Abstract
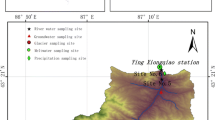
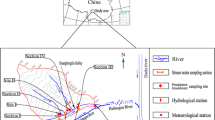
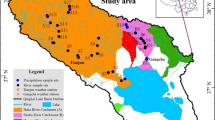
Poyang Lake, whose hydrological characteristics are impacted by the operation of the Three Gorges Dam, is the largest freshwater lake in China. However, water cycle mechanisms in the Poyang Lake Basin remain poorly understood. In this study, stable isotopes (δD and δ18O) of water samples (taken in April, July, and November 2013) and hydrological data are used to investigate the interactions between precipitation, river water, lake water, and shallow groundwater in the Poyang Lake region. The isotopic results show seasonal variations in precipitation, surface water, and groundwater, which provides a set of tools to identify waters that have different histories. The similar isotopic compositions of river water and groundwater suggest a close hydrological connection. Hydrological data present a positive correlation between river run-off and precipitation; however, isotopic results show that rivers in the Poyang Lake Basin in different seasons are primarily recharged by subsurface run-off with different proportion between base flow and near-surface quick flow, rather than by surface run-off directly formed by concurrent rainfall. Due to the geological characteristics of stratum in the Poyang Lake Basin, it is easier for precipitation to infiltrate into soil and recharge groundwater than to form direct surface flow that feeds rivers. The groundwater system is like a huge reservoir which can effectively impound rainfall water, playing an important role in restraining floodwater during the flood season and in ensuring river run-off supply during the dry season.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Z, Porter SC, Kutzbach JE, Xihao W, Suming W, Xiaodong L, Xiaoqiang L, Weijian Z (2000) Asynchronous Holocene optimum of the East Asian monsoon. Quaternary Sci Rev 19(8):743–762
Araguás-Araguás L, Froehlich K, Rozanski K (1998) Stable isotope composition of precipitation over southeast Asia. J Geophys Res Atmos (1984-2012) 103(D22):28721–28742
Beddows PA, Mandić M, Ford DC, Schwarcz HP (2016) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic variations between adjacent drips in three caves at increasing elevation in a temperate coastal rainforest, Vancouver Island, Canada. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 172:370–386
Bocanegra E, Londono OQ, Martínez DE, Romanelli A (2013) Quantification of the water balance and hydrogeological processes of groundwater–lake interactions in the Pampa Plain, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 68(8):2347–2357
Brunke M, Gonser TOM (1997) The ecological significance of exchange processes between rivers and groundwater. Freshw Biol 37(1):1–33
Buttle JM (1994) Isotope hydrograph separations and rapid delivery of pre-event water from drainage basins. Prog Phys Geogr 18(1):16–41
Chen J, Wang CY, Tan H, Rao W, Liu X, Sun X (2012) New lakes in the Taklamakan Desert. Geophys Res Lett 39:L22402
Chen J, Liu X, Sun X, Su Z, Yong B (2014) The origin of groundwater in Zhangye Basin, northwestern China, using isotopic signature. Hydrogeol J 22(2):411–424
Chiogna G, Santoni E, Camin F, Tonon A, Majone B, Trenti A, Bellin A (2014) Stable isotope characterization of the Vermigliana catchment. J Hydrol 509:295–305
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133(3465):1702–1703
Deng T, Wu Y, Yu X, Guo Y, Chen YW, Belzile N (2014) Seasonal variations of arsenic at the sediment–water interface of Poyang Lake, China. Appl Geochem 47:170–176
Feng L, Hu C, Chen X, Li R, Tian L, Murch B (2011) MODIS observations of the bottom topography and its inter-annual variability of Poyang Lake. Remote Sens Environ 115(10):2729–2741
Gao JH, Jia J, Kettner AJ, Xing F, Wang YP, Xu XN, Yang Y, Zou XQ, Gao S, Qi S, Liao F (2014) Changes in water and sediment exchange between the Changjiang River and Poyang Lake under natural and anthropogenic conditions, China. Sci Total Environ 481:542–553
