Abstract
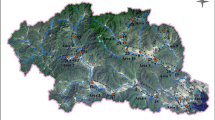
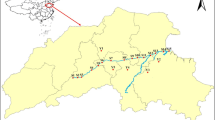
The seasonal and spatial variations of 12 selected antibiotics belonging to four groups, including sulfonamides, quinolones, tetracyclines, and macrolides, were investigated in three main tributaries of Liao River in Jilin Province, northeast China. The concentrations of the antibiotics in the surface water and surface sediments were determined by HPLC–MS/MS. The results indicated that oxytetracycline (OTC), erythromycin (ETM), and ofloxacin (OFL) were dominant antibiotics in the water, with mean concentration of 174.9 ± 266.9, 103.2 ± 95.5, and 67.1 ± 77.3 ng/L, respectively, while OFL, OTC, and norfloxacin were prominent antibiotics in sediments, with mean concentration of 152.2 ± 108.3, 149.5 ± 147.6, and 62.8 ± 83.3 ng/g, respectively. The total antibiotic concentrations in water at each sampling site were 1.2–3 times higher in autumn (November 2015) than those in summer (July 2015), whereas antibiotic concentrations in sediments showed no significant seasonal variation. The highest total antibiotic concentrations in water and sediments were observed around cities with large populations of humans and livestock. Risk assessment based on single antibiotic exposure revealed that OFL, ETM, and OTC were main antibiotics with potential adverse ecological consequences for aquatic organisms. In addition, the mixtures of selected antibiotics posed medium to high risk for aquatic organisms in the Liao River in Jilin Province.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai YW, Meng W, Xu J, Zhang Y, Guo CS (2014) Occurrence, distribution and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in the Liao River Basin in China. Environ Sci Proc Impacts 16:586–593
Ben WW, Pan X, Qiang ZM (2013) Occurrence and partition of antibiotics in the liquid and solid phases of swine wastewater from concentrated animal feeding operations in Shandong Province, China. Environ Sci Proc Impacts 15:870–875
Carlsson C, Johansson AK, Alvan G, Bergman K, Kühler T (2006) Are pharmaceuticals potent environmental pollutants?: part I: environmental risk assessments of selected active pharmaceutical ingredients. Sci Total Environ 364:67–87
Chen K, Zhou JL (2014) Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 95:604–612
Cheng DM, Liu XH, Wang L, Gong WW, Liu GN, Fu WJ, Cheng M (2014) Seasonal variation and sediment-water exchange of antibiotics in a shallower large lake in North China. Sci Total Environ 476:266–275
Davis JG, Truman CC, Kim SC, Ascough JC, Carlson K (2006) Antibiotic transport via runoff and soil loss. J Environ Qual 35:2250–2260
Dong DM, Liu XX, Guo ZY, Hua XY, Su YL, Liang DP (2015) Seasonal and spatial variations of heavy metal pollution in water and sediments of China’s Tiaozi River. Pol J Environ Stud 24:2371–2379
Figueroa RA, MacKay AA (2005) Sorption of oxytetracycline to iron oxides and iron oxide-rich soils. Environ Sci Technol 39:6664–6671
Figueroa RA, Leonard A, MacKay AA (2004) Modeling tetracycline antibiotic sorption to clays. Environ Sci Technol 38:476–483
Gao PP, Mao DQ, Luo Y, Wang LM, Xu BJ, Xu L (2012) Occurrence of sulfonamide and tetracycline-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in aquaculture environment. Water Res 46:2355–2364
Grujić S, Vasiljević T, Laušević M (2009) Determination of multiple pharmaceutical classes in surface and ground waters by liquid chromatography–ion trap–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216:4989–5000
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Fernández-Alba AR, Barceló D (2006) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 69:334–342
Hoa PTP, Managaki S, Nakad N, Takada H, Shimizu A, Anh DH, Viet PH, Suzuki S (2011) Antibiotic contamination and occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquatic environments of northern Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 409:2894–2901
Huang CH, Renew JE, Smeby KL, Pinkston K, Sedlak DL (2011) Assessment of potential antibiotic contaminants in water and preliminary occurrence analysis. J Contemp Water Res Educ 120:4
Jiang L, Hu XL, Yin DQ, Zhang HC, Yu ZY (2011) Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 82:822–828
Jiao SJ, Zheng SR, Yin DQ, Wang LH, Chen LY (2008) Aqueous photolysis of tetracycline and toxicity of photolytic products to luminescent bacteria. Chemosphere 73:377–382
Khetan SK, Collins TJ (2007) Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: a challenge to green chemistry. Chem Rev 107:2319–2364
Kim SC, Carlson K (2007) Temporal and spatial trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in aqueous and river sediment matrices. Environ Sci Technol 41:50–57
Kümmerer K (2009) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review–part I. Chemosphere 75:417–434
Leung HW, Minh TB, Murphy MB, Lam JC, So MK, Martin M, Lam PKS, Richardson BJ (2012) Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environ Int 42:1–9
