis (factor 2). The CCA and Pearson correlation analysis showed that sediment DOC was correlated significantly with sediment variables (TN, OM, and conductivity), water quality variables (TN, PO4 3−, and Chl a), and DOM components C1 and C3. All DOM components were related significantly to different environment variables, including water quality variables especially nutrient elements (NO3 −, TN, Chl a, and DOC) and sediment variables (OM, NH4 +, and HCl–P). The relationship between DOC and the lake comprehensive nutritive index TLI was marginally significant.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker A, Inverarity R (2004) Protein-like fluorescence intensity as a possible tool for determining river water quality. Hydrol Process 18:2927–2945
Bao SD, Jiang RF, Yang CG, Xu GH, Han XR (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, pp 39–56, 70–82
Birdwell JE, Engel AS (2010) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in cave and spring waters using UV–Vis absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy. Org Geochem 41:270–280
Birdwell JE, Valsaraj KT (2010) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in fogwater by excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Atm Environ 44(27):3246–3253
Carstea EM, Baker A, Bieroza M, Reynolds DM, Bridgeman J (2014) Characterisation of dissolved organic matter fluorescence properties by PARAFAC analysis and thermal quenching. Water Res 61:152–161
Coble PG (1996) Characterisation of marine and terrestrial dissolved organic matter in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Mar Chem 51:325–346
Colin AS, Rasmus B (2008) Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 6:572–579
Cuss CW, Guéguen C (2013) Distinguishing dissolved organic matter at its origin: size and optical properties of leaf-litter leachates. Chemosphere 92:1483–1489
D’Angelo EM, Reddy KR (1994) Diagenesis of organic-matter in a wetland receiving hypereutrophic lake water. 1. Distribution of dissolved nutrients in the soil and water column. J Environ Qual 23:928–936
D’Elia CFP, Steudler A, Corwin N (1977) Determination of total nitrogen in aqueous samples using persulfate digestion. Limnol Oceanogr 22:760–764
Detenbeck NE, Brezonik PL (1991) Phosphorus sorporion by sediments from a soft-water seepage lake. 1. Effects of pH and sediment composition. Environ Sci Technol 25:403–409
Eadie BJ, Chambers RL, Gardner WS, Bell GL (1984) Sediment trap studies in Lake Michigan-resuspension and chemical fluxes in the southern basin. J Great Lakes Res 10:307–321
Fu PQ, Liu CQ, Wu FC, Wei ZQ, Li W, Mei Y, Huang RG (2004) Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopic characterization of dissolved organic matter in sediment pore water in lake Erhai. Quatern Sci 24(6):696–700 (In Chinese with English abstract)
GB 11892-89 (1990) Water quality-determination of Permanganate index. The State Environmental Protection Administration of China
Ghosh R, Banerjee DK (1997) Complexation of trace metals with humic acids from soil, sediment and Sewage. Chem Spec Bioavailab 9(1):15–19
Guo XJ, He LS, Li Q, Yuan DH, Deng Y (2014) Investigating the spatial variability of dissolved organic matter quantity and composition in Lake Wuliangsuhai. Ecol Eng 62:93–101
Huang ZC, Chen TB, Lei M (2002) Effect of DOM derived from sewage sludge an Cd absorption on different soil in ChinaI. Different in latitudinal zonal soil. Acta Sci Circum 22(3):349–353 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Hudson N, Baker A, Reynolds D (2007) Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters-a review. River Res Appl 23:631–649
Hur J, Lee BM, Shin HS (2011) Microbial degradation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and its influence on phenanthrene—DOM interactions. Chemosphere 85:1360–1367
Inamdar S, Finger N, Singh S, Mitchell M, Levia D, Bais H, Scott D, McHale P (2012) Dissolved organic matter (DOM) concentration and quality in a forested mid-Atlantic watershed, USA. Biogeochemistry 108:55–76
