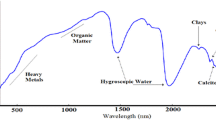
Abstract
Despite environmental damage of cow meet production residues, specific methods to evaluate its spatial impact on soil contamination are sparse and time consuming. This study aimed to evaluate the potential of spectroscopy (400–2500 nm) to detected soil contaminated with organic compounds. It was conducted two experiments: (1) Three soils were incubated with pure and diluted blood from slaughterhouse in a greenhouse, and spectral data were obtained in laboratory with a FieldSpec sensor. (2) Field experiment was conducted to prove its approach. Soil spectral responses were evaluated by qualitative and quantitative methods, and chemical analyses were carried out. The addition of residues increased levels mostly of Na (92.9 %), Ca (80.9 %) and K (82.7 %). N and C increased 52.7 %. This high significant addition resulted on a decrease in soil reflectance intensity in all spectral ranges. These changed slightly at 650, 1450, 1550, 1900 and 2100 nm indicating alteration due to cation on the CEC of minerals. Principal components and soil line analyses corroborated the discrimination of samples quantification of Na, K, Ca and Mg, where R 2 vary from 0.68 until 0.85. In field areas with and without the waste also showed different spectra. Spectra were also able to analyze samples located downhill from the area with waste, indicating the presence of the waste close to streams, which came by leaching. The results indicate that it is possible to identify areas with organic residue by a quick method as compared with traditional soil analysis, helping man power inspection.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo SR, Demattê JAM, Bellinaso H (2013) Analysing the effects of applying agricultural lime to soils by VNIR spectral sensing: a quantitative and quick method. Int J Remote Sens 34:4570–4584. doi:10.1080/01431161.2013.779045
Araújo SR, Demattê JAM, Vicente S (2014a) Soil contaminated with chromium by tannery sludge and identified by vis-NIR-mid spectroscopy techniques. Int J Remote Sens 35:3579–3593. doi:10.1080/01431161.2014.907940
Araújo SR, Wetterlind J, Demattê JAM, Stenberg B (2014b) Improving the prediction performance of a large tropical vis-NIR spectroscopic soil library from Brazil by clustering into smaller subsets or use of data mining calibration techniques. Eur J Soil Sci 65:718–729. doi:10.1111/ejss.12165
Baret F, Jacquemoud S, Hanocq JF (1993) The soil line concept in remote sensing. Remote Sens Rev 7:65–82. doi:10.1080/02757259309532166
Barton CVM (2012) Advances in remote sensing of plants stress. Plant Soil 354:41–44. doi:10.1007/s11104-011-1051-0
Bellaver C (2002) Resíduos industriais (farinhas, óleos e sebos), onde colocá-los frente às restrições de mercado. IV Seminário internacional da industrialização da carne. https://www.agencia.cnptiaembrapa.br/Repositorio/. Accessed 15 Jan 2016
Bowers SA, Hanks RJ (1965) Reflection of radiant energy from soils. Soil Sci 100:130–138
Brown SD (1995) Chemical systems under indirect observation: latent properties and chemometrics. Appl Spectrosc 49:14–31. doi:10.1366/0003702953965876
Buring P (1970) Introduction to the study of soils in tropical and subtropical regions. Pudoc, Wageningen
Camargo AO, Moniz AC, Jorge JA, Valadares JM (1986) Métodos de análise química, mineralógica e física de solos do IAC. Techinical Report 106. Instituto Agronômico, Campinas, 94 p
Chodak M, Niklinska M, Beese B (2007) Near infrared spectroscopy for analysis of chemical and microbiological properties of forest soil organic horizons in heavy metal polluted areas. Biol Fertil Soils 44:171–180. doi:10.1007/s00374-007-0192-z
Clark RN, Roush TL (1984) Reflectance spectroscopy: quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 89:6329–6340. doi:10.1029/JB089iB07p06329
Cohen M, Prenger JP, Debrusk WF (2005) Visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for rapid, non-destructive assessment of wetland soil quality. J Environ Qual 34:1422–1434. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0353
Costa ACS, Bigham JM (2009) Óxidos de Ferro. In: Melo VF, Alleoni LRF (eds) Química e Mineralogia do solo. SBCS, Viçosa, pp 505–572
Costa MSS, Costa LAM, Decarli LD, Pelá A, Silva CJ, Matter UF, Olibone D (2009) Composting of slaughterhouse solid waste. Rev Bras Eng Agríc Ambient 13:100–107. doi:10.1590/S1415-43662009000100015