Li B, Zhang T, Xu ZY, Fang HHP (2009) Rapid analysis of 21 antibiotics of multiple classes in municipal wastewater using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 645:64–72
Li WH, Shi YL, Gao LH, Liu JM, Cai YQ (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 89:1307–1315
Liang XM, Chen BW, Nie XP, Shi Z, Huang XP, Li XD (2013) The distribution and partitioning of common antibiotics in water and sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Chemosphere 92:1410–1416
Liaoyuan Statistical Bureau (2014) Liaoyuan Statistics Year Book 2014. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Loftin KA, Adams CD, Meyer MT, Surampalli R (2008) Effects of ionic strength, temperature, and pH on degradation of selected antibiotics. J Environ Qual 37:378–386
Luo Y, Mao DQ, Rysz M, Zhou QX, Zhang HJ, Xu L, Alvarez PJJ (2010) Trends in antibiotic resistance genes occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ Sci Technol 44:7220–7225
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang YQ, Zhang H, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45:1827–1833
Lützhøft HCH, Halling-Sørensen B, Jørgensen SE (1999) Algal toxicity of antibacterial agents applied in Danish fish farming. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:1–6
MacKay AA, Canterbury B (2005) Oxytetracycline sorption to organic matter by metal-bridging. J Environ Qual 34:1964–1971
Miao XS, Bishay F, Chen M, Metcalfe CD (2004) Occurrence of antimicrobials in the final effluents of wastewater treatment plants in Canada. Environ Sci Technol 38:3533–3541
Moreno-Bondi MC, Marazuela MD, Herranz S, Rodriguez E (2009) An overview of sample preparation procedures for LC–MS multiclass antibiotic determination in environmental and food samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:921–946
Rabølle M, Spliid NH (2000) Sorption and mobility of metronidazole, olaquindox, oxytetracycline and tylosin in soil. Chemosphere 40:715–722
Richardson BJ, Lam PKS, Martin M (2005) Emerging chemicals of concern: pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Asia, with particular reference to Southern China. Mar Pollut Bull 50:913–920
Robinson AA, Belden JB, Lydy MJ (2005) Toxicity of fluoroquinolone antibiotics to aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:423–430
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall ABA (2006) A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65:725–759
Siping Statistical Bureau (2014) Siping Statistics Yearbook 2014. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Thuy HTT, Nga LP, Loan TTC (2011) Antibiotic contaminants in coastal wetlands from Vietnamese shrimp farming. Environ Sci Pollut R 18:835–841
Tolls J (2001) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ Sci Technol 35:3397–3406
Xu WH, Zhang G, Li XD, Zou SC, Li P, Hu ZH, Li J (2007a) Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res 41:4526–4534
Xu WH, Zhang G, Zou SC, Li XD, Liu YC (2007b) Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Pollut 145:672–679
Yang JF, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Tao R, Su HC, Liu YS (2011) Spatial and seasonal distribution of selected antibiotics in surface waters of the Pearl Rivers, China. J Environ Sci Heal B 46:272–280
Zhang JQ, Dong YH (2008) Effect of low-molecular-weight organic acids on the adsorption of norfloxacin in typical variable charge soils of China. J Hazard Mater 151:833–839
Zhang DD, Lin LF, Luo ZX, Yan CZ, Zhang X (2011) Occurrence of selected antibiotics in Jiulongjiang River in various seasons, South China. J Environ Monit 13:1953–1960
Zhao JL, Ying GG, Liu YS, Chen F, Yang JF, Wang L, Yang XB, Stauber JL, Warne MSJ (2010) Occurrence and a screening-level risk assessment of human pharmaceuticals in the Pearl River system, South China. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:1377–1384
Zhou LJ, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Yang JF, Wang L, Yang B, Liu S (2011) Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in northern China. Environ Pollut 159:1877–1885
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment in China [No. 2012ZX07202009], the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 21577047, 21307041 and 21277056], the Science and Technology Development Program of Jilin Province [No. 20150520078JH], and the Science and Technology Program of Department of Education of Jilin Province [No. 2015-494]. The authors would like to thank Dr. Alejandra C. Ortiz for providing valuable comments and revising the English style, thank Dr. Xun Zhang and Dr. Daihui Zhang for the determination of antibiotics, and thank Lufeng Li and Yaojing Xie for the sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, D., Zhang, L., Liu, S. et al. Antibiotics in water and sediments from Liao River in Jilin Province, China: occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1202 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6008-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6008-4