Ishii SKL, Boyer TH (2012) Behavior of reoccurring PARAFA components in fluorescent dissolved organic matter in natural and engineered systems: a critical review. Environ Sci Technol 46:2006–2017
Jiang FH, Lee FSC, Wang X, Dai DJ (2008) The application of exciation/emission matrix spectroscopy combined with multivariate analysis for the characterization and source identification of dissolved organic matter in seawater of Bohai Sea, China. Mar Chem 110:109–119
Jin XC, Tu QY, Zhang ZS, Jiang XC, Wang Y, Zhu X, Shu JH, Xu NN, Huang CZ, Xu RX et al (1990) Speci-cations for Lake Eutrophication Survey (2nd Edition). China Environment Science Press, Beijing, pp 291–295
Jones MN, Bryan ND (1998) Colloidal properties of humic substances. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 78:1–48
Kaiser K, Zech W (1998) Rate of dissolved organic matter release and sorption in forest soils. Soil Sci 163(9):714–725
Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park J-H, Michalzik B, Matzner E (2000) Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: a review. Soil Sci 165(4):277–304
Kenney WF, Brenner M, Jason H, Curtis JH, Arnold TE, Schelske CL (2016) A holocene sediment record of phosphorus accumulation in shallow lake Harris, Florida (USA) offers new perspectives on recent cultural eutrophication. Plos One. doi:10.1371/Journal.pone.0147331
Li H, Zhong QP, Wirth S, Wang WW, Hao YT, Wu SG, Zou H, Li WX, Wang GT (2015) Diversity of autochthonous bacterial communities in the intestinal mucosa of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) (Valenciennes) determined by culture-dependent and culture-independent techniques. Aquac Res 46:2344–2359
Louis Y, Pernet-Coudrier B, Varrault G (2014) Implications of effluent organic matter and its hydrophilic fraction on zinc(II) complexation in rivers under strong urban pressure: aromaticity as an inaccurate indicator of DOM–metal binding. Sci Total Environ 490:830–837
Lovley DR, Coates JD, Blunt-Harris EL, Phillips EJP, Woodward JC (1996) Humic substances as electron acceptors for microbial respiration. Nature 382:445–448
Łukawska-Matuszewska K, Kiełczewska J, Bolałek J (2014) Factors controlling spatial distributions and relationships of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur in sediments of the stratified and eutrophic Gulf of Gdansk. Cont Shelf Res 85:168–180
Malmqvist B, Maki M (1994) Benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in north Swedish streams-environmental relationships. Ecography 17:9–16
Mei Y, Wu FC, Wang LY, Bai YC, Li W, Liao HQ (2009) Binding characteristics of perylene, phenanthrene and anthracene to different DOM fractions from lake water. J Environ Sci 21(4):414–423
Neculita CM, Dudal Y, Zagury GJ (2011) Using fluorescence-based microplate assay to assess DOM-metal binding in reactive materials for treatment of acid mine drainage. J Environ Sci 23(6):891–896
Papista E, Acs E, Boeddi B (2002) Chlorophyll-a determination with ethanol e a critical test. Hydrobiologia 485:191–198
Rochelle-Newall EJ, Fisher TR (2002) Production of chromophoric dissolved organic matter fluorescence in marine and estuarine environments: an investigation into the role of phytoplankton. Mar Chem 77:7–21
Romera-Gastillo C, Chen ML, Yamashita Y, Jaffe R (2014) Fluorescence characteristics of size-fractionated dissolved organic matter: implications for a molecular assembly based structure? Water Res 55:40–51
Ruban V, Brigault S, Demare D, Philippe AM (1999) An investigation of the origin and mobility of phosphorus in freshwater sediments from Bort-Les-Orgues Reservoir, France. J Environ Monit 4:403–407
Ruban V, López-Sánchez JF, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller PH (2001) Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments—a synthesis of recent works. Fresen J Anal Chem 370(3):224–228
Singh S, D’Sa EJ, Swenson EM (2010) Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) variability in Barataria Basin using excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). Sci Total Environ 408:3211–3222