Cruz MCP, Nakamura AM, Ferreira ME (1987) Boronadsorption bysoil: effects of boron concentration and soil pH. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 22:621–626
Daniel KW, Tripathi NK, Honda K (2003) Artificial neural network analysis of laboratory and in situ spectra for the estimation of macronutrients in soils of Lop Buri (Thailand). Soil Res 41:47–59. doi:10.1071/SR02027
Demattê JAM (2002) Characterization and discrimination of soils by their reflected electromagnetic energy. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 37:1445–1458. doi:10.1590/S0100-204X2002001000013
Demattê JAM, Garcia GJ (1999) Alteration of soil properties through a weathering sequence as evaluated by spectral reflectance. Soil Sci Soc Am J63:327–342. doi:10.2136/sssaj1999.03615995006300020010x
Demattê JAM, Terra FS (2014) Spectral Pedology: a new perspective on evaluation of soils along pedogenetic alterations. Geoderma 217–218:190–200. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.11.012
Demattê JAM, Garcia GJ, Prochnow LI (1998) Influence of induced chemical properties of three soils from paraná state on the spectral reflectance. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 22:479–490. doi:10.1590/S0100-06831998000300014
Demattê JAM, Gama MAP, Cooper M, Araújo JC, Nanni MR, Fiorio PR (2004) Effect of fermentation residue on the spectral reflectance properties of soils. Geoderma 120:187–200. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2003.08.016
Demattê JAM, Silva MLS, Rocha GC, Carvalho LA, Formaggio AR, Firme LP (2005) Spectral variations in soils amended with filter cake. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 29:317–326. doi:10.1590/S0100-06832005000300001
Demattê JAM, Bellinaso H, Romero DJ, Fongaro CT (2014) Morphological Interpretation of Reflectance Spectrum (MIRS) using libraries looking towards soil classification. Sci Agric 71:509–520. doi:10.1590/0103-9016-2013-0365
Dierssen HM (2010) Perspectives on empirical approaches for ocean color remote sensing of chlorophyll in a changing climate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:17073–17078. doi:10.1073/pnas.0913800107
Elrashidi MA, O’Connor GA (1982) Boron sorption and desorption in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:27–31. doi:10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600010005x
Embrapa (1999) Sistema brasileiro de classificação de solos. Embrapa - Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos, Brasília
Fernandes RBA, BarrónV Torrent J, Fontes MPF (2004) Quantification of iron oxides in Brazilian latosols by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 28:245–257. doi:10.1590/S0100-06832004000200003
Ferreira MMC, Antunes AM, Melgo MS, Volpe PLO (1999) Chemometrics I: multivariate calibration, a tutorial. Quím Nova 22:724–731. doi:10.1590/S0100-40421999000500016
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–892. doi:10.1126/science.1136674
Galvão LS, Formaggio AR, Couto EG, Roberts DA (2008) Relationships between the mineralogical and chemical composition of tropical soils and topography from hyperspectral remote sensing data. ISPRS J Photogramm 63:259–271. doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2007.09.006
Goldberg S, Forster HS, Heick EL (1993) Boron adsorption mechanisms on oxides, clay minerals and soils inferred from ionic strength effects. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:704–708. doi:10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700030013x
Havlin JL, Beaton JD, Tisdale SL, Nelson WL (2005) Soil fertility and fertilizers: an introduction to nutrient management. Pearson, Upper Saddle River
Hayward HE, Wadleigh CH (1949) Plant growth on saline and alkali soils. Adv Agron 1:1–38. doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(08)60745-2
Helmke PA (1999) The chemical composition of soils. In: Summer ME (ed) Handbook of soil science, 1st edn. CSC Press, New York, pp B3–B24
Horta A, Malone B, Stockmann U, Minasny B, Bishop TFA, McBratney AB, Pallaser R, Pozza L (2015) Potential of integrated field spectroscopy and spatial analysis for enhanced assessment of soil contamination: a prospective review. Geoderma 240:180–209. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.11.024