Gat JR (1971) Comments on the stable isotope method in regional groundwater investigations. Water Resour Res 7(4):980–993
Hamed Y, Zairi M, Ali W, Dhia HB (2010) Estimation of residence times and recharge area of groundwater in the Moulares mining basin by using carbon and oxygen isotopes (South Western Tunisia). J Environ Prot Ecol 1(04):466–474
Han X, Chen X, Feng L (2015) Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens Environ 156:426–437
Harrington GA, Cook PG, Herczeg AL (2002) Spatial and temporal variability of ground water recharge in central Australia: a tracer approach. Ground Water 40(5):518–527
Hu C, Zhou W, Xia S (2011) Characteristics of major ions and the influence factors in Poyang Lake catchment. Environ Chem 30(9):1620–1626 (in Chinese)
Hu C, Froehlich K, Zhou P, Lou Q, Zeng S, Zhou W (2013a) Seasonal variation of oxygen-18 in precipitation and surface water of the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Isot Environ Health Stud 49(2):188–196
Hu C, Tong L, Wan Q, Li M, Fu C, Zhou W (2013b) Spatial and temporal variation of shallow groundwater chemical characteristics around Poyang Lake. Environ Chem 32(6):974–979 (in Chinese)
Huang YM (2013) Study of variable characteristics of stable water isotope composition in water cycle and its influence mechanism in the Dongting Lake Basin. Dissertation, Hunan Normal University. (in Chinese)
Huang L, Shao Q, Liu J (2012) Forest restoration to achieve both ecological and economic progress, Poyang Lake basin, China. Ecol Eng 44:53–60
Jeelani G, Bhat NA, Shivanna K (2010) Use of δ 18 O tracer to identify stream and spring origins of a mountainous catchment: a case study from Liddar watershed, western Himalaya, India. J Hydrol 393(3):257–264
Jiao L (2009) Scientists line up against dam that would alter protected wetlands. Science 326(5952):508–509
Lai X, Liang Q, Jiang J, Huang Q (2014a) Impoundment effects of the Three-Gorges-Dam on flow regimes in two China’s largest freshwater lakes. Water Resour Manag 28(14):5111–5124
Lai X, Shankman D, Huber C, Yesou H, Huang Q, Jiang J (2014b) Sand mining and increasing Poyang Lake’s discharge ability: a reassessment of causes for lake decline in China. J Hydrol 519:1698–1706
Li Y, Zhang Q, Li X (2013a) Multi-objectives model calibration for distributed hydrological model in the Poyang Lake watershed. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 22(5):565–572 (in Chinese)
Li Y, Zhang Q, Yao J, Werner AD, Li X (2013b) Hydrodynamic and hydrological modeling of the Poyang Lake catchment system in China. J Hydrol Eng 19(3):607–616
Lischeid G, Kolb A, Alewell C (2002) Apparent translatory flow in groundwater recharge and runoff generation. J Hydrol 265(1):195–211
Liu J, Song X, Yuan G, Sun X, Liu X, Wang Z, Wang S (2008) Stable isotopes of summer monsoonal precipitation in southern China and the moisture sources evidence from δ18O signature. J Geogr Sci 18(2):155–165
Liu J, Song X, Yuan G, Sun X (2014) Stable isotopic compositions of precipitation in China. Tellus B 66:22567
Muñoz‐Villers LE, McDonnell JJ (2012) Runoff generation in a steep, tropical montane cloud forest catchment on permeable volcanic substrate. Water Resour Res 48:W09528
Nakayama T, Shankman D (2013) Impact of the Three-Gorges Dam and water transfer project on Changjiang floods. Glob Planet Change 100:38–50
Qian H, Wu J, Zhou Y, Li P (2014) Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes as indicators of lake water recharge and evaporation in the lakes of the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrol Process 28(10):3554–3562
Seto EY, Wu W, Liu HY, Chen HG, Hubbard A, Holt A, Davis GM (2008) Impact of changing water levels and weather on Oncomelania hupensis hupensis populations, the snail host of Schistosoma japonicum, downstream of the Three Gorges Dam. EcoHealth 5(2):149–158
Sophocleous M (2002) Interactions between groundwater and surface water: the state of the science. Hydrogeol J 10(1):52–67