Song K, Li L, Li Z, Tedesco L, Hall B, Shi K (2013) Remote detection of cyanobacteria through phycocyanin for water supply source using three-band model. Ecol Inf 15:22–33
Spears BM, Carvalho L, Perkins R, Paterson DM (2008) Effects of light on sediment nutrient flux and water column nutrient stoichiometry in a shallow lake. Water Res 42:977–986
Stedmon CA, Bro R (2008) Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial. Limnol Oceanogr Meth 6:572–579
Stedmon CA, Markager S, Bro R (2003) Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy. Mar Chem 82(3–4):239–254
Thomas JD (1997) The role of dissolved organic matter, particularly free amino acids and humic substances, in freshwater ecosystems. Freshw Biol 38:1–36
Wang SM, Dou HS (1998) Chinese Lakes. Science Press, Beijing, pp 191–218
Wang SR, Jin XC, Pang Y, Zhao HC, Zhou XN, Wu FC (2005a) Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption characteristics in relation to the sediment compositions of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region, China. J Coll Interf Sci 289:339–346
Wang SR, Jin XC, Zhao HC, Zhou XN (2005b) Effect of DOM on phosphate sorption in lake sediments. Environ Sci 42(5):805–811 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Wang SR, Jin XC, Zhao HC, Zhou XN, Wu FC (2007) Effect of organic matter on the sorption of dissolved organic and inorganic phosphorus in lake sediments. Colloid Surf A 297:154–162
Wang ZG, Cao J, Meng FF (2015) Interactions between protein-like and humic-like components in dissolved organic matter revealed by fluorescence quenching. Water Res 68:404–413
Ward JV (1994) Ecology of Alpine streams. Freshw Boil 32:277–294
Williams CJ, Yamashita Y, Wilson HF, Jaffe´ R, Xenopoulos MA (2010) Unraveling the role of land use and microbial activity in shaping dissolved organic matter characteristics in stream ecosystems. Linmol Oceanogr 55(3):1159
Wu HY, Zhou ZY, Zhang YX, Chen T, Wang HT, Lu WJ (2012) Fluorescence-based rapid assessment of the biological stability of landfilled municipal solid waste. Bioresour Technol 110:174–183
Xiang B, Song JW, Wang XY, Zhen J (2015) Improving the accuracy of estimation of eutrophication state index using a remote sensing data-driven method: a case study of Chaohu Lake, China. Water Res 41:753–761
Xu XG, Li W, Fujibayashi M, Nomura M, Nishimura O, Li XN (2015) Asymmetric response of sedimentary pool to surface water in organics from a shallow hypereutrophic lake: the role of animal consumption and microbial utilization. Ecol Indic 58:346–355
Yamashita Y, Tanoue E (2003) Chemical characterization of protein-like fluorophores in DOM in relation to aromatic amino acids. Mar Chem 82:255–271
Yan PC, Wang J, Xiao GQ, Bi YH (2015) Characteristics of phytoplankton community and its relationship with water environment in lakes from the Jianghan Plain. Lake Sci 27(2):297–304 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Yao X, Zhang YL, Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Feng LQ, Cai LL, Gao G (2011) Resolving the variability of CDOM fluorescence to differentiate the sources and fate of DOM in Lake Taihu and its tributaries. Chemosphere 82:145–155
Yao LL, Xu X, Yu HB (2013) Evaluation of dissolved organic matter removal in municipal wastewater based on fluorescence regional integration. Chin J Environ Eng 7(2):411–416
Zhu GW, Chen YX (2001) A review of geochemical behaviors and environmental effects of organic matter in sediments. J Lake Sci 13(3):272–279
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Mega-projects of Science Research for Water Environment Improvement of China (Program No. 2012ZX07101-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Li, Y., Lv, J. et al. Influence of sediment DOM on environmental factors in shallow eutrophic lakes in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Environ Earth Sci 76, 142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6427-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6427-x