Huete AR, Post DF, Jackson RD (1984) Soil spectral effects on 4-space vegetation discrimination. Remote Sens Environ 15:155–165. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(84)90043-9
IAC (2010) Instituto Agronômico de Campinas - Exame proficiência. Campinas
IBGE (2007) Censo Agropecuário 2006: dados preliminares, Rio de Janeiro
Kuang B, Mahmood HS, Quraishi MZ, Hoogmoed WB, Mouazen AM, van Henten EJ (2012) Sensing soil properties in the laboratory, in situ, and on-line: a review. Adv Agron 114:155–223. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-394275-3.00003-1
Malley DF, Yesmin L, Eilers RG (2002) Rapid analysis of hog manure and manure-amended soils using near-infrared spectroscopy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1677–1686. doi:10.2136/sssaj2002.1677
MAPA (2014). http://www.agricultura.gov.br/animal/mercado-interno. Accessed 10 Jan 2016
Martens H, Naes T (1989) Multivariate calibration. Wiley, Chinchester
Martens H, Nielsen JP, Engelsen SB (2003) Light scattering and light absorbance separated by extended multiplicative signal correction. Application to near-infrared transmission analysis of powder mixtures. Anal Chem 75:394–404. doi:10.1021/ac020194w
McBratney AB, Mendonça Santos ML, Minasny B (2003) On digital soil mapping. Geoderma 117:3–52. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00223-4
Messias AS, Tavora BE, Silva RCR, Nascimento AE (2006) Percolação de sódio através de solos do Estado de Pernambuco, Brasil. Bioterra 1:65–72
Mouazen AM, Karoui R, De Baerdemaeker J, Ramon H (2005) Classification of soil texture classes by using soil visual near infrared spectroscopy and factorial discriminant analysis techniques. J Near Infrared Spectrosc 13:231–240. doi:10.1255/jnirs.541
Nakagawa J (1992) Compostagem: obtenção e uso. In: Guerrini IE and Bull LT (eds) Encontro sobre matéria orgânica do solo: problemas e Soluções, 1st edn. Botucatu
Nanni MR, Demattê JAM (2006a) Soil line behavior obtained by laboratorial spectroradiometry for different soil classes. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 30:1031–1038. doi:10.1590/S0100-06832006000600012
Nanni MR, Demattê JAM (2006b) Spectral reflectance methodology in comparison to traditional soil analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:393–407. doi:10.2136/sssaj2003.0285
Näsholm T, Kielland K, Ganeteg U (2008) Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol 182:31–48. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02751.x
Nunes WAGA, Menezes JFS, Benites VM, Lima Junior SAO, Anderson S (2015) Use of organic compost produced from slaughterhouse waste as fertilizer in soybean and corn crops. SciAgric 72:343–350. doi:10.1590/0103-9016-2014-0094
Odlare M, Pell M, Svensson K (2008) Changes in soil chemical and microbiological properties during 4 years of application of various organic residues. Waste Manage 28:1246–1253. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2007.06.005
Park SJ, Vlek PLG (2002) Environmental correlation of three-dimensional soil spatial variability: a comparison of three adaptive techniques. Geoderma 109:117–140. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00146-5
Ramirez Lopez L (2009) Pedologia quantitativa: espectrometria VIS-NIR-SWIR e mapeamento digital de solos. Dissertation, Luiz de Queiroz College of Agriculture, University of São Paulo (USP)
Rhoades JD, Chanduvi F, Leach S (1999) Soil salinity assessment: methods and interpretation of electrical conductivity measurements (FAO Irrigation and Drainage Book 57). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Ribeiro AG, Galbiatti JA (2004) Nitrate and sodium contamination in percolated water and leaf tissue in lettuce crop irrigated with domestic sewage water. Holos Environ 4:56–67
Russell EJ, Wild A (1992) Condiciones del suelo desarrollo de las plantas segun Russell. Mundiprensa, Madri
Saeys W, Mouazen AM, Ramon H (2005) Potential for onsite and online analysis of pig manure using visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Biosyst Eng 91:393–402. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.05.001
SAS Institute (2001) SAS/STAT: user’s guide (Release 8.0). SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC
