Abstract
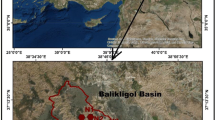
The study area lies between latitudes 6°02′N and 6°24′N, and longitudes 8°00′E and 8°16′E. The area is underlain by Abakaliki shale which belongs to Asu River Group of Albian age. The study determines different water types (facies) via analysis of major ion concentration of water samples using spectrophotometer of HACH DR/2010 series. Twenty (20) water samples were collected and analyzed. The laboratory results were further induced to statistical evaluations using Aqua Chem, and it showed that the groundwater of the area is hard and fresh. The results can be classified into five hydrochemical facies, namely Ca–Mg–Cl–S04, Ca–Mg–HCO3–Cl–SO4, Ca–Mg–HCO3, Na–K–HCO3 and Na–K–Cl–SO4, all of which are dominantly alkaline water. Static water level was measured from hand-dug wells to determine hydraulic heads which delineated local potentiometric surface. Flow directions were deduced, and it showed isolated system of groundwater movement. Such localized pattern of water occurrence can be attributed to the underlying shaley aquiclude across the area. The hydraulic head info was correlated with facie analysis to interpret groundwater recharge zones.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahiarakwem CA (2004) Physical and chemical properties of Ubaha spring water, southeastern Nigeria. J Niger Assoc Hydrogeol 14, 15(2):6–8
Chebotarev II (1955) Metamorphism of natural water in the crust of weathering. Geochim Cosmochem Acta 8:198–212
Davis SN, De Wiest RJM (1966) Hydrogeology. Wiley, New York, p 463p
Freeze AR, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Kevin MH (2005) Hydrogeology (principles and practice). Blackwell, Oxford, UK, p 389
Nton ME, Adejumo SA, Elueze AA (2007) Hydrochemical assessment of surface water and groundwater quality. Glob J Geol Sci 5(1, 2):13–23
Nwankwo EB (1988) Hydrogeology of Enugu and environs. Unpublished M.Sc. thesis. University of Nigeria Nsukka
Offodile ME (2002) Groundwater study and development in Nigeria. Mecon Geology and Engineering Services Ltd, Nigeria, p 453
Okogbue CO, Ukpai SN (2013) Evaluation of trace element contents in groundwater in Abakaliki Metropolis and around the abandoned mine sites in the southern part, Southeastern Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 70:3351–3362
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Reyment RA (1965) Aspects of the geology of Nigeria. Ibadan University Press, Ibadan, p 148
Sawyer GN, McCarthy DL (1967) Chemistry of sanitary Engineers, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, New York, p 518
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley, New York
World Health Organization (WHO) (2004) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 3rd edn
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ukpai, S.N., Nnabo, P.N. & Eze, H.N. Groundwater facie analysis in the upper Cross River basin, southeast Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6139-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6139-7