Sun S, Chen H, Ju W, Yu M, Hua W, Yin Y (2014) On the attribution of the changing hydrological cycle in Poyang Lake Basin, China. J Hydrol 514:214–225
Turner KW, Wolfe BB, Edwards TW (2010) Characterizing the role of hydrological processes on lake water balances in the Old Crow Flats, Yukon Territory, Canada, using water isotope tracers. J Hydrol 386(1):103–117
Uchida T, Kosugi K, Mizuyama T (2002) Effects of pipe flow and bedrock groundwater on runoff generation in a steep headwater catchment in Ashiu, central Japan. Water Resour Res 38(7):24-1-24-14
Woessner WW (2000) Stream and fluvial plain ground water interactions: rescaling hydrogeologic thought. Ground Water 38(3):423–429
Wu X, Zhu X, Pan M, Zhang M (2014) Seasonal variability of oxygen and hydrogen stable isotopes in precipitation and cave drip water at Guilin, southwest China. Environ Earth Sci 72(8):3183–3191
Xie L, Wei G, Deng W, Zhao X (2011) Daily δ 18 O and δD of precipitations from 2007 to 2009 in Guangzhou, South China: implications for changes of moisture sources. J Hydrol 400(3):477–489
Xu L, Zhu M, He B, Wang X, Zhang Q, Jiang J, Razafindrabe BH (2014a) Analysis of water balance in Poyang Lake Basin and subsequent response to climate change. J Coast Res 68(sp1):136–143
Xu X, Zhang Q, Li Y, Li X, Wang X (2014b) Inner-annual variation of soil water content and groundwater level in a typical islet wetland of Lake Poyang. J Lake Sci 26(2):260–268 (in Chinese)
Yang L, Song X, Zhang Y, Han D, Zhang B, Long D (2012) Characterizing interactions between surface water and groundwater in the Jialu River basin using major ion chemistry and stable isotopes. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16(11):4265–4277
Ye X, Zhang Q, Liu J, Li X, Xu CY (2013) Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J Hydrol 494:83–95
Yin L, Hou G, Su X, Wang D, Dong J, Hao Y, Wang X (2011) Isotopes (δD and δ18O) in precipitation, groundwater and surface water in the Ordos Plateau, China: implications with respect to groundwater recharge and circulation. Hydrogeol J 19(2):429–443
Zhai D, Yang Z, Liu Q, Xia X, Hou Q, Yu T, Yuan G, Feng H (2012) Major ion chemistry and influencing factors of river in Poyang Lake Basin. Earth Sci Front 19(1):264–276 (in Chinese)
Zhan L, Chen J, Zhang S, Huang D, Li L (2015) Relationship between Dongting Lake and surrounding rivers under the operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Isot Environ Health Sci 51(2):255–270
Zhang LY (1986) Research report of the quaternary geology for the Poyang Lake region in Jiangxi province. National Geological Information Data Center. http://www.ngac.org.cn/Data/FileList.aspx?Mdidnt=x00072301&MetaId=E928A10211447A73E0430100007F3D67. Accessed 11 May 2016
Zhang YB (2000) 1:6000000 scale China hydrogeological map. National Geological Information Data Center. http://www.ngac.org.cn/Data/FileList.aspx?Mdidnt=x00093431&MetaId=E928A10C20707A73E0430100007F3D67. Accessed 11 May 2016
Zhang Q (2011) Development and application of an integrated hydrological model for lake watersheds. Procedia Environ Sci 10:1630–1636
Zhang L, Yin J, Jiang Y, Wang H (2012a) Relationship between the hydrological conditions and the distribution of vegetation communities within the Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. Ecol Inform 11:65–75
Zhang Q, Li L, Wang YG, Werner AD, Xin P, Jiang T, Barry DA (2012a) Has the Three‐Gorges Dam made the Poyang Lake wetlands wetter and drier? Geophys Res Lett 39:L20402
Zhang Z, Ke C, Shang Y (2014) Studying changes in land use within the Poyang Lake region. J Indian Soc Remote 42(3):633–643
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB417005) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51578212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, L., Chen, J., Zhang, S. et al. Isotopic signatures of precipitation, surface water, and groundwater interactions, Poyang Lake Basin, China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6081-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6081-8