Savitzky A, Golay MJ (1964) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem 36:1627–1639. doi:10.1021/ac60214a047
Scarassati D, Carvalho RF, Delgado VL,Coneglian CMR, Brito NN, Tonso S, Dragoni Sobrinho G, Pelegrini R (2003) Tratamento de efluentes de matadouros e frigoríficos. III Fórum de Estudos Contábeis, Rio Claro
Schlegelmilch M, Streese J, Biedermann W, Herold T, Stegmann R (2005) Odour control at biowaste composting facilities. Waste Manage 25:917–927. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2005.07.011
Schwertmann U (1991) Solubility and dissolution of iron oxides. Plant Soil 130:1–25. doi:10.1007/BF00011851
Schwertmann U, Fechter H (1984) The influence of aluminium on iron oxides. XI. Aluminium substituted maghemite in soils and its formation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:1462–1463. doi:10.2136/sssaj1984.03615995004800060054x
Shepherd KD, Walsh MG (2002) Development of reflectance spectral libraries for characterization of soil properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:988–998. doi:10.2136/sssaj2002.9880
Silva MS, Mendonça CLA, Vilas Boas MA, Silva MS (1997) Compostagem de resíduos sólidos de frigorífico, visando o saneamento ambiental e a produção de adubo orgânico. In: Congresso Brasileiro de Ciência do Solo, Rio de Janeiro
Soil Survey Staff (2013) Keys to soil taxonomy. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington
Sonesson U, Björklund A, Carlsson M, Dalemo M (2000) Environmental and economic analysis of management systems for biodegradable waste. Resour Conserv Recycl 28:29–53. doi:10.1016/S0921-3449(99)00029-4
Song Y, Li F, Yang Z, Ayoko GA, Frost RL, Ji J (2012) Reflectance spectroscopy for monitoring potentially toxic elements in the agricultural soils of Changjiang River Delta, China. Appl Clay Sci 64:75–83. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2011.09.010
Soriano-Disla JM, Janik LJ, Viscarra Rossel RA, MacDonald LM, McLaughlin MJ (2014) The performance of visible, near-, and mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy for prediction of soil physical, chemical and biological properties. Appl Spectrosc Rev 49:139–186. doi:10.1080/05704928.2013.811081
Stenberg B, Viscarra Rossel RA (2010) Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for high-resolution soil sensing. In: Viscarra Rossel RA, McBratney A, Minasny B (eds) Proximal soil sensing. Progress in soil science. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 29–47
Stoner ER, Baumgardner MF (1981) Characteristics variations in reflectance of surface soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45:1161–1165. doi:10.2136/sssaj1981.03615995004500060031x
Vågen TG (2006) Remote sensing of complex land use change trajectories—a case study from the highlands of Madagascar. Agric Ecosyst Environ 115:219–228. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.01.007
Van Raij B, Andrade JC, Cantarella H, Quaggio JA (2001) Análise química para avaliação de solos tropicais. Instituto Agronômico de Campinas, Campinas
Viscarra Rossel RA (2008) ParLeS: software for chemometric analysis of spectroscopic data. Chemometr Intell Lab 90:72–83. doi:10.1016/j.chemolab.2007.06.006
Viscarra Rossel RA, Webster R (2012) Predicting soil properties from the Australian soil visible-near infrared spectroscopic database. Eur J Soil Sci 63:848–860. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2012.01495.x
Wetterlind J, Stenberg B, Söderström M (2008) The use of near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy to improve soil mapping at the farm scale. Precis Agric 9:57–69. doi:10.1007/s11119-007-9051-z
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) for the financial support p.n. 2009/54144-8 and 2005/59691-6 and to GeoCis Research Group, Luiz de Queiroz College of Agriculture, University of São Paulo (http://esalqgeocis.wix.com/geocis).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demattê, J.A.M., Oliveira, J.d., Tavares, T.R. et al. Soil chemical alteration due to slaughterhouse waste application as identified by spectral reflectance in São Paulo State, Brazil: an environmental monitoring useful tool. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1277 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6042-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6042-2